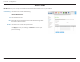
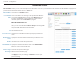
Section 4 - Configuration DMZ Sometimes you may want a computer exposed to the Internet for certain types of applications. If you choose to expose a computer, you can enable Demilitarized Zone (DMZ). This option will expose the chosen computer completely to the Internet. This is not recommended for normal use. Enable SPI: Enabling Stateful Packet Inspection (SPI) helps to prevent cyber attacks by validating that the traffic passing through the session conforms to the protocol.
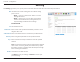
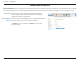
Section 4 - Configuration Virtual Server The device can be configured as a virtual server so that users can access services such as Web or FTP via the public (WAN) IP address of the router. You can also allow the settings to run on a specified schedule. Well-known This contains a list of pre-defined services. You can select a service, Services: select a rule ID, then click the Copy to button to copy the default settings for that service to the specified rule ID.
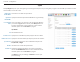
Section 4 - Configuration URL Filter URL Filter allows you to set up a list of websites that will be blocked from users on your network. URL Filtering: Check the box to enable URL Filtering. URL FILTERING RULES ID: This identifies the rule. URL: Enter URL that you would like to block. All URLs that begin with this address will be blocked. Enable: Check the box to enable the specified rule. Click Apply to save your settings, or Refresh to revert to your previous settings.
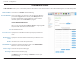
Section 4 - Configuration Routing The Routing page allows you to specify custom routes that determine how data is moved around your network. RIP: Check the box to enable routing, then select which routing protocol to use: • RIPv1: Protocol in which the IP address is routed through the Internet. • RIPv2: Enhanced version of RIPv1 with added features such as authentication, routing domain, next hop forwarding, and subnet-mask exchange. ROUTING RULES ID: This identifies the rule.
Section 4 - Configuration QoS The QoS Engine improves your online gaming or streaming media experience by ensuring that your game or media traffic is prioritized over other network traffic, such as FTP or web. Enable QOS Select this box to enable the QoS feature. Packet Filter: Upstream Specify the maximum upstream bandwidth here (e.g. 400 Kbps). Bandwidth: Use Schedule Select a schedule to use and copy to the specified rule ID when Rule: you click the Copy to button.
Section 4 - Configuration MAC Address Filter The MAC (Media Access Controller) Address Filter option is used to control network access based on the MAC address of the network adapter. A MAC address is a unique ID assigned by the manufacturer of the network adapter. This feature can be configured to ALLOW or DENY network/ Internet access. MAC Address Check this box to enable MAC Filtering.
Section 4 - Configuration Outbound Filter Outbound Filter enables you to control what packets are allowed to be sent out to the Internet. The outbound filter applies to all outbound packets. Outbound Filter: Select this box to Enable outbound filtering. Use Schedule Rule: Select a schedule to use and copy to the specified rule ID when you click the Copy to button. You may select Always On or use a specific schedule that you have defined. To create and edit schedules, please refer to Schedules on page 59.
Section 4 - Configuration Inbound Filter Inbound Filter enables you to control what packets are allowed to come in to your network from the Internet. The inbound filter only applies to packets that are destined for Virtual Servers or DMZ hosts. Inbound Filter: Select this box to Enable the filter. Use Schedule Select a schedule to use and copy to the specified rule ID when Rule: you click the Copy to button. You may select Always On or use a specific schedule that you have defined.
Section 4 - Configuration SNMP SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol) is a widely used network monitoring and control protocol that reports activity on each network device to the administrator of the network. SNMP can be used to monitor traffic and statistics of the DWR-922. The DWR-922 supports SNMP v1 and v2c. SNMP Local: Select whether to Enable or Disable local SNMP administration. SNMP Remote: Select whether to Enable or Disable remote SNMP administration.
Section 4 - Configuration Advanced Network Advanced Network contains settings which can change the way the router handles certain types of traffic. We recommend that you do not change any of these settings unless you are already familiar with them or have been instructed to make the change by one of our support personnel. Enable UPnP: Check the box to enable the Universal Plug and Play (UPnP™) feature. UPNP provides compatibility with various networking equipment, software, and peripherals.
Section 4 - Configuration Network Scan This page lets you set whether to allow the DWR-922 to automatically select a 3G/4G network based on the inserted SIM/UICC card, and allows you to manually scan for networks and select one to connect to. 3G/4G Network Leave this setting on Auto to allow the DWR-922 to automatically Selection select a cellular network to connect to. If you need to select a Method: network manually, select Manual, click the Scan button, then select an available network to connect to.
Section 4 - Configuration System Time Settings This section will help you set the time zone that you are in and an NTP (Network Time Protocol) server to use. Daylight Saving can also be configured to adjust the time when needed. Time Zone: Select the appropriate Time Zone from the drop-down box. Enable Daylight Check the box to allow for daylight saving adjustments. Use the Saving: drop-down boxes to specify a start date and end date for daylight saving time adjustments.
Section 4 - Configuration Administration The Admin page allows you to change the Administrator password and enable Remote Management. The admin has read/write access while users only have read-only access. Only the admin has the ability to change both admin and user account passwords. Admin Password: Enter and confirm the password that the admin account will use to access the router’s management interface. Remote Tick this check box to enable remote management.
Section 4 - Configuration Reboot & Reset Here, you can save the current system settings to a local hard drive. Save Settings To Use this option to save your current router configuration settings Local Hard Drive to a file. Click Save to open a file dialog, and then select a location and file name for the settings. Load Settings Use this option to load previously saved router configuration From Local Hard settings.
Section 4 - Configuration Firmware Upgrade Here, you can upgrade the firmware of your router. Make sure the firmware you want to use is on the local hard drive of the computer and then click Browse to upload the file. You can check for and download firmware updates at the D-Link support site at http://support.dlink.com. Current Firmware Displays your current firmware’s version. Version: Current Firmware Displays your current firmware’s release date.
Section 4 - Configuration System Logs The DWR-922 keeps a running log of events and activities occurring on the router. You may send these logs to a Syslog server on your network. Enable Logging to Check the box to send the router logs to a Syslog server. Syslog Server: Syslog Server IP Enter the IP address of the Syslog server that the router will send Address: the logs to. Click Apply to save your settings, or Refresh to revert to your previous settings.
Section 4 - Configuration Schedules This section allows you to manage schedule rules for various firewall and parental control features. Click Apply to save your settings, or Refresh to revert to your previous settings. Enable Schedule: Check this box to enable schedules. Edit: Click this icon to edit the selected rule. (see below) Delete: Click this icon to delete the selected rule. Previous Page: Click this button to go to the previous page of rules.
Section 4 - Configuration Connection Reset This feature allows you to reset the Internet connection on your router by periodically resetting the connection. You can choose to have this happen on a predetermined schedule by configuring the options on this page. Auto-Reboot: Select whether the connection reset feature should be enabled or disabled. Reboot-Schedule: If the connection reset feature is enabled, select when it should activate via the hour and minute from the dropdown boxes.
Section 5 - Connecting to a Wireless Network Connect a Wireless Client to your Router WPS Button The easiest and most secure way to connect your wireless devices to the router is with WPS (Wi-Fi Protected Setup). Most wireless devices such as wireless adapters, media players, Blu-ray DVD players, wireless printers and cameras will have a WPS button (or a software utility with WPS) that you can press to connect to the DWR-922 router.
Section 4 - Connecting a Wireless Client Connecting to a Wireless Network Windows® 10 To connect to a wireless network using Windows 10, you will need to know the wireless network name (SSID) and Wi-Fi password (security key) of the device you are connecting to. To join an existing network, locate the wireless network icon in the taskbar, next to the time display and click on it. Wireless Icon Clicking on this icon will display a list of wireless networks which are within range of your computer.
Section 4 - Connecting a Wireless Client To connect to the network, click Connect. To automatically connect when your device is in range, click the Connect Automatically check box. Your computer will now automatically connect to this wireless network whenever it is detected. You will then be prompted to enter the Wi-Fi password (network security key) for the wireless network. Enter the password into the box and click Next to connect to the network.
Section 5 - Connecting to a Wireless Network Windows® 8 WPA/WPA2 It is recommended that you enable wireless security (WPA/WPA2) on your wireless router or access point before configuring your wireless adapter. If you are joining an existing network, you will need to know the security key (Wi-Fi password) being used. To join an existing network, locate the wireless network icon in the taskbar next to the time display.
Section 5 - Connecting to a Wireless Network You will then be prompted to enter the network security key (Wi-Fi password) for the wireless network. Enter the password into the box and click Next. If you wish to use Wi-Fi Protected Setup (WPS) to connect to the router, you can also press the WPS button on your router during this step to enable the WPS function.
Section 5 - Connecting to a Wireless Network Windows® 7 WPA/WPA2 It is recommended that you enable wireless security (WPA/WPA2) on your wireless router or access point before configuring your wireless adapter. If you are joining an existing network, you will need to know the security key or passphrase being used. 1. Click on the wireless icon in your system tray (lower-right corner). Wireless Icon 2. The utility will display any available wireless networks in your area.
Section 5 - Connecting to a Wireless Network 3. Highlight the wireless connection with Wi-Fi name (SSID) you would like to connect to and click the Connect button. If you get a good signal but cannot access the Internet, check your TCP/IP settings for your wireless adapter. Refer to Networking Basics on page 88 for more information. 4. The following window appears while your computer tries to connect to the router.
Section 5 - Connecting to a Wireless Network 5. Enter the same security key or passphrase (Wi-Fi password) that is on your router and click Connect. You can also connect by pushing the WPS button on the router. It may take 20-30 seconds to connect to the wireless network. If the connection fails, please verify that the security settings are correct. The key or passphrase must be exactly the same as the one on the wireless router.
Section 5 - Connecting to a Wireless Network WPS The WPS feature of the DWR-922 can be configured using Windows® 7. Carry out the following steps to use Windows® 7 to configure the WPS feature: 1. Click the Start button and select Computer from the Start menu. 2. Click Network on the left side.
Section 5 - Connecting to a Wireless Network 3. Double-click the DWR-922. 4. Input the WPS PIN number (on the router label) in the Setup > Wireless Setup menu in the Router’s Web UI) and click Next.
Section 5 - Connecting to a Wireless Network 5. Type a name to identify the network. 6. To configure advanced settings, click the icon. Click Next to continue.
Section 5 - Connecting to a Wireless Network 7. The following window appears while the router is being configured. Wait for the configuration to complete. 8. The following window informs you that WPS on the router has been set up successfully. Make a note of the security key as you may need to provide this security key if adding an older wireless device to the network in the future. 9. Click Close to complete WPS setup.
Section 5 - Connecting to a Wireless Network Windows Vista® Windows Vista® users may use the built-in wireless utility. If you are using another company’s wireless utility, please refer to the user manual of your wireless adapter for help connecting to a wireless network. Most wireless utilities will have a “site survey” option similar to the Windows Vista® utility as seen below. If you receive the Wireless Networks Detected bubble, click on the center of the bubble to access the utility.
Section 5 - Connecting to a Wireless Network WPA/WPA2 It is recommended that you enable wireless security (WPA/WPA2) on your wireless router or access point before configuring your wireless adapter. If you are joining an existing network, you will need to know the security key or passphrase being used. 1. Open the Windows Vista® Wireless Utility by right-clicking on the wireless computer icon in your system tray (lower right corner of screen). Select Connect to a network. 2.
Section 5 - Connecting to a Wireless Network 3. Enter the same security key or passphrase (Wi-Fi password) that is on your router and click Connect. It may take 20-30 seconds to connect to the wireless network. If the connection fails, please verify that the security settings are correct. The key or passphrase must be exactly the same as the one on the wireless router.
Section 5 - Connecting to a Wireless Network Windows® XP Windows® XP users may use the built-in wireless utility (Zero Configuration Utility). The following instructions are for Service Pack 2 users. If you are using another company’s utility, please refer to the user manual of your wireless adapter for help with connecting to a wireless network. Most utilities will have a “site survey” option similar to the Windows® XP utility as seen below.
Section 5 - Connecting to a Wireless Network WPA/WPA2 It is recommended to enable WPA on your wireless router or access point before configuring your wireless adapter. If you are joining an existing network, you will need to know the WPA key being used. 1. Open the Windows® XP Wireless Utility by right-clicking on the wireless computer icon in your system tray (lower-right corner of screen). Select View Available Wireless Networks. 2.
Section 5 - Connecting to a Wireless Network 3. The Wireless Network Connection box will appear. Enter the WPAPSK Wi-Fi password and click Connect. It may take 20-30 seconds to connect to the wireless network. If the connection fails, please verify that the WPA-PSK settings are correct. The Wi-Fi password must be exactly the same as on the wireless router.
Section 6 - Troubleshooting Troubleshooting This chapter provides solutions to problems that can occur during the installation and operation of the DWR-922. Read the following descriptions if you are having problems. The examples below are illustrated in Windows® XP. If you have a different operating system, the screenshots on your computer will look similar to these examples. 1. Why can’t I access the web-based configuration utility? When entering the IP address of the D-Link router (192.168.0.
Section 6 - Troubleshooting • Configure your Internet settings: • Go to Start > Settings > Control Panel. Double-click the Internet Options Icon. From the Security tab, click the button to restore the settings to their defaults. • Click the Connection tab and set the dial-up option to Never Dial a Connection. Click the LAN Settings button. Make sure nothing is checked. Click OK. • Go to the Advanced tab and click the button to restore these settings to their defaults. Click OK three times.
Section 6 - Troubleshooting 3. Why can’t I connect to certain sites or send and receive emails when connecting through my router? If you are having a problem sending or receiving email, or connecting to secure sites such as eBay, banking sites, and Hotmail, we suggest lowering the MTU in increments of ten (Ex. 1492, 1482, 1472, etc). To find the proper MTU Size, you’ll have to do a special ping of the destination you’re trying to go to. A destination could be another computer, or a URL.
Section 6 - Troubleshooting You should start at 1472 and work your way down by 10 each time. Once you get a reply, go up by 2 until you get a fragmented packet. Take that value and add 28 to the value to account for the various TCP/IP headers. For example, lets say that 1452 was the proper value, the actual MTU size would be 1480, which is the optimum for the network we’re working with (1452+28=1480). Once you find your MTU, you can now configure your router with the proper MTU size.
Appendix A - Wireless Basics Wireless Basics D-Link wireless products are based on industry standards to provide easy-to-use and compatible high-speed wireless connectivity within your home, business, or public access wireless networks. Strictly adhering to the IEEE standard, the D-Link wireless family of products will allow you to securely access the data you want, when, and where you want it. You will be able to enjoy the freedom that wireless networking delivers.
Appendix A - Wireless Basics What is Wireless? Wireless or Wi-Fi technology is another way of connecting your computer to the network without using wires. Wi-Fi uses radio frequency to connect wirelessly so you have the freedom to connect computers anywhere in your home or office network. Why D-Link Wireless? D-Link is the worldwide leader and award winning designer, developer, and manufacturer of networking products. D-Link delivers the performance you need at a price you can afford.
Appendix A - Wireless Basics Wireless Personal Area Network (WPAN) Bluetooth is the industry standard wireless technology used for WPAN. Bluetooth devices in WPAN operate in a range up to 30 feet away. Compared to WLAN the speed and wireless operation range are both less than WLAN, but in return it doesn’t use nearly as much power. This makes it ideal for personal devices, such as mobile phones, PDAs, headphones, laptops, speakers, and other devices that operate on batteries.
Appendix A - Wireless Basics Where is wireless used? Wireless technology is expanding everywhere, not just at home or office. People like the freedom of mobility and it’s becoming so popular that more and more public facilities now provide wireless access to attract people. The wireless connection in public places is usually called “hotspots”.
Appendix A - Wireless Basics Security Don’t let your next-door neighbors or intruders connect to your wireless network. Secure your wireless network by turning on the WPA or WEP security feature on the router. Refer to the product manual for detail information on how to set it up. Wireless Modes There are basically two modes of networking: • Infrastructure – All wireless clients will connect to an access point or wireless router.
Appendix B - Networking Basics Networking Basics Check your IP address After you install your new D-Link adapter, by default, the TCP/IP settings should be set to obtain an IP address from a DHCP server (i.e. wireless router) automatically. To verify your IP address, please follow the steps below. Click on Start > Run. In the run box type cmd and click OK. (Windows® 7/Vista® users type cmd in the Start Search box.) At the prompt, type ipconfig and press Enter.
Appendix B - Networking Basics Statically Assign an IP address If you are not using a DHCP capable gateway/router, or you need to assign a static IP address, please follow the steps below: Step 1 Windows® 7 Click on Start > Control Panel > Network and Internet > Network and Sharing Center. Windows Vista® - Click on Start > Control Panel > Network and Internet > Network and Sharing Center > Manage Network Connections. Windows® XP Click on Start > Control Panel > Network Connections.
Appendix B - Networking Basics Wireless Security This section will show you the different levels of security you can use to protect your data from intruders. The DWR-922 offers the following types of security: • WPA2 (Wi-Fi Protected Access 2) • WPA (Wi-Fi Protected Access) • WPA2-PSK (Pre-Shared Key) • WPA-PSK (Pre-Shared Key) What is WPA? WPA (Wi-Fi Protected Access), is a Wi-Fi standard that was designed to improve the security features of WEP (Wired Equivalent Privacy).
Appendix C - Technical Specifications Technical Specifications LTE Band1 • Category 3: Band 2/4/5/13/17/25 VPN • L2TP/PPTP/IPSEC/VPN Pass-through CDMA Mode 1xRTT and EV-DO Rev A. • BC0/1/10 (800/1900 MHz) Antenna • Two detachable 3G/4G antennas Pentaband UMTS/HSDPA/HSUPA/HSPA+/DC-HSPA+ Band1 • 850/900/1700/1900/2100 MHz Ports • Four LAN ports (RJ-45) • WAN port (RJ-45) GSM Quad-band1 • 850 / 900 / 1800 / 1900 MHz Data Rates2 • Up to 300 Mbps with 802.
Appendix D - Regulatory Information Regulatory Information Federal Communication Commission Interference Statement This device complies with part 15 of the FCC Rules. Operation is subject to the following two conditions: (1) This device may not cause harmful interference, and (2) this device must accept any interference received, including interference that may cause undesired operation.