User manual
CRADLEPOINT COR | USER MANUAL Firmware ver. 4.2.0
© 2013 CRADLEPOINT, INC. PLEASE VISIT HTTP://KNOWLEDGEBASE.CRADLEPOINT.COM/ FOR MORE HELP AND RESOURCES PAGE 78
6.7 Routing Protocols
A routing protocol is a protocol that specifies how routers communicate with each other, disseminating information that
enables them to select routes between any two nodes on a computer network. Routing algorithms choose the route. Each
router has a prior knowledge only of networks attached to it directly. A routing protocol shares this information first among
immediate neighbors, and then throughout the network. This way, routers gain knowledge of the topology of the network.
Choose from the following tabs to configure routing protocols:
• BGP Routing Protocol
• OSPF Routing Protocol
• RIP Routing Protocol
• Route Maps and Filters
6.7.1 BGP Routing Protocol
The latest version of BGP (Border Gateway Protocol) is version 4. BGP-4
is one of the Exterior Gateway Protocols and de facto standard of Inter
Domain routing protocol. BGP-4 is described in RFC1771, A Border
Gateway Protocol 4 (BGP-4). BGP is a distance vector routing protocol,
and the AS-Path framework provides distance vector metric and loop
detection to BGP. RFC1930.
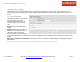
BGP Editor
• Name: Unique name of the policy.
• ASN: The AS (Autonomous System) number is one of the
essential elements of BGP.
• Router-ID: This sets the router-ID of the BGP process. The router-
ID may be an IP address of the router, but need not be - it can be
any arbitrary 32bit number. However it MUST be unique within the
entire BGP domain to the BGP speaker - bad things will happen if