Technical data
Technology objects
CPU 317T: Technology Functions
3-20 A5E00251798-03
3.4.3 Gearing
At the MC_GearIn and MC_GearInSuperImposed technology functions, you define
the gear ratio as a function of the ratio between two integers, and the offset. You
can modify the offset at later time by means of the MC_Phasing and
MC_PhasingSuperImposed technology functions.
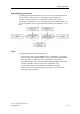
Response characteristics
The response characteristic for gearing can be expressed as a linear relationship
between the control value and the slave value.
Following value = g • control value + φ
g = gear ratio (transmission ratio)
φ
= offset
Direction
The gear ratio can be defined as positive or negative value. The resultant
response:
• Positive gear ratio: All axes run in the same direction.
• Negative gear ratio: The axes run in countering direction.
Absolute or relative gearing
Absolute or relative gearing can be set at input parameter Absolute.
• Absolute gearing establishes an absolute relationship between the leading
and following axes.
An offset between the leading and following axes is compensated during
synchronization based on the value defined at the technology function.
• Relative gearing establishes a relative relationship between the leading and
following axes.
Any offset developing between the axes after the start of synchronization is not
compensated. The offset between the positions of the axes is set at random
and is determined by the time of their synchronization.