Specifications
Table Of Contents
- Imprint
- Documentation Representative
- © HYDAC FILTER SYSTEMS GMBH
- Contents
- Preface
- Safety information
- Storing the CS
- Decoding the model code label
- Checking the scope of delivery
- CS1000 Features
- CS1000 Restrictions on use
- CS1x1x dimensions (without display)
- CS1x2x dimensions (with display)
- Hydraulic connection types
- Fastening / mounting the CS1000
- Display rotatable/Adjustable As Needed
- CS1000 hydraulic installation
- Electrical connection of the CS1000
- Setting the measuring mode
- Operating the CS1x2x using the keypad
- Overview of menu structure
- Using switching output
- Setting limit values
- Reading the analog output
- Status Messages
- Connecting CSI-D-5 (Condition Sensor Interface)
- Connecting the CS1000 to an RS-485 bus
- Communicating with the CS1000 via the RS-485 bus
- Taking the CS1000 out of operation
- Disposing of CS1000
- Spare Parts and Accessories
- Cleanliness classes - brief overview
- Checking/resetting default settings
- Technical data
- Recalibration
- Customer Service
- Model Code
- EC declaration of conformity
ContaminationSensor CS 1000 Cleanliness classes - brief overview
HYDAC FILTER SYSTEMS GMBH
en(us)
Page 96/112
BeWa CS1000 3764916 300 en-us 2012-08-29.doc 2012-08-29
Cleanliness classes - brief overview
Cleanliness class - ISO 4406:1999
In ISO 4406:1999, particle counts are determined cumulatively, i.e. > 4 µm
(c)
, >6
µm
(c)
and >14 µm
(c)
(manually by filtering the fluid through an analysis membrane or
automatically using particle counters) and allocated to measurement references.
The goal of allocating particle counts to references is to facilitate the assessment of
fluid cleanliness ratings.
In 1999 the "old" ISO 4406:1987 was revised and the size ranges of the particle
sizes undergoing analysis redefined. The counting method and calibration were also
changed.
This is important for the user in his everyday work: even though the measurement
references of the particles undergoing analysis have changed, the cleanliness code
will change only in individual cases. When drafting the "new" ISO 4406:1999 it was
ensured that not all the existing cleanliness provisions for systems had to be
changed.
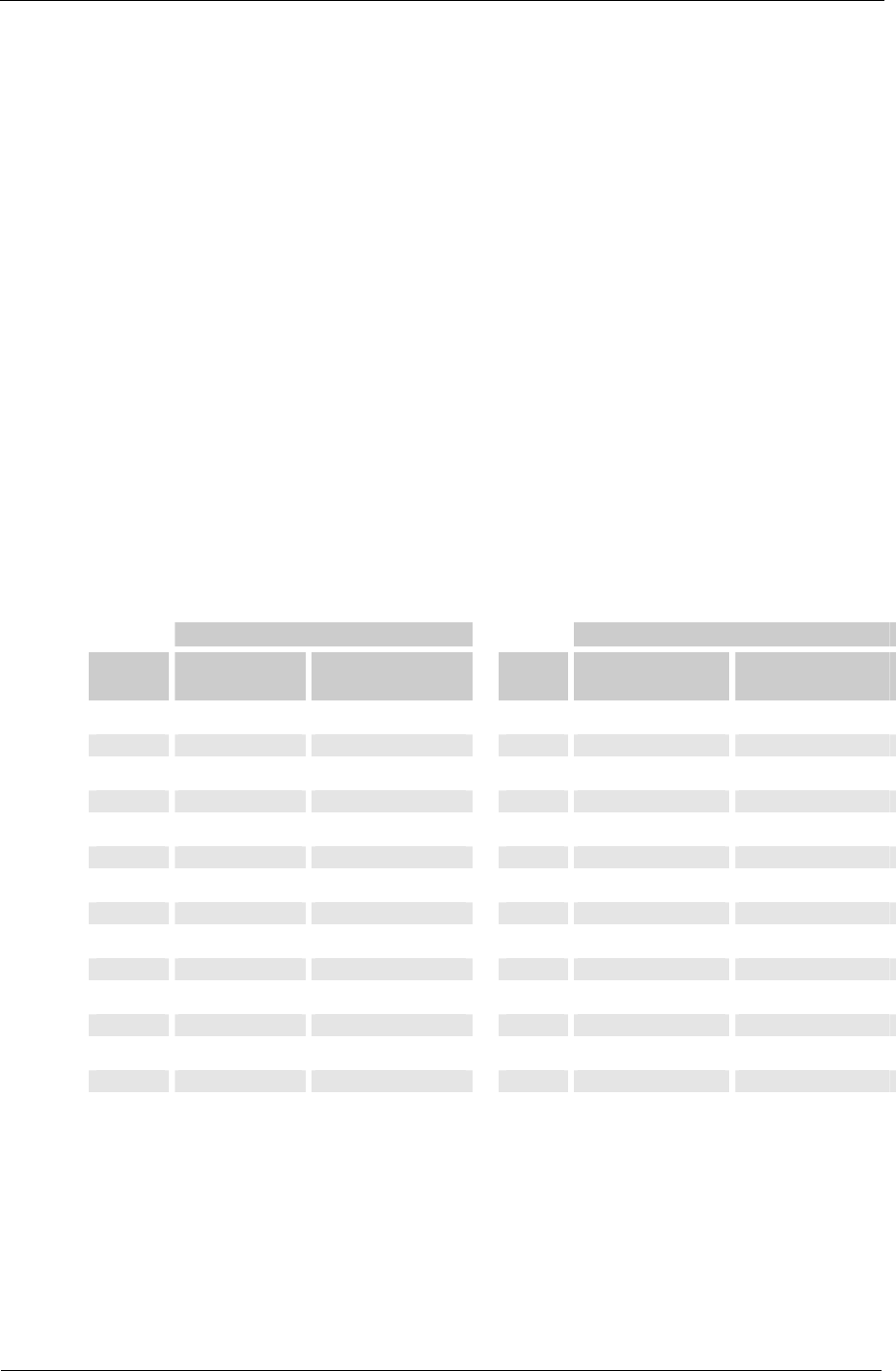
Table - ISO 4406
Assignment of particle counts to cleanliness classes:
Particle count / 100 ml
Particle count / 100 ml
Class More than Up to (and
including)
Class More than Up to (and
including)
0
0 1
15
16,000 32,000
1
1 2
16
32,000 64,000
2
2 4
17
64,000 130,000
3
4 8
18
130,000 250,000
4
8 16
19
250,000 500,000
5
16 32
20
500,000 1,000,000
6
32 64
21
1,000,000 2,000,000
7
64 130
22
2,000,000 4,000,000
8
130 250
23
4,000,000 8,000,000
9
250 500
24
8,000,000 16,000,000
10
500 1,000
25
16,000,000 32,000,000
11
1,000 2,000
26
32,000,000 64,000,000
12
2,000 4,000
27
64,000,000 130,000,000
13
4,000 8,000
28
130,000,000 250,000,000
14
8,000 16,000










