User guide
Table Of Contents
- MSA1000 User Guide
- Contents
- About this Guide
- Chapter 1: Introduction
- Chapter 2: Operating System Specific Information
- Chapter 3: MSA1000 Setup and Sample Configurations
- Chapter 4: Operation and Management
- Chapter 5: Array Configuration Utility (ACU)
- Installing the ACU on the Server
- Accessing the ACU
- Description of Screen Regions
- Configuring a New Controller
- Modifying an Existing Controller
- Probability of Logical Drive Failure
- Chapter 6: Command Line Interface (CLI)
- CLI Overview
- CLI Setup
- Help Commands
- Display Commands
- Array Controller Configuration Commands
- LUN Management Commands
- Server Connection Commands
- Selective Storage Presentation/Access Control List Commands
- Appendix A: Regulatory Compliance Notices
- Appendix B: Electrostatic Discharge
- Appendix C: Specifications
- Appendix D: Hard Drive Arrays
- Appendix E: Recovering from Hard Drive Failure
- Appendix F: Controller Display Messages
- Appendix G: Recovery ROM and ROM Cloning
- Appendix H: SCSI ID Assignments
- Index
Hard Drive Arrays
180 Modular SAN Array 1000 User Guide
RAID ADG—Advanced Data Guarding
RAID ADG is similar to RAID 5 in that parity information is generated (and
stored) to protect against data loss caused by drive failure. With RAID ADG,
however, two different sets of parity data are used, allowing data to still be
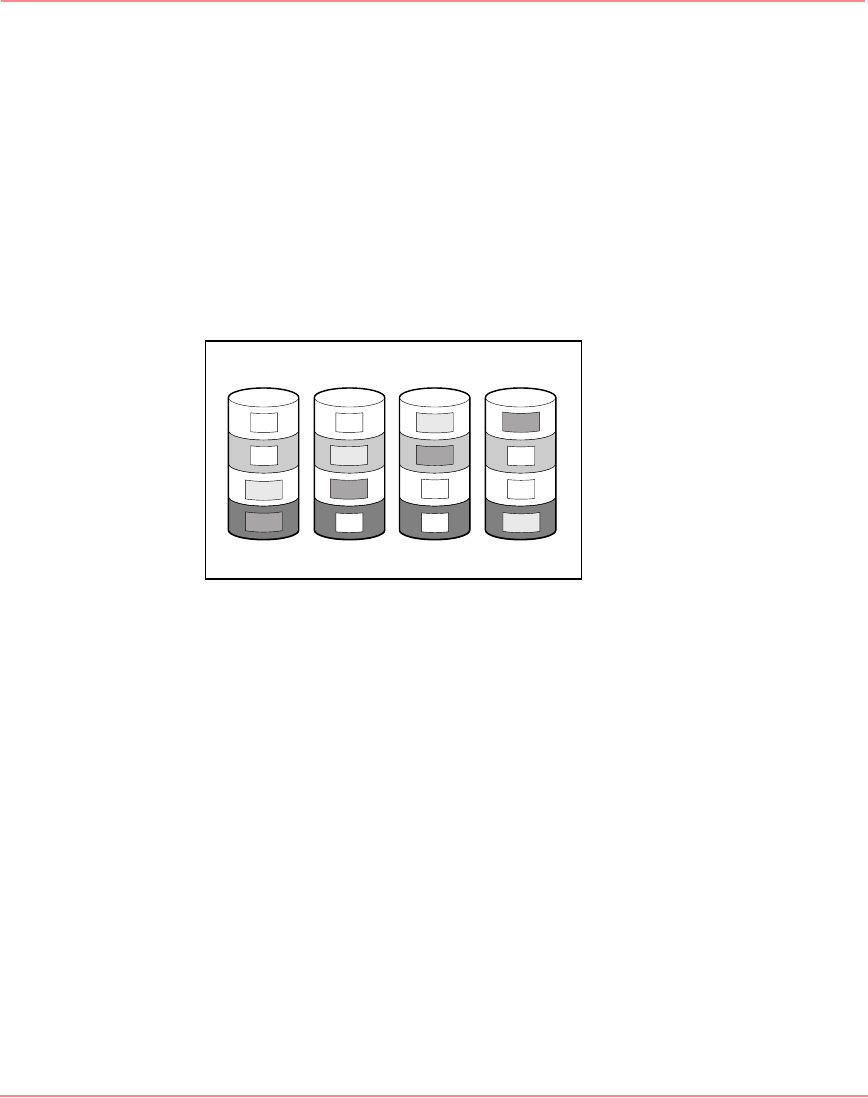
preserved if two drives fail. As can be seen in Figure 68, each set of parity data
uses up a capacity equivalent to that of one of the constituent drives.
This method is most useful when data loss is unacceptable, but cost must also be
minimized. The probability that data loss will occur when arrays are configured
with RAID ADG is less than when they are configured with RAID 5.
Figure 68: Advanced data guarding (RAID ADG)
Advantages
■ High read performance
■ High data availability—any two drives can fail without loss of critical data
■ More drive capacity usable than with RAID 1+0—parity information requires
only the storage space equivalent to two physical drives
Disadvantage
The only significant disadvantage of RAID ADG is a relatively low write
performance (lower than RAID 5), because of the need for two sets of parity data.
Table 18 summarizes the important features of the different kinds of RAID
methods described here. The decision chart in Table 19 may help you to determine
which option is best for your situation.
B1
B3
P5,6
Q7,8
B2
B7
P3,4
Q5,6
B5
B8
P1,2
Q3,4
B4
B6
P7,8
Q1,2
230941-005_MSA1000_UG.book Page 180 Thursday, April 17, 2003 5:53 PM










