User guide
Table Of Contents
- MSA1000 User Guide
- Contents
- About this Guide
- Chapter 1: Introduction
- Chapter 2: Operating System Specific Information
- Chapter 3: MSA1000 Setup and Sample Configurations
- Chapter 4: Operation and Management
- Chapter 5: Array Configuration Utility (ACU)
- Installing the ACU on the Server
- Accessing the ACU
- Description of Screen Regions
- Configuring a New Controller
- Modifying an Existing Controller
- Probability of Logical Drive Failure
- Chapter 6: Command Line Interface (CLI)
- CLI Overview
- CLI Setup
- Help Commands
- Display Commands
- Array Controller Configuration Commands
- LUN Management Commands
- Server Connection Commands
- Selective Storage Presentation/Access Control List Commands
- Appendix A: Regulatory Compliance Notices
- Appendix B: Electrostatic Discharge
- Appendix C: Specifications
- Appendix D: Hard Drive Arrays
- Appendix E: Recovering from Hard Drive Failure
- Appendix F: Controller Display Messages
- Appendix G: Recovery ROM and ROM Cloning
- Appendix H: SCSI ID Assignments
- Index
Hard Drive Arrays
174 Modular SAN Array 1000 User Guide
For data in the logical drive to be readable, the data block sequence must be the
same in every stripe. This sequencing process is performed by the array controller,
which sends the data blocks to the drive write heads in the correct order.
A natural consequence of the striping process is that each physical drive in a given
logical drive will contain the same amount of data. If one physical drive has a
larger capacity than other physical drives in the same logical drive, the extra
capacity is wasted because it cannot be used by the logical drive.
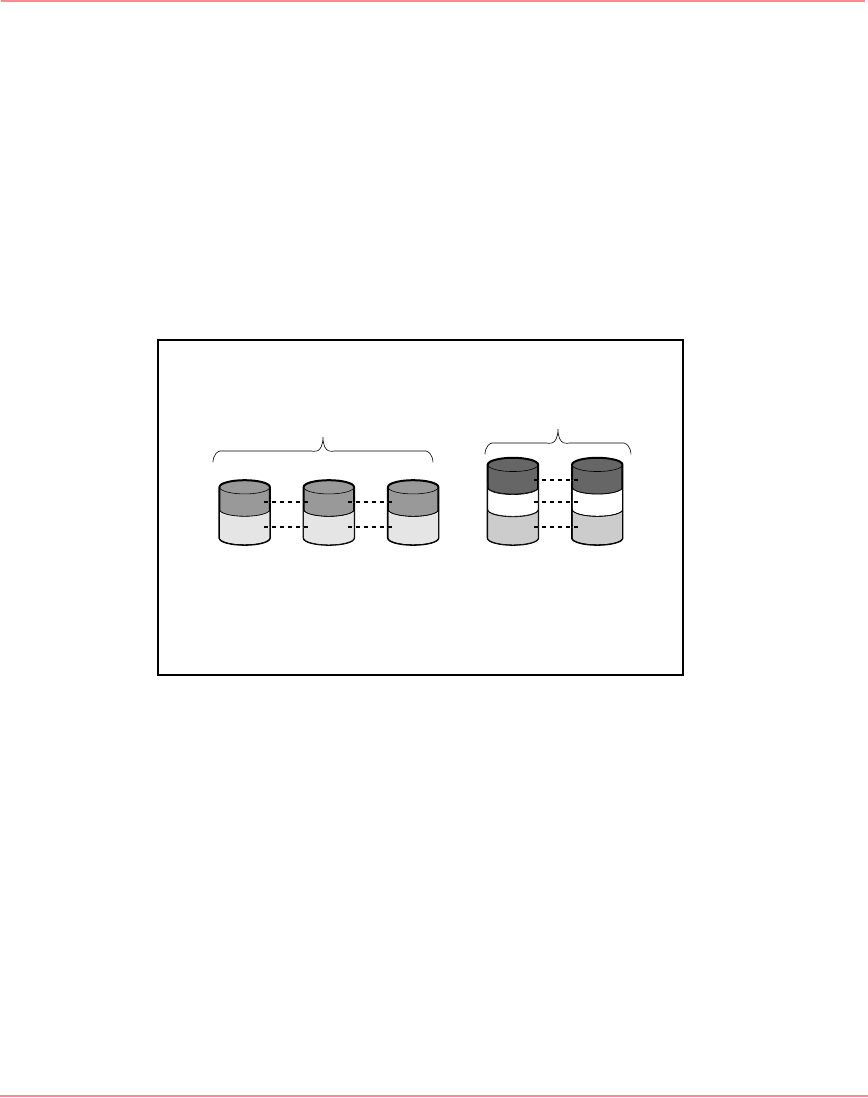
The group of physical drives containing the logical drive is called a drive array
(or just array). An array can contain several logical drives, each of a different size
(refer to Figure 64.)
Figure 64: Two arrays (A1, A2) containing five logical drives
Each logical drive in an array is distributed over all of the physical drives within
the array. A logical drive can also extend over more than one port on the same
controller, but it cannot extend over more than one controller.
L4
L5
L3
A1
L1
L2
A2
230941-005_MSA1000_UG.book Page 174 Thursday, April 17, 2003 5:53 PM










