Technical data
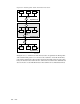
Figure 9–1: Routing IPv6 Traffic from Host A to Host F
Host A Host B Host C
Host D Host E Host F
Host G Host H Host I
Department A
Department B
Department C
v4/v6 v4/v6 v4/v6
v4 v4 v4/v6
v4 v4 v4/v6
Router A
v4/v6
Router B
v4/v6
Router C
v4
VM-0950A-AI
In Figure 9–2, to communicate with host I, host A sends an IPv6 packet to router
A. Router A forwards the IPv6 packet to router B. Router B encapsulates the IPv6
packet and sends the IPv4 packet over a router-to-host tunnel to Host I, which
decapsulates the IPv4 packet. The IPv4 infrastructure routes the packet to host I.
For hosts, the host-to-router tunnel is more efficient because host A, host B, and
host C administrators do not need to create individual host-to-host tunnels for
each destination host.
IPv6 9–5