Technical data
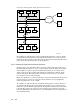
Figure 9–5: Routing IPv6 Traffic from Host A to Host K
Host A Host B Host C
Host D Host E Host F
Host G Host H Host I
Department A
Department B
Department C
v4/v6 v4/v6 v4/v6
v4 v4 v4/v6
v4 v4 v4/v6
Router A
v4/v6
Host J Host K Host L
Department D
v4 v4v4/v6
Router E
v4/v6
Router B
v4/v6
Router C
v4
VM-0954A-AI
Internet
9.4 Porting Existing IPv4 Applications
The OpenVMS operating system provides the basic application programming
interfaces (APIs) as defined in RFC 2553. You can use the APIs and the AF_INET6
sockets in your existing applications (or in new applications) to communicate with
IPv4 nodes today. Your ported applications will continue to communicate with IPv4
nodes and will be ready to communicate with IPv6 nodes. For more information,
refer to the Compaq TCP/IP Services for OpenVMS Sockets API and System
Services Programming manual and the Compaq TCP/IP Services for OpenVMS
Guide to IPv6 manual.
9.5 Obtaining IPv6 Addresses
IPv6 addresses are now being deployed by the regional registries. To obtain an
IPv6 address or block of addresses, contact your Internet Service Provider (ISP).
If you are an Internet Service Provider, contact your upstream registry or one of
the registries at the following locations:
• APNIC (Asia-Pacific Network Information Center)
• ARIN (American Registry for Internet Numbers)
• RIPE NCC (Réseau IP Européens)
Because of the need to test various implementation of the IPv6 RFCs, the Internet
Engineering Task Force (IETF) has defined a temporary IPv6 address allocation
scheme. You can assign the addresses in this scheme to hosts and routers for
IPv6 9–9