User's Guide
Table Of Contents
- 0. Preface
- 1. Systems Description
- 2. Getting Started
- 2.1 Identifying your Device
- 2.2 Unpacking your Nano Transmitter
- 2.3 Unpacking your HD Nano Transmitter
- 2.4 About the Labels on your Nano Transmitter
- 2.5 Planning the Hardware Installation
- 2.6 Identifying the Variants of Nano Transmitter
- 2.7 Identifying the Options of Nano Transmitter
- 2.1 Identifying the Variants of HD Nano Transmitter
- 2.2 Identifying the Options of HD Nano Transmitter
- 2.3 About the Software with your Nano Transmitter
- 3. Controls, Connections and Indicators
- 3.1 About Controls, Connections and Indicators
- 3.2 Exploring the Top Panel – Nano Transmitter
- 3.3 Exploring the Bottom Panel – Nano Transmitter
- 3.4 Exploring the Side Panel – Nano Transmitter
- 3.5 Exploring the Top Panel – HD Nano Transmitter
- 3.6 Exploring the Bottom Panel – HD Nano Transmitter
- 3.7 Exploring the Side Panel – HD Nano Transmitter
- 4. Setting up your Nano Transmitter
- 5. Basic Operation
- 6. Advanced Operation
- 7. Advanced Setup
- 7.1 About Advanced Setup
- 7.2 Installing the Nano TX Controller on your PC
- 7.3 Connecting your PC to the Nano TX using Serial
- 7.4 Exploring the Nano TX Controller Main Window
- 7.5 Performing a Quick Setup
- 7.6 Working with the Unit Status Panel
- 7.7 Working with the Switch Panel
- 7.8 Working with the Unit Tab
- 7.9 Working with the Modulation Tab
- 7.10 Working with the Audio Tab
- 7.11 Working with the Video Tab
- 7.12 Working with the Misc Tab
- 8. Appendix A – Cautions and Warnings
- 9. Appendix B - Care and Maintenance
- 10. Appendix C-Glossary
- 11. Appendix D – Reference Material
Solo7 Nano Transmitter
Commercial in
Confidence
Video, Transmitters, Solo7 Nano
Transmitter
100145
Revision: 8.0
Commercial in
Confidence
Page 7-55
No
Name
Options
Notes
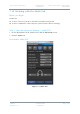
1
Bandwidth
Narrowband:
2.5MHz
1.25MHz
625kHz
UMVL:
6MHz
7MHz
8MHz
Cobham Narrowband, Ultra-Narrowband
and Ultra-X modes provide excellent range
and efficient use of available channel
bandwidth.
Cobham Ultra Mobile Video Link modes
provide higher data throughput than
Narrowband by using the same bandwidths
as DVB-T. UMVL will provide an advantage
over DVB-T at C/X-band in short range
mobile environments.
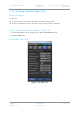
2
Constellation
QPSK, 16QAM,
BPSK and 8PSK
The COFDM constellation in use. On a
sliding scale:
16QAM-more user data, less robust, less
range.
QPSK
8PSK
BPSK-less user data, more robust, more
range.
3
FEC Rate
1/3 or 2/3
This field indicates the forward error
correction (FEC) rate which is being applied.
Think ‘data bits/all bits’
1/3 means 1 bit out of 3 bits is data and
therefore 2 bits are used for error
correction.
Little user data means less picture quality,
but more error correction means a more
robust signal and therefore more range.
2/3 means 2 bits out of 3 bits are data and
therefore 1 bit is used for error correction.
More user data means better picture
quality, but less error correction means less
robust signal and therefore less range.