Instruction Manual
Table Of Contents
- The Eclipse Omega Matrix System: An Overview
- Operation
- The Eclipse Omega Matrix and Circuit Cards
- Front-Panel Controls and Lights
- Central Processor Unit (CPU) Card Description
- Analog Port Card Description
- Power Supply Description
- Connecting the Matrix
- Eclipse Fiber Linking
- Eclipse E-QUE Interface
- Eclipse IVC-32 Interface
- Eclipse LMC-64 Interface
- Installation
- Reconnecting the CPU Card’s Backup Battery
- Verifying the Shipment
- Unpacking the System
- Installing the Eclipse Omega Matrix
- Installing Power Supplies
- Installing the Rear RJ-45 Connector Panels
- Installing Rear RJ-45 Connector Panels in the Field
- Installing CPU Cards
- Installing Analog Port and Expansion Cards
- Wiring Audio Devices to the Matrix
- Wiring CPU Card Interfaces
- GPI/RLY Interface Connector
- RS-232 DB-9 Connector
- Alarm I/O Connector
- General-Purpose Outputs Connector (GP OUT)
- General-Purpose Inputs Connector (GP IN)
- Local Area Network Connectors (LAN1 and LAN2)
- E1/T1 Matrix to Matrix Crossover Cable
- E1/T1 Straight Cable Connections
- E1 to FreeSpeak/CellCom Antenna Pinout
- Maintenance
- Specifications
- Glossary
- Limited Warranty
- Technical Support & Repair Policy

Clear-Com
Eclipse Omega Instruction Manual
3-9
Loss of a Single Node
If a node is lost on the ring the nodes adjacent to the failed node will
loop-back their connections to the failed node healing the ring using
the working remains of the ring. The configuration software (ECS) will
report the failure.
This applies to the situation where the fiber card itself has failed rather
than the matrix.
Loss of Two Fiber Connections
If two adjacent fiber connections are lost on the ring this will be
handled as for the loss of a single node where the nodes adjacent to
the failed node will loop-back their connections to the failed node
healing the ring. The configuration software will report the failure
correctly as two failed cables . If two non-adjacent fiber connections
are lost on the ring the nodes adjacent to the failures will loop-back
their connections to the failed cables healing the ring into 2 separate
smaller rings. The configuration software will report the failure.
Note that in this instance the two sub-rings will be dependent on their
Ethernet connections for configuration and data transmission but there
will be no audio path between them.
Loss of Two Nodes
If two adjacent nodes are lost on the ring this will be handled as for the
loss of a single node where the nodes adjacent to the failed node will
loop-back their connections to the failed nodes healing the ring. The
configuration software will report the failure correctly as two failed
nodes . If two non-adjacent nodes are lost on the ring the nodes
adjacent to the failures will loop-back their connections to the failed
nodes healing the ring into 2 separate smaller rings. The configuration
software will report the failure. Note that in this instance the two
sub-rings will be dependent on their Ethernet connections for
configuration and data transmission but there will be no audio path
between them.
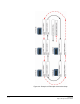
DUAL CARD SET REDUNDANCY
This is shown as in Figure 3-5 with both "Card set A" and "Card set B"
fitted in each node of the ring. In this case each Matrix Frame contains
two Fiber-optic Linking card sets. This approach affords full
redundancy, offering protection against component failure within a
single Fiber-optic Linking Card Set. Again in the absence of an
Uninterrupted Power Supply this configuration will not protect against
loss of the node or Matrix Frame itself.