Instant Web Publishing Guide
Table Of Contents
- Chapter 1 About publishing FileMaker Pro databases on the web
- Chapter 2 Publishing your database on the web
- Chapter 3 Working with FileMaker databases on the web
- Chapter 4 Designing a database for Instant Web Publishing
- Tips for designing layouts for Instant Web Publishing
- Tips for working with data in a web browser
- General database design considerations
- Working with graphics, sounds, and movies on the web
- Setting the initial layout and view
- Hiding the status area to customize the interface
- Specifying the sort order for web users
- Scripts and Instant Web Publishing
- Hosting databases with FileMaker Server Advanced: an overview
- Documenting your solution
- Chapter 5 Testing, monitoring, and securing your site
- Index
Designing a database for Instant Web Publishing 27
Scripts and Instant Web Publishing
The ScriptMaker feature in FileMaker Pro is useful for automating frequently performed tasks, or
for combining several tasks. When used in Instant Web Publishing, it can allow web users to
perform more tasks, or to easily perform a series of tasks simply by clicking a button.
FileMaker Pro now supports over 70 script steps with Instant Web Publishing and Custom Web
Publishing. Web users can perform a variety of automated tasks when you provide buttons on your
FileMaker
Pro layouts or set scripts to run when a database is opened or logged out. To see script
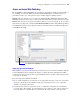
steps that are not supported, select the
Indicate Web Compatibility checkbox in the Edit Script dialog
box. Dimmed script steps are not supported on the web. For information on individual script steps,
see FileMaker
Pro Help.
Script steps tips and considerations
Although many script steps work identically on the web, there are several that work differently due
to design limitations. Before sharing your database, evaluate all scripts and buttons that will be
executed from a web browser. Be sure to log in with different user accounts to make sure they work
as expected for all clients.
Keep these tips and considerations in mind:
1 Use accounts and privileges to restrict the set of scripts that a web user can execute. Verify that
the scripts contain only web-compatible script steps, and only provide access to scripts that
should be used from a web browser.
1 Consider the side effects of scripts that execute a combination of steps that are controlled by
access privileges. For example, if a script includes a step to delete records, and a web user does
not log in with an account that allows record deletion, the script will not execute the Delete
Select Indicate web compatibility to dim script steps that are not web-compatible