Troubleshooting guide
1-21
Cisco Wide Area Application Services Configuration Guide
OL-26579-01
Chapter 1 Configuring Traffic Interception
Configuring WCCP on WAEs
(The Return Method drop-down list is shown only for devices using WAAS versions earlier than 5.0. For
later WAAS versions, the return method is set the same as the redirect method.)
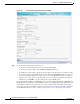
Step 15 (Optional) From the Egress Method drop-down list, choose the method to use to return optimized packets
to the router or switch:
• Generic GRE (available and set as the default only if Redirect Method is WCCP GRE)
• IP Forwarding
• L2 (available and set as the default only if Redirect Method is WCCP L2)
• WCCP GRE (available only if Redirect Method is WCCP GRE)
For devices using WAAS versions earlier than 5.0, the choices are as follows: IP Forwarding (the
default), WCCP Negotiated Return, or Generic GRE. For more details on choosing the egress method,
see the “Configuring Egress Methods for WCCP Intercepted Connections” section on page 1-29.
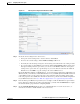
Step 16 (Optional) Modify the current advanced settings in the Advanced WCCP Settings area as follows:
a. Check the Enable Flow Protection check box to keep the TCP flow intact and to avoid
overwhelming the device when it comes up or is reassigned new traffic. For more information, see
the “Information About WCCP Flow Redirection on WAEs” section on page 1-16. Flow protection
is disabled by default.
b. In the Flow Protection Timeout field, specify the amount of time (in seconds) that flow protection
should be enabled. The default is 0, which means it stays enabled with no timeout. (The Flow
Protection Timeout field is not shown for devices using WAAS versions earlier than 5.0.)
c. In the Shutdown Delay field, specify the maximum amount of time (in seconds) that the chosen
device waits to perform a clean shutdown of WCCP. The default is 120 seconds.
The WAE does not reboot until either all connections have been serviced or the maximum wait time
(specified through this Shutdown Delay field) has elapsed for WCCP.
d. In the Failure Detection Timeout drop-down list, choose the failure detection timeout value (9, 15,
or 30 seconds). The default is 30 seconds and is the only value supported on WAAS versions prior
to 4.4.1. This failure detection value determines how long it takes the router to detect a WAE failure.
(The Failure Detection Timeout field is not shown for devices using WAAS versions earlier than
4.4.)
The failure detection timeout value is negotiated with the router and takes effect only if the router
also has the variable timeout capability. If the router has a fixed timeout of 30 seconds and you have
configured a failure detection value on the WAE other than the default 30 seconds, the WAE is not
able to join the farm and an alarm is raised (“Router unusable” with a reason of “Timer interval
mismatch with router”).
e. In the Weight field, specify the weight value that is used for load balancing. The weight value ranges
from 0 to 10000. If the total of all the weight values of the WAEs in a service group is less than or
equal to 100, then the weight value represents a literal percentage of the total load redirected to the
device for load-balancing purposes. For example, a WAE with a weight of 10 receives 10 percent of
the total load in a service group where the total of all weight values is 50. If a WAE in such a service
group fails, the other WAEs still receive the same load percentages as before the failure; they will
not receive the load allocated to the failed WAE.
If the total of all the weight values of the WAEs in a service group is between 101 and 10000, then
the weight value is treated as a fraction of the total weight of all the active WAEs in the service
group. For example, a WAE with a weight of 200 receives 25 percent of the total load in a service
group where the total of all the weight values is 800. If a WAE in such a service group fails, the other
WAEs will receive the load previously allocated to the failed WAE. The failover handling is different
than if the total weights are less than or equal to 100.