User guide
HP Virtual Connect for Cisco Network Administrators (version 4.x)
Document Number: C01386629 Date: January 2014
page 36
in regards to networking technology in order to better understand Virtual Connect.
A Description of the VMware Components:
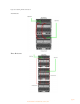
Referencing the figure below, the VMware ESX server (left) is a single physical server running
server virtualization software (VMware) that allows the physical server to host one or more
instances of a virtual server, called a Virtual Machine (VM). In addition, the VMware ESX server
provides external network connectivity to the internal servers (VMs) using a virtual (software)
implementation of a layer 2 bridge, called a vSwitch. The VM virtual NICs (vNics) are assigned to
one of the vSwitches and the vSwitches are then associated with real physical NICs residing in I/O
slots on the VMware ESX server. The vSwitches can have one or more physical NICs (uplinks)
assigned to them to provide external network connectivity. If more than one physical NIC is
assigned to the same vSwitch, network redundancy and/or load balancing is provided for the
internal servers (VMs) assigned to that vSwitch. The physical NICs then present one or more
MAC addresses to the external network, depending on the number of VMs communicating to the
external network through each physical
NIC.
A Comparative Description of the VC Components:
Referencing the figure below, the c-Class enclosure (right) is a single physical enclosure that hosts
one or more real physical servers, called a blade server. In addition, the c-Class enclosure provides
external network connectivity to the internal servers (blade servers) using a hardware
implementation of a layer 2 bridge, called a Virtual Connect Ethernet network (vNet). The blade
server physical NICs (pNics) are assigned to one of the vNets and the vNets are then associated with
real physical VC uplink ports from VC-Enet modules residing in the I/O bays on the c-Class enclosure.
The vNets can have one or more VC uplinks assigned to them to provide external network
connectivity. If more than one VC uplink is assigned to the same vNet, network redundancy and/or
load balancing is provided for the internal servers (blade servers) assigned to that vNet. The VC
uplinks then present one or more MAC addresses to the external network, depending on the number
of blade servers communicating to the external network through each VC uplink.
Figure 18. VMware ESX server Compared to Virtual Connect Enclosure