Specifications
© 2006 Cisco Systems, Inc.
All rights reserved.
Product Features 2-60
NAM / Traffic Analyzer v3.5 Tutorial
© 2006 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
Product Features 2-60
NAM / Traffic Analyzer v3.5 Tutorial
Basic NAM-1/2 Configuration
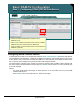
Step 1: Configuring SPAN / RSPAN Data Sources
Basic NAM-1/2 Configuration
Step 1: Configuring SPAN / RSPAN Data Sources
NAM-1, NAM-2 Only
NAM-1, NAM-2 Only
1. Types of SPAN / RSPAN Sessions
a. One or more ports from various modules
b. One or more VLANS
c. Single RSPAN VLAN
d. One or more Ether Channels
2. If source is a port, first select switch module
where port is located
3. If NAM-2, specify SPAN destination Data
Port (1 or 2); One type of SPAN session per
Data Port
4. If Port, VLAN, or Ether Channel select the
direction of traffic to send to the NAM
5. Select the actual source (Ports, VLANs,
Ether Channels) to send to the NAM
NAM Data Port
(NAM-1)
NAM Data Port
(NAM-1)
Port 2/1 Tx
NAM Data Port 1
(NAM-2)
NAM Data Port 1
(NAM-2)
VLAN 1 Tx
VLAN 3 Tx
NAM Data Port 2
(NAM-2)
NAM Data Port 2
(NAM-2)
Port 2/1 Rx
Port 2/7 Rx
Port 3/1 Rx
Examples
Configuring SPAN / RSPAN Data Sources
You have the option of choosing ports, VLANs, or Cisco EtherChannel
®
tunnels as a SPAN source. The
importance of defining your SPAN source is tied implicitly to what problem you are trying to solve or how you
want to view the data. For example, if you choose to use SPAN on a port, then all graphs, tables, and charts
will be derived from the data that the NAM collects on the port(s) you have spanned. Furthermore, you will be
able to view VLAN information only for VLANs that are active on the spanned port(s). If you are more
interested in how your VLANs consume switch and network resources, then choosing VLAN spanning will
provide you with charts and statistics by the VLANs you have spanned. The same is true for Cisco Ether
Channel tunnel.
Once the type of SPAN has been selected, the user further configures additional parameters:
• If spanning ports, first select the switch module where the port(s) are located; then select the port(s)
you wish to span from a list.
• If a NAM-2 module is being utilized, select the data port to SPAN this traffic to.
• Select the direction of traffic you want to monitor—transmitted (Tx), received (Rx), or both (bi-
directional). Since packets can be counted twice, you may want to review the spanning concepts
covered earlier in this chapter or in the references in Chapter 5 before choosing or changing the
default parameters on direction.
• Select the actual ports, VLANs, or Ether Channels to be spanned.
Note(s):
• When spanning any source, it is important to keep in mind the volume of traffic that your SPAN
session generates, because this will affect the overall performance of the NAM and the reliability of
your data.
• When spanning Rx ports, many can be selected. When spanning Tx or bi-directional ports, only one
can be selected. For VLANs, it doesn’t matter.