Product data
Table Of Contents
- Contents
- Introduction
- Networked Storage Overview
- Storage Concepts and Technologies
- Conclusion
- Obtaining Technical Assistance
- Appendix A
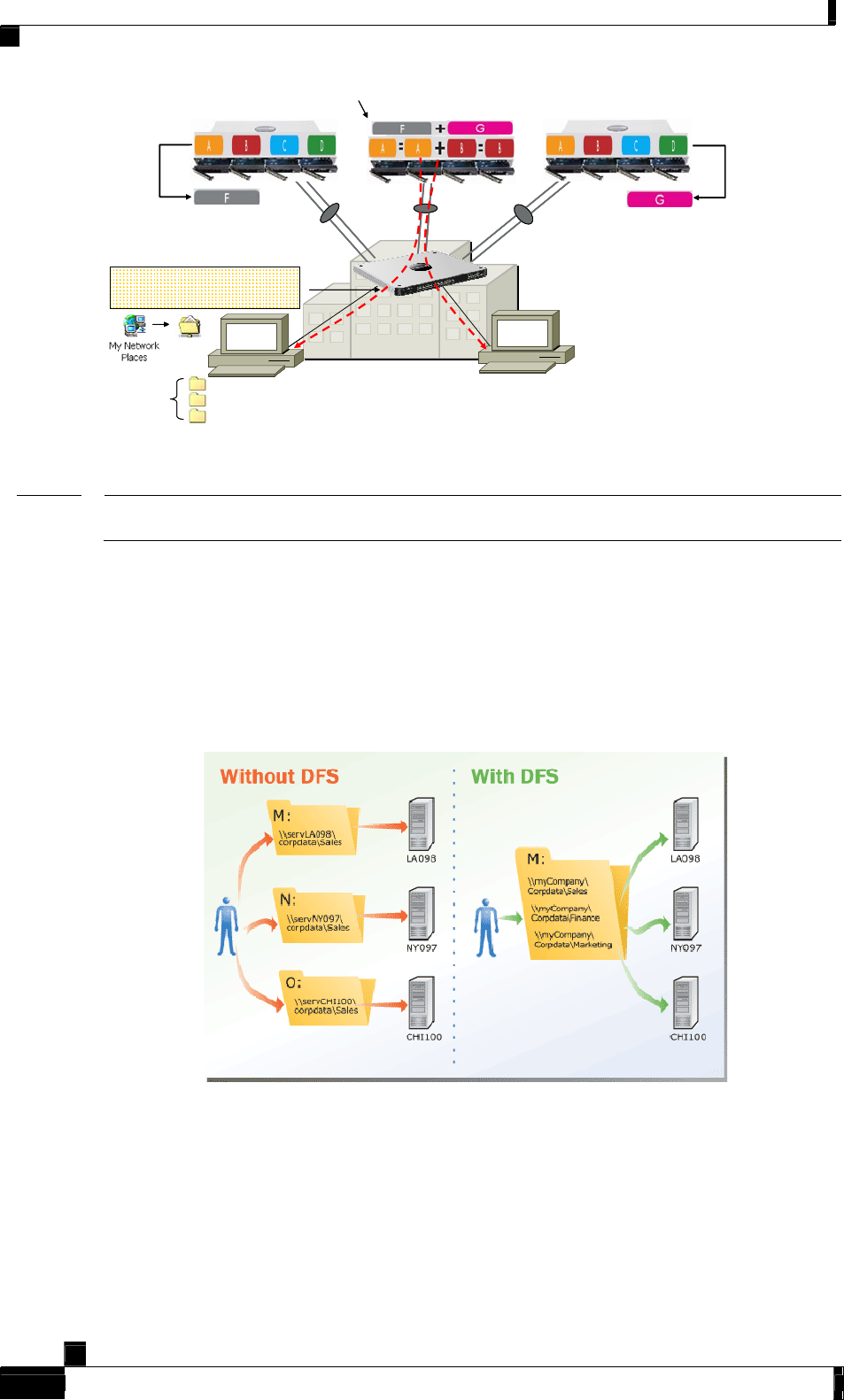
Storage Concepts and Technologies
NSS6000 Master
JBOD (Set F + Set G)
And RAID Mirror
CIFS or NFS Sessions
“Network Drives”
NSS4000 Slave
RAID Stripe = Set G
NSS6000 Slave
RAID Stripe = Set F
Exported
Exported
Imported
NAS
shares
Mirror A
Mirror B
JBOD (F + G)
3 folders
Current: JBOD only
Under consideration:
RAID sets (enables
RAID across multiple
NSS devices)
NSS6000 Master
JBOD (Set F + Set G)
And RAID Mirror
CIFS or NFS Sessions
“Network Drives”
CIFS or NFS Sessions
“Network Drives”
NSS4000 Slave
RAID Stripe = Set G
NSS6000 Slave
RAID Stripe = Set F
Exported
Exported
Imported
NAS
shares
NAS
shares
Mirror AMirror A
Mirror BMirror B
JBOD (F + G)JBOD (F + G)
3 folders
Current: JBOD only
Under consideration:
RAID sets (enables
RAID across multiple
NSS devices)
Figure 6: Virtualized Storage
Note
Virtualization can be done with both the NSS6000 and NSS4000. However, a virtualization
master may only be an NSS6000 series. A slave may be an NSS4000 or NSS6000.
Distributed File System
While virtualization can assist the administrator in managing storage capacity, Microsoft
Distributed File System (DFS) is designed to make it easier for Windows users to find files
when storage is defined on multiple volumes. DFS provides access via a single set of shares
with a unified hierarchy, rather than defining one share per volume (Figure 7). DFS support
is enabled/disabled on a per share basis.
Figure 7: Distributed File System (DFS)
RAID
RAID (Redundant Array of Inexpensive or Independent Disks) is a method employed in a
network for using multiple hard drives (in a storage array) to improve performance and/or
reliability in information storage. Your choice of RAID will impact both the reliability and
the total usable storage capacity of the NAS appliance.
White Paper: Network Storage LINKSYS © 2007
9 EDCS-593805 v1.0
A printed copy of this document is considered uncontrolled










