Product data
Table Of Contents
- Contents
- Introduction
- Networked Storage Overview
- Storage Concepts and Technologies
- Conclusion
- Obtaining Technical Assistance
- Appendix A
Networked Storage Overview
Linksys NSS are NAS appliances that are dedicated to disk-based storage and attach to the
user LAN through an ordinary network connection. Storage can be aggregated as volumes or
as “virtualized” sets over multiple local NSS devices. Virtualization is the ability to export
disks or RAID sets from ‘secondary’ NSS devices that are in your network and import them
to a ‘master’ NSS device. Virtualization reduces downtime and optimizes storage utilization.
The reference storage solution architecture is illustrated in Figure 2:
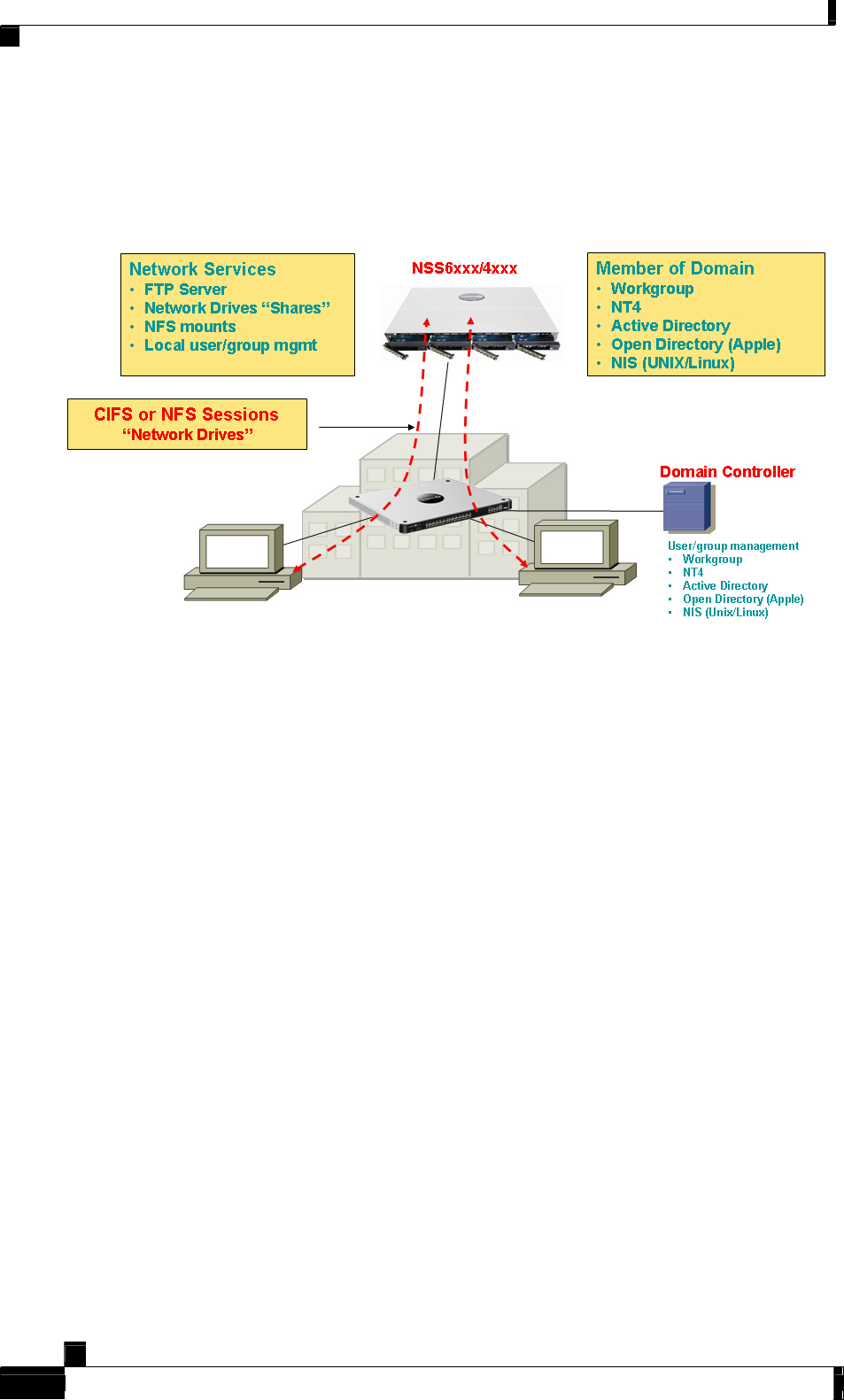
Figure 2: Storage Solution Reference Architecture
In Figure 2, the Linksys NSS appears as a native file server for clients within the network.
Cross-platform file systems are supported including: Windows, Apple Macintosh, UNIX and
Linux. Files retain their native file format when stored on the NSS.
File servers sit on the LAN and are connected to the NSS by a standard Ethernet network.
Client systems use standard file access protocols such as CIFS (Common Internet File
System) or NFS (Network File System) to make storage requests. Functionally, CIFS or NFS
file system ‘shares’ appear as folders within the corresponding system directory. Users
typically map a NSS as a network drive on their PC, or access it via FTP. Multiple users on
disparate systems can access data simultaneously. Logically, the drives appear to be directly
attached their own computer. On the Windows or Linux system the NSS will appear as
another disk drive or mount point.
Local file system calls from the clients are redirected to the NSS device, which provides
shared file storage for all clients. If the clients are server systems, the NSS offloads the data
management overhead from the servers. If the clients are desktop systems, the NSS provides
"serverless" file serving.
Volumes are used to partition the space that is available on an NSS array set as follows:
• On-disk data encryption is either enabled or disabled for each volume when it is
created.
• Existing volumes can be expanded, but not contracted.
• Each volume contains one or more shares, which logically subdivide the volume, such
that users using one share cannot see files that belong to another share.
• One volume must be assigned at initial system configuration as the Home Directory
Location (the volume that contains the home directory for all user profiles).
White Paper: Network Storage LINKSYS © 2007
5 EDCS-593805 v1.0
A printed copy of this document is considered uncontrolled










