Product data
Table Of Contents
- Contents
- Introduction
- Networked Storage Overview
- Storage Concepts and Technologies
- Conclusion
- Obtaining Technical Assistance
- Appendix A
Storage Concepts and Technologies
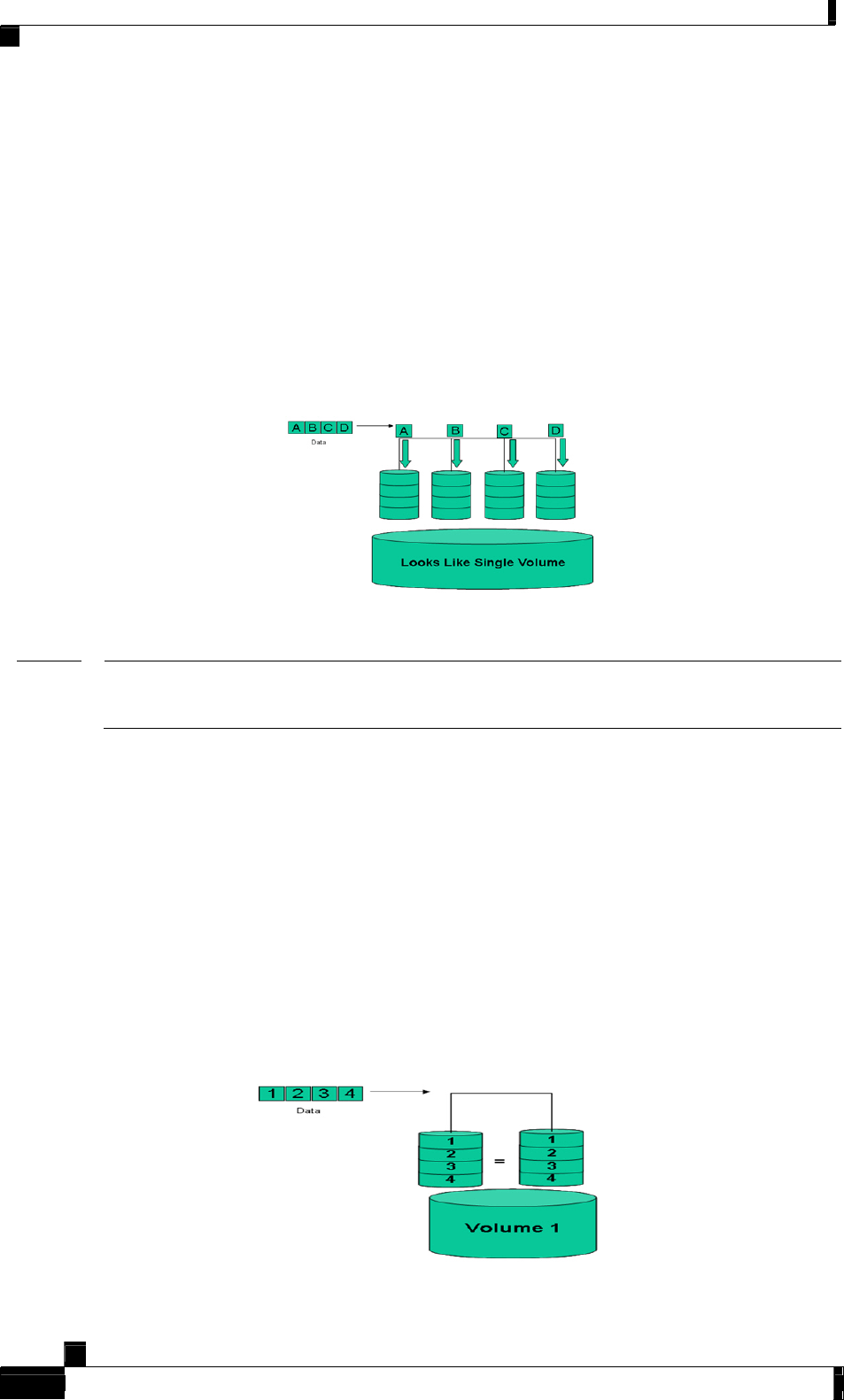
RAID 0 (Striped Set)
RAID 0 splits data evenly across two or more disks. Data is written in blocks across multiple
disks. Because it contains no parity information, it offers no redundancy. Because the data is
striped across all the disks in the array, the reliability of a given RAID 0 array is equal to the
average reliability of each disk divided by the number of disks in the array. For example, a
set of two disks is roughly half as reliable as a single disk (Figure 8). RAID 0 is useful where
redundancy is not a requirement. The following design considerations apply:
• This RAID level should not be used for mission-critical systems.
• Minimum Number of Disks: 2
• Advantages: High performance. All storage on the disks is usable.
• Disadvantage: No fault tolerance. If one drive fails, the entire array becomes
inaccessible.
Figure 8: RAID 0
Note
When you stripe disks of different sizes together, the storage space added to the array is no
larger than that of the smallest disk in the array. For example, if you put three disks of sizes
100 GB, 120 GB, and 120 GB into the array, the total storage space of the array is 300 GB.
RAID 1 (Mirror)
RAID 1 provides data redundancy by writing data to one, two or three other hard disk
drives in the array. The mirrored disks have 2x, 3x or 4x the Read transaction rate of a single
disk and the same Write transaction rate and transfer rate per block as a single disk (Figure
9). The following design considerations apply:
• Use this RAID level for systems where high-availability is critical.
• Minimum Number of Disks: 2
• Advantages: Best data protection of the RAID levels as it is 100% redundant.
• Disadvantages: Highest disk overhead (i.e., 100%) of the RAID levels. For example, if
there are two 80 GB disks, with a total of 160 GB of raw space, the amount of protected
space equals 80 GB.
Figure 9: RAID 1
White Paper: Network Storage LINKSYS © 2007
11 EDCS-593805 v1.0
A printed copy of this document is considered uncontrolled










