User Guide
Table Of Contents
Cisco AnyConnect Secure Mobility Solution Guide
Supported Architectures
10
Cisco AnyConnect Secure Mobility Solution Guide
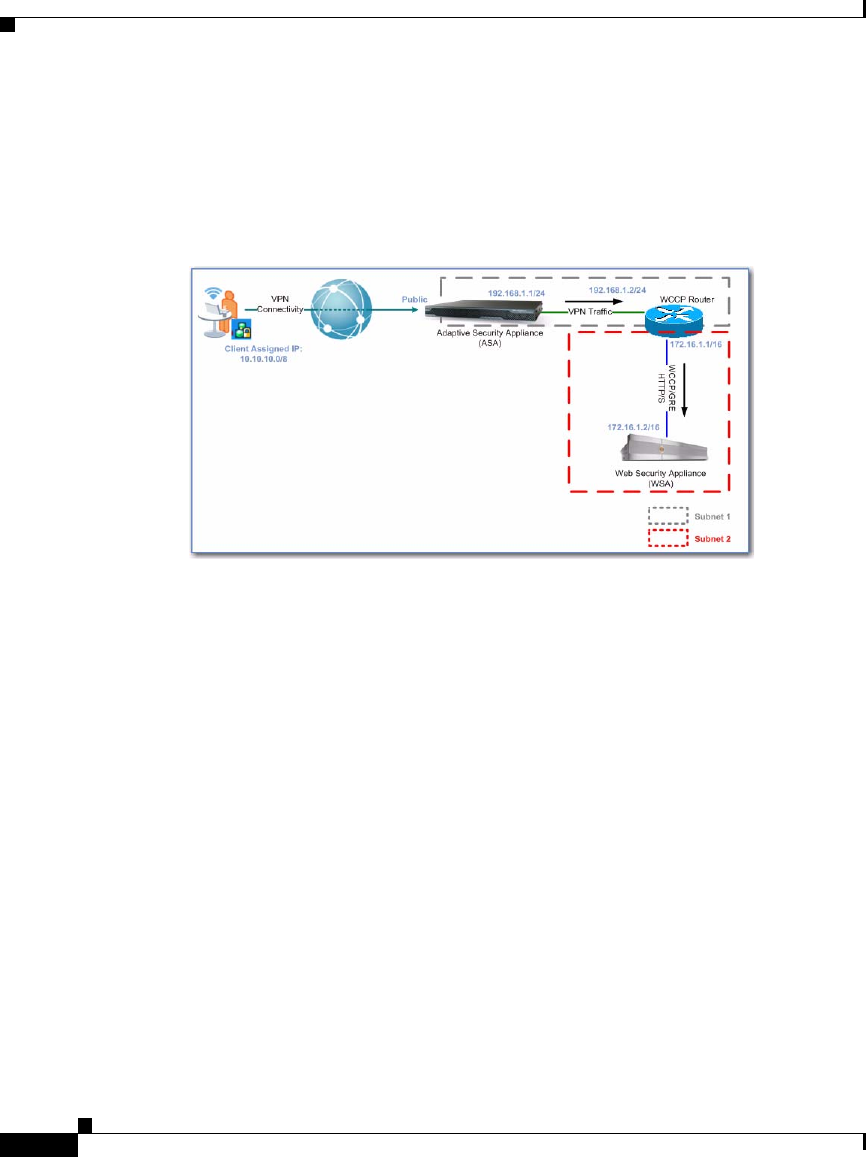
Architecture Scenario 2, Multiple Subnets
Figure 2 illustrates the architecture described in this section.
Figure 2 Single Site and Multiple Subnets
The deployment scenario in Figure 2 depicts an architecture similar to Figure 1
on page 8. However, this architecture introduces WCCP with Generic Routing
Encapsulation (GRE) redirection which is required when the WSA is on a
different subnet than the WCCP router. Like the architecture depicted in
Figure 1,
the traffic flow is essentially the same. Nevertheless, you must consider Layer 3
(L3) redirection which includes GRE as the redirection method. In addition, you
must consider alternative routing entries on the WSA to route traffic back to the
ASA.
You might want to use the architecture in Figure 2 instead of Figure 1 if your
network topology prevents you from placing the WSA on the same subnet as the
WCCP router or if you want all web traffic to enter the WCCP router from a
separate subnet as other network traffic. Isolating traffic destined for the Internet
like this can allow network administrators to more easily monitor and report on
web traffic. Additionally, you can create firewall policies to block web traffic
from all users unless their traffic goes through the WSA Web Proxy.
The WCCP router automatically negotiates the redirection method with the WSA,
encapsulates the web traffic in a GRE header, and routes it to the WSA based on
its routing table. Non-web traffic destined for the Internet is forwarded to its
default route (
ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 192.168.1.1), which in this case is










