Manual
Cisco Packet Data Serving Node (PDSN) Release 2.0
System Overview
7
12.3(11)T
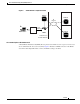
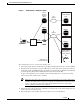
Figure 5 CDMA Network —Mobile IP Scenario
The communication process occurs in the following order:
1. The mobile station registers with its Home Agent (HA) through an FA; in this case, the Cisco PDSN.
2. The HA accepts the registration, assigns an IP address to the mobile station, and creates a tunnel to
the FA. This results in a PPP link between the mobile station and the FA (or PDSN), and an IP-in-IP
or Generic Routing Encapsulation (GRE) tunnel between the FA and the HA.
As part of the registration process, the HA creates a binding table entry to associate the mobile
station’s home address with its Care-of address.
Note While away from home, the mobile station is associated with a care-of address. This address
identifies the mobile station’s current, topological point of attachment to the Internet, and is
used to route packets to the mobile station. In IS-835-B networks, the foreign agent’s
address is always used as the Care-of address.
3. The HA advertises that the network is reachable to the mobile station, and tunnels datagrams to the
mobile station at its current location.
4. The mobile station sends packets with its home address as the source IP address.
42690
Home Access
Provider Network
Home IP Network
Broker Network
HLR
RADIUS
RADIUS
HA
Home IP Network,
Private Network,
Home Access
Provider Network
RAN
Visited Access
Provider Network
R-P
Interface
Visitor
Location
Register
(VLR)
SS7
network
IP
network
RADIUS
PDSN
M
obile station