Cisco Packet Data Serving Node (PDSN) Release 2.0 Feature History Release Modification 12.2(8)BY This feature was introduced on the Cisco 7200 Series Router. 12.2(8)ZB This feature was introduced on the Cisco Catalyst 6500 Switch. 12.2(8)ZB1 This feature was introduced on the Cisco 7600 Internet Router. 12.2(8)ZB5 Four new CLI commands were added. 12.2(8)ZB6 Two CLI commands were added or modified. 12.2(8)ZB7 Six CLI commands were added or modified. 12.2(8)ZB8 One new CLI command was added.
Cisco Packet Data Serving Node (PDSN) Release 2.0 Feature Overview • AAA Authentication and Authorization Profile, page 96 • Attributes, page 99 • Glossary, page 112 • Appendix A, “Command Reference” Feature Overview A PDSN provides access to the Internet, intranets, and Wireless Application Protocol (WAP) servers for mobile stations using a Code Division Multiple Access 2000 (CDMA2000) Radio Access Network (RAN).
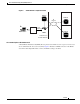
Cisco Packet Data Serving Node (PDSN) Release 2.0 System Overview Figure 1 The CDMA Network Subscribed Access Provider Network AAA BTS IP Network BSC PCF RAN PDSN R-P Interface IP Network Visited Access Provider Network Visited AAA BTS Mobile station Home IS Priv BSC PCF Home Serv IP Network RAN Home A PDSN R-P Interface As the illustration shows, the mobile station, which must support either Simple IP or Mobile IP, connects to a radio tower and BTS.
Cisco Packet Data Serving Node (PDSN) Release 2.0 System Overview How PDSN Works When a mobile station makes a data service call, it establishes a Point-to-Point Protocol (PPP) link with the Cisco PDSN. The Cisco PDSN authenticates the mobile station by communicating with the AAA server. The AAA server verifies that the user is a valid subscriber, determines available services, and tracks usage for billing.
Cisco Packet Data Serving Node (PDSN) Release 2.0 System Overview Figure 3 CDMA Network - Simple IP Scenario Home IP Network RADIUS RADIUS IP network Broker Network R-P Interface RADIUS Mobile station PDSN RAN 42691 Visited Access Provider Network Cisco PDSN Simple IP with VPDN Scenario A Virtual Private Data Network (VPDN) allows a private network dial-in service to span to remote access servers called Network Access Servers (NAS).
Cisco Packet Data Serving Node (PDSN) Release 2.0 System Overview Figure 4 CDMA Network —Simple IP with VPDN Scenario Home RADIUS R IP network Brok R-P Interface Mobile station R PDSN Network Access Server (NAS) RAN Tun Visited Access Provider Network A VPDN connection is established in the following order: 1. A PPP peer (mobile station) connects with the local NAS (the Cisco PDSN). 2. The NAS begins authentication when the client dials in.
Cisco Packet Data Serving Node (PDSN) Release 2.0 System Overview Figure 5 CDMA Network —Mobile IP Scenario Visitor Location Register (VLR) Home Access Provider Network SS7 network HLR Home IP Network RADIUS RADIUS IP network Broker Network R-P Interface Mobile station RADIUS PDSN RAN Home IP Network, Private Network, Home Access Provider Network HA 42690 Visited Access Provider Network The communication process occurs in the following order: 1.
Cisco Packet Data Serving Node (PDSN) Release 2.0 System Overview Note 5. Packets destined for the mobile station go through the HA; the HA tunnels them through the PDSN to the mobile station using the care-of address. 6. When the PPP link is handed off to a new PDSN, the link is re-negotiated and the Mobile IP registration is renewed. 7. The HA updates its binding table with the new care-of address. For more information about Mobile IP, refer to the Cisco IOS Release 12.
Cisco Packet Data Serving Node (PDSN) Release 2.0 Features PDSN on MWAM The MWAM supports the feature set of PDSN Release 2.0, and functionality remains the same as on the Cisco 7200 platforms. The significant difference between the Cisco PDSN on the Cisco 7200 router and on the MWAM is that a Cisco Catalyst 6500 or Cisco 7600 chassis will support a maximum of 6 application modules. Each application module supports 5 IOS images, each with access to 512 Megabytes of RAM.
Cisco Packet Data Serving Node (PDSN) Release 2.0 Features Note • Hardware IPSec Acceleration Using IPSec Acceleration Module—Static IPSec • 1xEV-DO Support • Integrated Foreign Agent (FA) • AAA Support • Packet Transport for VPDN • Proxy Mobile IP • Multiple Mobile IP Flows • PDSN Clustering Peer-to-Peer and Controller / Member Architecture The Cisco PDSN software offers several feature options which are available on four different images.
Cisco Packet Data Serving Node (PDSN) Release 2.0 Features PDSN Performance Metrics Cisco PDSN Release 2.0 delivers the following performance improvements compared to Release 1.2: • Significant improvements in Mobile IP call setup rate Performance metrics for the Cisco PDSN with Release 2.0 software on 7200 Platform are: • 20000 user sessions per on 7206VXR with NPE-400 with 512MB DRAM and on 7206VXR NPE-G1 with 1G DRAM.
Cisco Packet Data Serving Node (PDSN) Release 2.0 Resource Management • Maximum of 8000 IPSec tunnels with VPNSM hardware support (This figure is for the chassis, IPSec resources are not linked with PDSN images on MWAM, it is a separate resource) • Maximum call set up rate for a cluster with n members configured in a controller/member cluster for Simple IP and Mobile IP Sessions with Release 2.0 Clustering enhancements.
Cisco Packet Data Serving Node (PDSN) Release 2.0 Resource Management • The STC VSA returned from AAA in access-accept message during FA-CHAP and HA-CHAP will be ignored, and local configuration on the PDSN and HA will take precedence. • Revocation extension and messages, even if not protected by FHAE or IPSec, will be accepted and processed by both PDSN and HA.
Cisco Packet Data Serving Node (PDSN) Release 2.0 Resource Management The Ballot version mentions that a Disconnect Request can be received at the Home Agent (HA,) but details on the action to be taken in such an event is not detailed. Hence the approach followed is to terminate a specific binding if Framed-IP-Address attribute is received along with NAI, or terminate all bindings for the NAI, if only NAI attribute is received in the Disconnect Request.
Cisco Packet Data Serving Node (PDSN) Release 2.0 Resource Management • VPDN sessions with authentication and authorization for the user performed at AAA. • Mobile IP sessions with FA-CHAP performed for the session/NAI at AAA. • Proxy mobile IP sessions with authentication and authorization for the user performed at AAA. Prepaid service is also available for sessions opened with MSID-based authentication access.
Cisco Packet Data Serving Node (PDSN) Release 2.0 Resource Management When the Billing Server successfully authorizes the user as a valid prepaid user, it notifies the HAAA that it supports prepaid service based on volume, or duration, or both, depending on the configuration at the Billing Server and capabilities as indicated by the PDSN.
Cisco Packet Data Serving Node (PDSN) Release 2.0 Resource Management When threshold for the quota is reached, the PDSN sends an Access Request to HAAA to retrieve more quota for the flow. In case the values of threshold for the quota and the quota allocated are same, then on quota expiry (when Quota = Threshold), the PDSN will treat this as flow as closed, and send an Access Request with Update-reason as “Quota reached”.
Cisco Packet Data Serving Node (PDSN) Release 2.0 Resource Management After the PDSN receives the Access-Accept message from AAA, it parses the RADIUS packet and retrieves the attributes inside it. The PDSN stores the information present in the packet regarding the quota allocated for the flow and the threshold corresponding to the allocated flow. It also stores the Quota-ID allocated in the user flow present in the message.
Cisco Packet Data Serving Node (PDSN) Release 2.0 Resource Management Step 8 The Billing Server does not allocate a new quota when the user indicates “Quota reached” for the prepaid flow. The Billing Server terminates the prepaid flow and indicates the same to the HAAA. The HAAA sends an Access-Accept message to the PDSN acknowledging the termination of the Prepaid packet data session by encapsulating Update Reason Sub-type as “Quota is reached” inside PPAQ VSA.
Cisco Packet Data Serving Node (PDSN) Release 2.0 Resource Management Once the flow for the user comes up (for example, an IP address assigned for Simple IP or MIP RRP received from the HA and sent to the MS), the PDSN starts the timer corresponding to the duration threshold value and duration quota value. Step 3 Once the timer expires for the threshold value of the allocated quota for the prepaid flow, the PDSN sends an Access-Request Message to AAA to refresh quota for the prepaid flow.
Cisco Packet Data Serving Node (PDSN) Release 2.0 Resource Management Step 6 The Billing Server does not allocate a new quota when the user indicates “Quota reached” for the prepaid flow. The Billing Server terminates the prepaid flow and indicates the same to the HAAA. HAAA sends an Access-Accept message to the PDSN acknowledging the termination of the Prepaid packet data session by encapsulating Update Reason Sub-type as “Quota is reached” inside PPAQ VSA.
Cisco Packet Data Serving Node (PDSN) Release 2.0 Resource Management The HAAA encapsulates the prepaid information received for the user from Billing Server in a RADIUS Access-Accept message and sends it to the PDSN.
Cisco Packet Data Serving Node (PDSN) Release 2.0 Resource Management The HAAA sends the information received from the Billing Server into a RADIUS Access-Accept message to be sent to the PDSN.
Cisco Packet Data Serving Node (PDSN) Release 2.0 Resource Management The Billing Server updates its database with the amount of quota utilized by the user. Since the user indicates quota renewal, the Billing Server apportions a fraction of prepaid account balance of the user. It also assigns a new Quota ID for the current allocated quota and a corresponding threshold value for the assigned quota. This information is passed on to the HAAA.
Cisco Packet Data Serving Node (PDSN) Release 2.0 Resource Management IS-835-B Compliant Static IPSec An IPSec Security Association is a unidirectional logical connection between two IPSec systems, and is uniquely identified by Security Parameter Index (SPI), IP Destination Address, and the Security Protocol (where the Security Protocol is Authenticate Header (AH) or Encapsulating Security Payload (ESP). The Security Association has two types: Transport and Tunnel.
Cisco Packet Data Serving Node (PDSN) Release 2.0 Resource Management The HA determines which type of security association (if any) is required with a PDSN. The HA uses the same security policy that is specified in the Home RADIUS server and returned to the PDSN in the 3GPP2 security level attribute. All MN will receive the same security level while accessing the same PDSN.
Cisco Packet Data Serving Node (PDSN) Release 2.0 Resource Management The policy described in the crypto map entries is used during the negotiation of security association, for IPSec to succeed between two IPSec peers, both peers’ crypto map entries must a contain compatible configuration statement. Only one crypto map set is applied to single interface; Multiple interfaces can share the same crypto map set.
Cisco Packet Data Serving Node (PDSN) Release 2.0 Resource Management On-Demand Address Pools (ODAP) A PDSN Cluster can consist of up to ten MWAM cards, with one Cluster Controller and a Backup Cluster Controller, and 48 PDSN IOS application image instances. While MWAM cards provide a higher density of PDSNs, they make it necessary to allocate IP addresses from a central source. This simplifies configuration so users will not have to configure a local pool of IP addresses in each PDSN.
Cisco Packet Data Serving Node (PDSN) Release 2.0 Resource Management • A Catalyst 6500 chassis contains up to 6 MWAM cards. The total number of local IP addresses needed in the pool for each chassis: – 6 MWAMs * 80,000 sessions = 480,000 IP addresses in the PDSN ODAP pool. In order to configure an ODAP subnet pool for Mobile IP Home Agent applications, determine the number IP addresses needed for each Home Agent.
Cisco Packet Data Serving Node (PDSN) Release 2.0 Resource Management • Always-on feature is not applicable for mobileip users. • Always-on feature is not supported for VPDN users. • Aging of Dormant PPP session's feature works independent of always-on users. The aging of dormant PPP session’s feature does not care for the always-on property of a session. NPE-G1 Platform Support PDSN Release 2.0 introduces support for the NPE-G1 router platform.
Cisco Packet Data Serving Node (PDSN) Release 2.0 Resource Management Conditional Debugging Support Under Clustering Feature The Cisco PDSN 2.0 Clustering feature adds additional support for the conditional debugging with the following clustering debug command on both controller and member: • Note Debug cdma pdsn cluster controller message {event | error | packet} PDSNs in controller-member mode and peer-to-peer mode cannot co-exist in the same cluster. They are mutually exclusive.
Cisco Packet Data Serving Node (PDSN) Release 2.0 Resource Management Step 3 When all the calls are brought down, upgrade the software to Release 2.0 or shutdown this member without disrupting the operation of the PDSN cluster. When the member comes online you can configure it to rejoin the cluster by issuing the following command: config# no cdma pdsn cluster member prohibit administratively Once the controller is updated with the status the new member PDSN will be selected for new incoming calls.
Cisco Packet Data Serving Node (PDSN) Release 2.0 Resource Management cCdmaPcfSoPppConnSuccesses, cCdmaPcfSoPppConnFails, cCdmaPcfSoPppConnAborts These objects are grouped under the following MIB group. cCdmaPcfSoPppSetupStats OBJECT IDENTIFIER ::= { cCdmaPerformanceStats 12 } As with previous releases, you can manage the Cisco PDSN with Cisco Works 2000 network management system using SNMP. In addition to the standard 7200 and 6500 MIBS, the Cisco CDMA PDSN MIB (CISCO_CDMA_PDSN_MIB.
Cisco Packet Data Serving Node (PDSN) Release 2.
Cisco Packet Data Serving Node (PDSN) Release 2.0 Resource Management How Prepaid Works in PDSN When a prepaid mobile user makes a data service call, the MS establishes a Point-to-Point Protocol (PPP) link with the Cisco PDSN. The Cisco PDSN authenticates the mobile station by communicating with the AAA server. The AAA server verifies that the user is a valid prepaid subscriber, determines what services are available for the user, and tracks usage for billing.
Cisco Packet Data Serving Node (PDSN) Release 2.0 Resource Management Step 12 When the user disconnects, the MS initiates release of the call and the traffic channel is released. The PDSN clears the session and sends an Accounting Request Stop record. The record includes the prepaid VSAs to report final usage. Step 13 The RADIUS Server updates its own records and sends final usage report to PBS. The PBS updates the user’s account and replies to the AR. And the AR sends the Accounting Response to PDSN.
Cisco Packet Data Serving Node (PDSN) Release 2.0 Resource Management Step 14 The AR updates its own records and sends final usage report to PBS, who updates the user’s account and replies to the AR. Step 15 The AR finally sends the Accounting Response to PDSN. Note This feature is a variant of the PDSN Release 2.0 software. Refer to the Feature Matrix to see which features are available on a specific image of PDSN 2.0.
Cisco Packet Data Serving Node (PDSN) Release 2.0 Resource Management Hardware IPSec Acceleration Using IPSec Acceleration Module—Static IPSec Note The Cisco PDSN Release on the Cisco 6500 and 7600 platforms requires the support of the Cisco IPSec Services Module (VPNSM), a blade that runs on the Catalyst 6500 switch and the Cisco 7600 Internet Router. VPNSM does not have any physical WAN or LAN interfaces, and utilizes VLAN selectors for its VPN policy.
Cisco Packet Data Serving Node (PDSN) Release 2.
Cisco Packet Data Serving Node (PDSN) Release 2.0 Resource Management Conditional Debugging Enhancements PDSN Release 2.0 supports additional conditional debugging for Mobile IP components. Mobile IP conditional debugging is supported based on NAI as well as the MN’s home address. Currently, when multiple conditional debugging is enabled, the debug output does not individually display the condition for which the debugs are printed for all the CDMA related debugs.
Cisco Packet Data Serving Node (PDSN) Release 2.0 Resource Management Conditional debugging is an IOS feature, and the following CLI are available across all images. router# debug condition ? application Application called called number calling calling glbp interface group interface interface ip IP address mac-address MAC address match-list apply the match-list standby interface group username username vcid VC ID The options calling, username, and ip are used by the CDMA/Mobile IP subsystems.
Cisco Packet Data Serving Node (PDSN) Release 2.0 Features Available From Previous PDSN Releases Features Available From Previous PDSN Releases The following features were introduced in previous PDSN software releases, and are still supported in Release 2.0. Integrated Foreign Agent (FA) The FA is an essential component to mobility, because it allows a mobile station to remotely access services provided by the station’s home network. The Cisco PDSN provides an integrated FA.
Cisco Packet Data Serving Node (PDSN) Release 2.0 Redundancy and Load Balancing The Cisco PDSN also supports service provisioning using AAA servers and a user service profile. This profile is defined by the user’s home network. It is referenced by the NAI. It is typically stored in the AAA server in the user’s home network, along with the user authentication information, and is retrieved as part of authorization reply. Packet Transport for VPDN The Cisco PDSN supports the transport of VPDN packets.
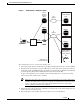
Cisco Packet Data Serving Node (PDSN) Release 2.0 Redundancy and Load Balancing Note It is not possible to configure Peer-to-Peer clustering for PDSN on the MWAM. This feature is only supported on the Cisco 7200 platform. Note The new PDSN Controller-Member clustering feature is only available on the -c6is-mz, and -c6ik9s-mz images. Figure 8 illustrates the Controller-Member architecture on the 6500 or 7600-based MWAM platform.
Cisco Packet Data Serving Node (PDSN) Release 2.0 Redundancy and Load Balancing Figure 8 PDSN Controller -Member Architecture for MWAM on the Catalyst 6500 Access-port/line card PCF 1 BSC, PCF PDSN addr configured: 1.1.1.1, 1.1.2.1 1.1.3.1 1.2.3.1 1.1.1.1 1.1.4.1 1.2.4.1 MWAM card Active Standby Controller’s part of HSRP group PCF 2 PCF-PDSN SAs configured for: 1.1.1.1, 1.1.2.1, 1.1.3.1, 1.1.4.1, ... 1.1.n.1 or global BSC, PCF 1.1.5.1 1.2.5.1 1.1.2.1 1.1.6.1 1.2.6.1 MWAM card 1.1.7.
Cisco Packet Data Serving Node (PDSN) Release 2.0 Redundancy and Load Balancing • The actual PDSN selection and load-balancing procedures are similar to the R1.1 implementation; however, different record tables are used. • Auto-configuration of a new PDSN controller added to the cluster—The new controller must be configured as such, and must be configured as a member of the HSRP group of routers.
Cisco Packet Data Serving Node (PDSN) Release 2.0 Redundancy and Load Balancing Load Balancing A controller maintains load information for all members in the cluster in order to perform PDSN Cluster Member selection. This load information is transferred from the members to the controller under the following conditions: • at periodic intervals. • when a session is established or dismantled in a member. In this case, the periodic timer is restarted. • requested from the members by the controller.
Cisco Packet Data Serving Node (PDSN) Release 2.0 Redundancy and Load Balancing Scalability In this release the PDSN uses a new scalability feature that allows PPP sessions to run on virtual-access subinterfaces that can support up to 20000 sessions. Note When using the virtual-access subinterfaces, not more than 20 percent (or a maximum of 4000) of the sessions should be compression sessions.
Cisco Packet Data Serving Node (PDSN) Release 2.0 Redundancy and Load Balancing If you enable high availability when the standby supervisor engine is running, image version compatibility is checked and if found compatible, the database synchronization starts. High availability compatible features continue from the saved states on the standby supervisor engine after a switchover.
Cisco Packet Data Serving Node (PDSN) Release 2.0 Supported Platforms Related Documents For additional information about the Cisco PDSN Release 2.0 software, refer to the following documents: • Release Notes for the Cisco PDSN 2.0 Feature in Cisco IOS Release 12.3(8)XW For more information about: • MWAM hardware and software information, refer to the Cisco Multi-processor WAN Application Module Installation and Configuration Note.
Cisco Packet Data Serving Node (PDSN) Release 2.0 Supported Standards, MIBs, and RFCs • CISCO_AHDLC_MIB.my • CISCO_AAA_CLIENT_MIB.my • CISCO_AAA_SERVER_MIB.my • CISCO_VPDN_MGMT_MIB.my • CISCO_VPDN_MGMT_EXT_MIB.my For descriptions of supported MIBs and how to use MIBs, see the Cisco MIB web site on CCO at http://www.cisco.com/public/sw-center/netmgmt/cmtk/mibs.shtml.
Cisco Packet Data Serving Node (PDSN) Release 2.0 Configuration Tasks Configuration Tasks This section describes the steps for configuring the Cisco PDSN software on both the 7200 and MWAM platforms. Prior to configuring instances of the PDSN on MWAM application cards, you must create a base Catalyst 6500 or 7600 configuration. Refer to the Cisco Multi-processor WAN Application Module Installation and Configuration Note for more information.
Cisco Packet Data Serving Node (PDSN) Release 2.
Cisco Packet Data Serving Node (PDSN) Release 2.0 Configuration Tasks Creating the CDMA Ix Interface To create the CDMA Ix interface, use the following commands in global configuration mode: Command Purpose Router(config)# interface cdma-Ix1 Defines the CDMA virtual interface for the R-P interface. Router(config-if)# ip address ip-address mask Assigns an IP address and mask to the CDMA-Ix virtual interface. This IP address will be used by the RAN to communicate with the PDSN.
Cisco Packet Data Serving Node (PDSN) Release 2.0 Configuration Tasks Enabling R-P Interface Signaling To enable the R-P interface signaling, use the following commands in global configuration mode: Command Purpose Router(config)# cdma pdsn secure pcf lower_addr [upper_addr] spi {spi_val | [inbound in_spi_val outbound out_spi_val]} key {ascii | hex} string Defines the PCF security association on the PDSN.
Cisco Packet Data Serving Node (PDSN) Release 2.0 Configuration Tasks To configure AAA in the PDSN environment, use the following commands in global configuration mode: Command Purpose Router(config)# aaa new-model Enables AAA access control. Router(config)# aaa authentication ppp default group radius Enables authentication of PPP users using RADIUS. Router(config)# aaa authorization configuration default group radius Enables Network Access Identifier (NAI) construction in the absence of CHAP.
Cisco Packet Data Serving Node (PDSN) Release 2.0 Configuration Tasks Configuring Prepaid in the PDSN Environment For the Cisco-specific prepaid solution, there are no configuration commands for prepaid. To configure prepaid, ensure that you include crb-entity-type=1 in the user profile. Enabling VPDN in a PDSN Environment To configure VPDN in the PDSN environment, use the following commands in global configuration mode: Command Purpose Router(config)# vpdn enable Enables VPDN.
Cisco Packet Data Serving Node (PDSN) Release 2.0 Configuration Tasks Command Purpose Router(config-if)# ip mobile foreign-service [reverse-tunnel [mandatory]] Enables Mobile IP FA service on this interface. Router(config-if)# ip mobile foreign-service registration Sets the R bit in an Agent Advertisement.
Cisco Packet Data Serving Node (PDSN) Release 2.0 Configuration Tasks Configuring IS835-B IPSec for the Cisco PDSN To configure IS835-B IPSec for the PDSN, use the following commands in global configuration mode: Command Purpose Router(config)# Router(config)# ip mobile cdma ipsec Enables or disables the CDMA IPSec feature. This is only present in crypto images for the Cisco 7200 Series Internet router, and non-crypto images for the Cisco MWAM.
Cisco Packet Data Serving Node (PDSN) Release 2.
Cisco Packet Data Serving Node (PDSN) Release 2.0 Configuration Tasks Configuring Peer-to-Peer PDSN Selection Command Purpose Router(config)# cdma pdsn secure cluster default spi spi_index [key ascii | hex value] Configures one common security association for all PDSNs in a cluster. Router(config)# cdma pdsn cluster member controller ipaddr Configures the PDSN to operate as a cluster member.
Cisco Packet Data Serving Node (PDSN) Release 2.0 Configuration Tasks Command Purpose Router(config)# cdma pdsn failure-history entries Specifies the maximum number of entries that can be maintained in the SNMP session failure table. Router(config)#no virtual-template snmp Prevents the virtual-access subinterfaces from being registered with the SNMP functionality of the router and reduces the amount of memory being used, thereby increasing the call setup performance.
Cisco Packet Data Serving Node (PDSN) Release 2.0 Configuration Tasks Configuring On Demand Address Pools To configure the DHCP Server with the ODAP Subnet Allocation Server, perform the following configuration tasks. This configuration can be either on a PDSN Cluster Controller or a Backup Cluster Controller. Command Purpose Router(config)# ip dhcp pool pdsn-pool Creates a name for the DHCP server address pool and places you in DHCP pool configuration mode (identified by the config-dhcp# prompt).
Cisco Packet Data Serving Node (PDSN) Release 2.0 Configuration Tasks For the ip dhcp pool pdsn-pool command, the subnet is 13.0.0.0 and the mask defines the size of the pool. The subnet prefix-length defines the size of the subnet chunks using standard CIDR bit count notation to determine the number of addresses that are configured in each subnet lease.
Cisco Packet Data Serving Node (PDSN) Release 2.0 Configuration Tasks Configure the following ODAP client and OSPF commands on the PDSN: Command Purpose Router(config)# ip dhcp ping packets 0 <<< disables ping test (range 0-10) Specifies the number of packets a Cisco IOS Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) Server sends to a pool address as part of a ping operation.
Cisco Packet Data Serving Node (PDSN) Release 2.0 Configuration Tasks access-list 11 permit 10.11.1.92 access-list 12 deny 128.0.0.0 0.0.0.255 access-list 12 permit any route-map MAP permit 10<<< only the CDMA-Ix update gets out match ip address 11 set tag 9 route-map DENY-MAP permit 10<<< blocks 128.x.x.x internal network between match ip address 12 the PC and sibytes on the MWAM card set tag 9 or summary-address 128.0.0.0 255.0.0.
Cisco Packet Data Serving Node (PDSN) Release 2.0 Configuration Tasks Configuring PoD on the PDSN To enable Packet of Disconnect on the PDSN, perform the following task: Command Purpose Router(config)# cdma pdsn radius disconnect Enables the RADIUS disconncect feature on the PDSN. Router(config)# aaa pod server [clients ipaddr1 [ipaddr2] [ipaddr3] [ipaddr4]] [port port-number] [auth-type {any | all | session-key}] server-key [encryption-type] string AAA command that enables listening for POD packets.
Cisco Packet Data Serving Node (PDSN) Release 2.0 Monitoring and Maintaining the PDSN Command Purpose Router(config)# cdma pdsn accounting time-of-day Sets triggers for accounting information for different times of day.
Cisco Packet Data Serving Node (PDSN) Release 2.0 Monitoring and Maintaining the PDSN Command Purpose Router# show cdma pdsn accounting session msid flow {mn-ip-address IP_address} Displays the accounting information for a specific flow that is associated with the session identified by the msid. Router# show cdma pdsn accounting session msid flow user username Displays accounting information for a flow with username that is associated with the session identified by the msid.
Cisco Packet Data Serving Node (PDSN) Release 2.0 Configuration Examples Command Purpose Router# show diag [slot] Displays diagnostic information about the controller, interface processor, and port adapters associated with a specified slot of a Cisco router. Router# show interfaces virtual-access number Displays a description of the configuration of the virtual access interface. Router# show ip mobile cdma ipsec profile Displays the configured IPSec profiles.
Cisco Packet Data Serving Node (PDSN) Release 2.0 Configuration Examples Cisco PDSN Configuration for Simple IP Figure 9 and the information that follows is an example of PDSN architecture for Simple IP and its accompanying configuration. Figure 9 PDSN for Simple IP—A Network Map CDMA-Ix1 virtual interface 2.2.2.x 6.6.6.6 255.0.0.0 pdsn1-7206 2.2.2.2 FE1/0 FE0/0 33.33.33.33 2.2.2.5 Local RADIUS 33.33.33.34 255.255.255.255 VLAN3 VLAN2 8.8.8.254 Loopback 0 virtual interface 59197 BSC PCF 23.23.23.
Cisco Packet Data Serving Node (PDSN) Release 2.0 Configuration Examples ! Interface to PCF - R-P ip address 2.2.2.2 255.255.255.0 half-duplex no cdp enable ! interface FastEthernet2/0 ! Interface to external network - Pi ip address 23.23.23.23 255.255.0.0 ! ! ! interface Virtual-Template1 ip unnumbered Loopback0 peer default ip address pool pdsn-pool ppp accm 0 ppp authentication chap pap optional ppp accounting none ppp timeout idle 2000 ! ip local pool pdsn-pool 8.8.8.1 8.8.8.
Cisco Packet Data Serving Node (PDSN) Release 2.0 Configuration Examples Cisco PDSN Configuration for Mobile IP Figure 10 and the information that follows is an example of PDSN architecture for Mobile IP service and its accompanying configuration. The example shows the configuration of PDSN1. Figure 10 PDSN for Mobile IP—A Network Map CDMA-Ix1 virtual interface 5.5.5.5 255.0.0.0 2.2.2.x/24 3.3.3.x/24 Home RADIUS pdsn1-7206 2.2.2.2 FE1/0 e rfac nte I P RBSC PCF 2.2.2.1 3.3.3.2 FE2/0 Mo bil eI 11.
Cisco Packet Data Serving Node (PDSN) Release 2.0 Configuration Examples ! interface FastEthernet0/0 description AAA NMS interface ip address 12.12.12.100 255.0.0.0 ! interface FastEthernet1/0 description R-P interface ip address 2.2.2.2 255.255.255.0 full-duplex ! ! interface FastEthernet2/0 description Pi interface ip address 3.3.3.2 255.255.255.
Cisco Packet Data Serving Node (PDSN) Release 2.0 Configuration Examples vpdn authen-before-forward virtual-profile aaa username HA password 0 rosebud username LNS password 0 cisco username PDSN password 0 cisco no ip gratuitous-arps ! interface Loopback0 ip address 8.8.8.254 255.255.255.255 ! interface CDMA-Ix1 ip address 6.6.6.6 255.0.0.0 ! interface FastEthernet0/0 ! Interface for communication with RADIUS server and NMS ip address 33.33.33.33 255.255.255.
Cisco Packet Data Serving Node (PDSN) Release 2.
Cisco Packet Data Serving Node (PDSN) Release 2.0 Configuration Examples ip subnet-zero ip cef ! ! ! interface Loopback1 no ip address ! interface GigabitEthernet0/0 no ip address ! interface GigabitEthernet0/0.401 encapsulation dot1Q 401 ip address 10.121.68.76 255.255.255.0 standby 1 ip 10.121.68.98 standby 1 priority 120 standby 1 preempt standby 1 name 6509-cluster ! router mobile ! ip classless ip route 10.10.72.1 255.255.255.255 10.121.68.72 ip route 10.10.73.1 255.255.255.255 10.121.68.
Cisco Packet Data Serving Node (PDSN) Release 2.0 Configuration Examples S96> S96> S96> S96>en S96#sh run S96#sh running-config Building configuration... Current configuration : 1182 bytes ! ! No configuration change since last restart ! version 12.
Cisco Packet Data Serving Node (PDSN) Release 2.0 Configuration Examples no login line vty 1 4 login line vty 5 15 login ! end S96# Verify active controller and standby controller S76#sh standby GigabitEthernet0/0.401 - Group 1 State is Active 2 state changes, last state change 00:27:09 Virtual IP address is 10.121.68.98 Active virtual MAC address is 0000.0c07.ac01 Local virtual MAC address is 0000.0c07.ac01 (default) Hello time 3 sec, hold time 10 sec Next hello sent in 2.
Cisco Packet Data Serving Node (PDSN) Release 2.0 Configuration Examples ! Last configuration change at 04:10:06 UTC Sun Sep 15 2002 ! version 12.2 service timestamps debug uptime service timestamps log uptime no service password-encryption service cdma pdsn ! hostname S73 ! aaa new-model ! ! aaa group server radius CSCO-30 server 10.1.1.244 auth-port 1645 acct-port 1646 server 10.1.1.
Cisco Packet Data Serving Node (PDSN) Release 2.0 Configuration Examples summary-address 7.3.0.0 255.255.0.0 redistribute connected subnets route-map MAP-DENY network 10.10.73.1 0.0.0.0 area 73 network 10.10.73.0 0.0.0.255 area 73 network 10.10.173.1 0.0.0.0 area 0 network 10.121.68.0 0.0.0.255 area 0 ! ip local pool pdsn-pool 7.3.1.0 7.3.16.255 ip local pool pdsn-pool 7.3.17.0 7.3.32.255 ip local pool pdsn-pool 7.3.33.0 7.3.48.255 ip local pool pdsn-pool 7.3.49.0 7.3.64.255 ip local pool pdsn-pool 7.3.65.
Cisco Packet Data Serving Node (PDSN) Release 2.0 Configuration Examples group: cluster Controller maximum number of load units = 1000 PDSN-CONTROLLER#show cdma pdsn cluster controller member load Secs until Seq seeks Member (past) seek no reply IPv4 Addr State Load Sessions ------------------------------------------------------------------6 0 20.6.84.1 ready 0 0 5 0 20.6.62.1 ready 0 0 1 0 20.6.64.1 ready 0 0 ------------------------------------------------------------------Controller IPv4 Addr 20.3.68.
Cisco Packet Data Serving Node (PDSN) Release 2.
Cisco Packet Data Serving Node (PDSN) Release 2.0 Configuration Examples cat6500 router#sh running-config Building configuration... Current configuration : 9838 bytes ! ! Last configuration change at 00:21:56 UTC Sat Sep 14 2002 by root ! NVRAM config last updated at 14:10:00 UTC Fri Sep 13 2002 by root ! version 12.
Cisco Packet Data Serving Node (PDSN) Release 2.
Cisco Packet Data Serving Node (PDSN) Release 2.0 Configuration Examples switchport access vlan 66 switchport mode access ! interface FastEthernet3/8 ip address 1.1.1.1 255.255.255.
Cisco Packet Data Serving Node (PDSN) Release 2.
Cisco Packet Data Serving Node (PDSN) Release 2.
Cisco Packet Data Serving Node (PDSN) Release 2.
Cisco Packet Data Serving Node (PDSN) Release 2.
Cisco Packet Data Serving Node (PDSN) Release 2.0 Configuration Examples ip address 172.19.23.16 255.255.254.0 ip nat outside ! interface Vlan309 no ip address ! interface Vlan310 ip address 10.1.1.222 255.255.255.0 ip nat inside ! interface Vlan401 ip address 10.121.68.200 255.255.255.0 ! router ospf 100 log-adjacency-changes network 10.10.10.10 0.0.0.0 area 0 network 10.121.68.0 0.0.0.
Cisco Packet Data Serving Node (PDSN) Release 2.0 PDSN Accounting exec-timeout 0 0 line vty 0 4 exec-timeout 0 0 password lab transport input lat pad mop telnet rlogin udptn nasi line vty 5 10 exec-timeout 0 0 ! ntp master 3 end PDSN Accounting The following RADIUS attributes are contained in the UDR sent by PDSN.
Cisco Packet Data Serving Node (PDSN) Release 2.
Cisco Packet Data Serving Node (PDSN) Release 2.
Cisco Packet Data Serving Node (PDSN) Release 2.
Cisco Packet Data Serving Node (PDSN) Release 2.
Cisco Packet Data Serving Node (PDSN) Release 2.0 AAA Authentication and Authorization Profile DevicePassword = 2. A User should have a profile configured at AAA (this is applicable to an NAI as well, in case of MoIP). A user profile contains username, password, and the base profile where attributes retrieved during authorization can be configured.
Cisco Packet Data Serving Node (PDSN) Release 2.0 AAA Authentication and Authorization Profile • Enable compression: cisco-avpair = “lcp:interface-config=compress stac” cisco-avpair = “lcp:interface-config=compress mppc” cisco-avpair = “lcp:interface-config=compress predictor” • Other Optional Parameters Framed-Protocol = PPP Framed-Routing = None Service-Type = Framed VPDN cisco-avpair = vpdn:tunnel-type=l2tp cisco-avpair = vpdn:ip-addresses=5.5.5.
Cisco Packet Data Serving Node (PDSN) Release 2.0 Attributes – Download Static ip pool name (at Home Agent): cisco-avpair = “mobileip:spi#0=spi 100 key ascii cisco” cisco-avpair = “mobileip:static-ip-pool=mypool” Prepaid (Optional) • cisco-avpair = “crb-entity-type=1” Attributes This section lists several of the various Accounting and Authentication attributes for the Cisco PDSN.
Cisco Packet Data Serving Node (PDSN) Release 2.0 Attributes Table 5 Table 5.Authentication and Authorization AVPs Supported by Cisco IOS (continued) Authentication and Authorization AVPs Supported By Cisco IOS Name Session-Time-out Type Vendor 27 NA Length Format Description 4 integer Maximum number of seconds service is to be provided to the user before session terminates. Allowed In Access Access Request Accept No Yes No Yes This attribute value becomes the per-user “absolute time-out.
Cisco Packet Data Serving Node (PDSN) Release 2.0 Attributes Table 5 Table 5.Authentication and Authorization AVPs Supported by Cisco IOS (continued) Authentication and Authorization AVPs Supported By Cisco IOS Name Inacl# Type Vendor 26/1 Cisco Allowed In Access Access Request Accept Length Format Description >=3 string ASCII access list identifier for an input access list to be installed and applied to an interface for the duration of the current connection.
Cisco Packet Data Serving Node (PDSN) Release 2.0 Attributes Table 5 Table 5.Authentication and Authorization AVPs Supported by Cisco IOS (continued) Authentication and Authorization AVPs Supported By Cisco IOS Name interface-config Type Vendor 26/1 Cisco Length Format Description >=3 string User-specific AAA interface configuration information with Virtual Profiles.
Cisco Packet Data Serving Node (PDSN) Release 2.0 Attributes Table 6 Table 6.Authentication and Authorization AVPs For Packet Data Services Authentication and Authorization AVPs Supported By Cisco IOS Name Type Vendor Length Format mobileip-mn-lifetime 26/1 Cisco >=3 string Defines lifetime used in Proxy MIP RRQ No Yes mobileip-mn-ipaddr 26/1 Cisco >=3 string MN IP address for static address assignment.
Cisco Packet Data Serving Node (PDSN) Release 2.0 Attributes Table 6 Table 6.Authentication and Authorization AVPs For Packet Data Services (continued) 3GPP2-Reverse-TunnelSpec 26/4 3GPP2 4 integer Indicates whether reverse tunneling is required or not. No Yes Yes Yes No Yes Supported values are: 3GPP2-Home-AgentAttribute 26/7 3GPP2 4 3GPP2-IP-Technology 26/22 3GPP2 4 • 0 for reverse tunneling not required. • 1 for reverse tunneling required.
Cisco Packet Data Serving Node (PDSN) Release 2.0 Attributes Table 7 Accounting AVPs For Packet Data Services (continued) Name Service-Type 3GPP2 Type NA AVP Type 6 Vendor Length NA 4 Format integer Description Reference Specs Attribute Present In start stop interim RFC 2865 Yes Yes Yes Framing protocol user is RFC 2865 using. Yes Yes Yes Type of service the user is getting.
Cisco Packet Data Serving Node (PDSN) Release 2.0 Attributes Table 7 Accounting AVPs For Packet Data Services (continued) 3GPP2 Type Name AVP Type Vendor Length Format Description Reference Specs Attribute Present In start stop interim Acct-Session- Id C1 44 NA 4 string A unique accounting ID RFC 2866 created by the PDSN that allows stop and start records to be matched in a log file.
Cisco Packet Data Serving Node (PDSN) Release 2.
Cisco Packet Data Serving Node (PDSN) Release 2.
Cisco Packet Data Serving Node (PDSN) Release 2.0 Attributes Table 7 Accounting AVPs For Packet Data Services (continued) Name 3GPP2ReleaseIndicator 3GPP2 Type F13 AVP Type 26/24 Vendor Length 3GPP2 4 Format integer Description Specifies reason for sending a Stop record.
Cisco Packet Data Serving Node (PDSN) Release 2.0 Attributes Table 7 Accounting AVPs For Packet Data Services (continued) 3GPP2 Type Name AVP Type Vendor Length Format Description Reference Specs Attribute Present In start stop interim 3GPP2-RPSession-ID Y2 26/41 3GPP2 4 integer RP Session ID associated with user session IS-835-B Yes Yes Yes 3GPP2-NumBytesReceived- Total G14 26/43 3GPP2 4 integer Count of all bytes received in the reverse direction by the HDLC layer in PDSN.
Cisco Packet Data Serving Node (PDSN) Release 2.
Cisco Packet Data Serving Node (PDSN) Release 2.
Cisco Packet Data Serving Node (PDSN) Release 2.
Cisco Packet Data Serving Node (PDSN) Release 2.0 Glossary 12.