User Guide
Table Of Contents
- Cover Page
- Table of Contents
- List of Figures
- Figure 1 : Central Controller
- Figure 2 : Peripheral and Peripheral Gateway
- Figure 3 : Administrative Workstation
- Figure 4 : WebView Server
- Figure 5 : Diagram of System Components
- Figure 6 : ICM Data Environment
- Figure 7 : Real-Time Data Moves to AW Local Database
- Figure 8 : Icons for Graphs and Tables
- Figure 9 : Deployment with Enterprise Routing
- Figure 10 : Sample Script for Enterprise Routing
- Figure 11 : Script Example for Agent Level Routing
- Figure 12 : Sample Script for Hybrid Routing
- Figure 13 : Agent State and Task State Relationship
- Figure 14 : Sample Routing Script for Information Gathering and Queuing
- Figure 15 : Call Type Data for Calls that Abandon after Call Type is Changed
- Figure 16 : Call Type Data for Calls that Abandon before Call Type is Changed
- Figure 17 : MultiChannel Options
- Figure 18 : Agent State Hierarchy
- Figure 19 : Call Abandoned While On Hold Scenario
- Preface
- Chapter 1: System Architecture and Reporting
- Chapter 2: Understanding Reporting
- Chapter 3: Understanding Routing and Queuing
- Chapter 4: Planning for Reporting
- Planning for Reporting at Unified ICM Setup
- Planning for Your Deployment
- Planning for Configuration and Scripting
- Planning for Agent Reporting
- Planning for Call Types
- Planning for Custom Reporting
- Planning for the HDS
- Planning for Enterprise Routing and Enterprise Reporting
- Planning for Service and Enterprise Service Reporting
- Planning for Service Level
- Planning for Short Calls
- Planning for Skill Groups and Enterprise Skill Groups
- Planning for Transfer and Conference Reporting
- Planning for Translation Routing
- Planning for Unexpected Scripting Conditions
- Planning for VRU Application Reporting
- Chapter 5: Reporting on Agents
- What Agent Data do you Want to See?
- Reporting on Agent Activity in Skill Groups
- Reporting on Agent States
- Reporting on Average Speed of Answer for Agents and Skill Groups
- Reporting on Agent Logout Reason Codes
- Reporting on Agent Not Ready Reason Codes
- Reporting on Agent Task Handling
- Reporting on Agent Performance for Outbound Option Dialing Campaign Calls
- Reporting on Agent Redirection on No Answer
- Reporting on Agent Call Transfers and Conferences
- Reporting on Agent Teams
- Chapter 6: Reporting on Customer Experience
- Chapter 7: Reporting on Operations
- Chapter 8: Reporting in a MultiChannel Environment
- Chapter 9: Sample Call Scenario
- Chapter 10: Reporting Implications of Data Loss and Component Failover
- Chapter 11: Troubleshooting Report Data
- Appendix A: List of All Unified ICM Report Templates
- Appendix B: Reporting Entities and Databases
- Appendix C: Configuration and Scripting for Reporting
- Configuration for Agent Reporting
- Configuring Call Types
- Configuration and Scripting for Conferences and Transfers
- Configuring Services and Enterprise Services
- Configuring and Scripting for Service Level Threshold and Type
- Configuring Short Calls
- Configuring Skill Groups and Enterprise Skill Groups
- Configuration and Scripting for the VRU
- Configuring Translation Routes
- Index
•
Voice Response Units (VRUs), page 18
•
System Deployment Model, page 19
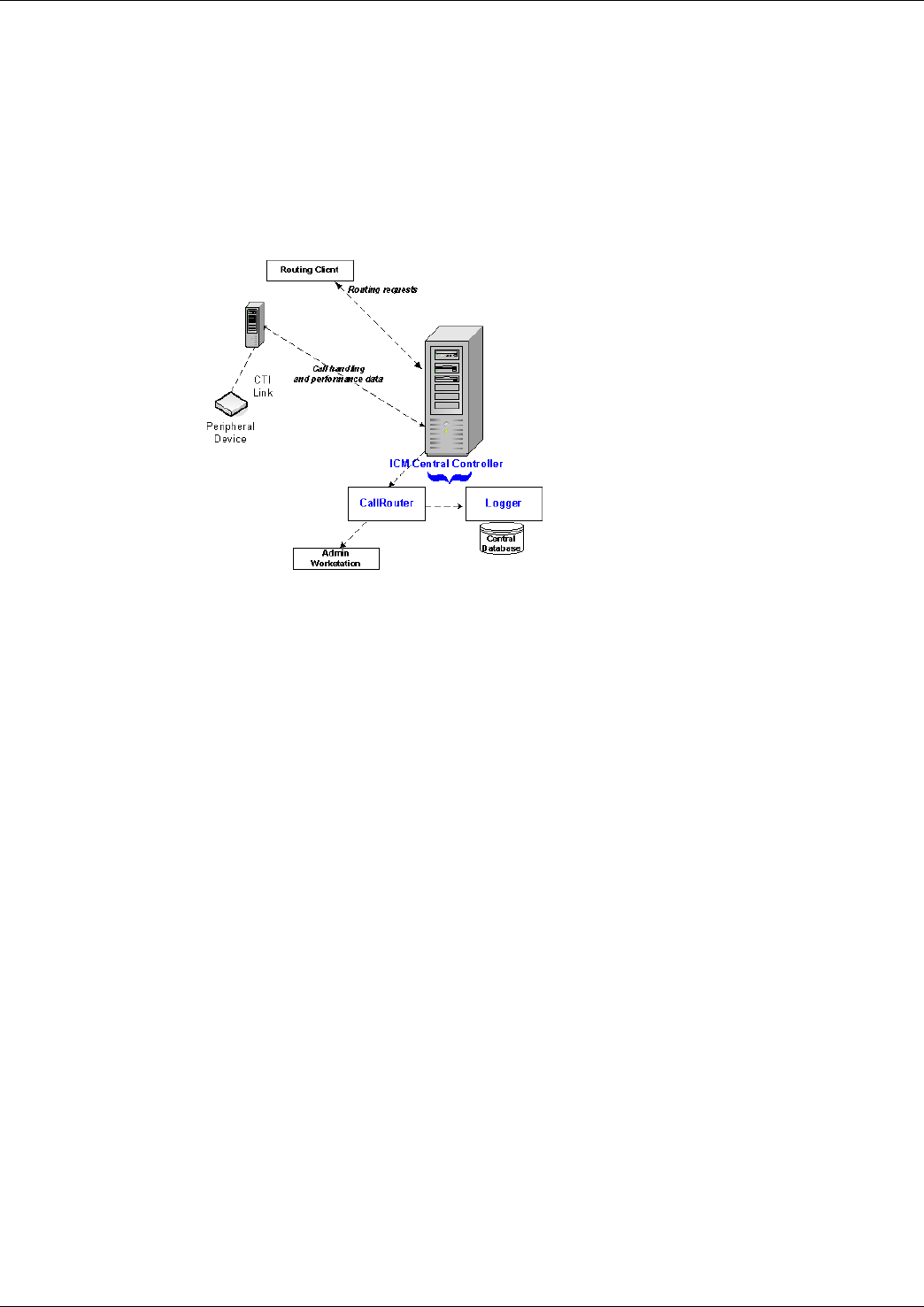
Central Controller
Figure 1: Central Controller
The Central Controller serves as the clearinghouse for routing and reporting data. It does this
by receiving route requests, making routing decisions, and monitoring data messages about
what is happening in the system.
The Central Controller is installed on one or more servers and comprises three major components:
the CallRouter (Router), the Logger, and the Central Database.
Note: Although illustrations in this section show the CallRouter, the Logger, and the Central
Database on the same computer, the CallRouter and the Logger can be installed on separate
computers. The Logger and the Central Database are always co-located on the same computer.
•
CallRouter (Router)
The Router receives notification from a Routing Client (such as a Network Interface Controller
or a Peripheral Gateway) that a call is in need of some form of routing. It then executes a
user-defined script that specifies how the Routing Client is to handle the call.
These routing scripts are created on the Administrative Workstation, are replicated and stored
in the Central Database, and are loaded into Router program memory.
In addition to receiving routing requests, the Router receives messages from all Peripheral
Gateways (page 9) that monitor real-time status events in the network.
These messages update the system's current representation of agents and system resources.
Awareness of the current status of these resources is essential to the routing scripts.
Reporting Guide for Cisco Unified ICM Enterprise & Hosted Release 7.2(1)
8
Chapter 1: System Architecture and Reporting
Central Controller










