Design Guide
16
LAN Baseline Architecture Overview—Branch Office Network
OL-11333-01
Multilayered Branch Architecture
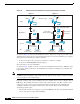
Figure 10 Multilayered Branch Architecture using External Distribution Switches
As shown in Figure 10, using external distribution switches, Option 1 is a single chassis solution at the
distribution layer that can also be used with redundant supervisor cards and redundant power supplies.
This option has the following two distinct advantages:
• It can provide sub-second convergence for both Layer 2 and Layer 3 failures.
• It can provide LACP/PAgP/EtherChannel support.
The disadvantage is the lack of flexibility.
As shown in Figure 10, Option 2 is more cost effective and flexible for branch offices. If IP Base image
is used, static routing can be used at the distribution layer without sacrificing the port scalability and
high availability.
Note Two kinds of binary files are available for the switches: IP base image is a standard multilayer image,
and EMI is enhanced multilayer image. Enhanced image supports a host of Layer 3 features in addition
to Layer 2 features of the standard image.
If dynamic routing is desired at the distribution layer, the stackable switch can be reconfigured with an
EMI image. The stackable switch behaves like a single switch with line cards. More switches can be
added to the stack to meet the growth requirements without sacrificing the high availability. The
scalability is limited to the number of switches that can be stacked. There are the following two
disadvantages of this option:
• The stackable switches do not support cross stack LACP/PAgP at the time of testing. EtherChannel
was the only option to achieve high availability.
Option 1 Option 2
180063
ISR at the edge
Access
Distribution
29xx or 35xx
29xx or 35xx
Access Switches
Edge
WAN
AP
Access Point Access Point
Access Switches
WAN
Access Point Access Point
Stackable Switch
Cross Stack
Ether-channel
Cross Stack
connection