Product manual
IPv6 : Points to Remember
1. IPv6 address is 128 bits in length represented in hexadecimal
2. IPv6 Loopback address is 0:0:0:0:0:0:0:1, also expressed as ::1.
3. IPv6 reserves two special addresses. They are 0:0:0:0:0:0:0:0 and 0:0:0:0:0:0:0:1.
4. Three transition strategies for migration from ipv6 to ipv4 are dual stacking, 6-to-4 tunneling and NAT-PT
cvcccccCisco
Cisco™ CCNA : IPv6 Addressing
Copyright © 2011 SimulationExams.com * All trademarks are duly recognised
* Best printed in landscape mode
CCNA Network Simulator CCNA Exam Simulator CCENT Exam Simulator CCNA ICND2 Exam Simulator CCNP BSCI Exam Simulator
EUI-64 Format
MAC to EUI-64 conversion inserts hex “FFFE” in the middle of a MAC addr, Then flips
the U/L bit to 1, in order to create a 64-bit interface ID from a 48-bit Mac address.
IPv6 Communication Types
Unicast : used for one-to-one communication.
There are 3 types of unicast addresses namely
global, unique-local and link-local
Multicast : used for one-to-many communication
IPv6 multicast address begins with "FF"
Anycast : used for one-to-one-of-many
communication
IPv6 Address Scopes
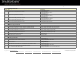
::/0----------------> Default Route
::/128------------> Unspecified
::1/128-----------> Loopback
FC00::/7---------> Unique Local Unicast
FE80::/10--------> Link-Local Unicast
FEC0::/10-------> Site-Local Unicast
FF00::/8----------> Multicast
IPv6 Addressing
IPv6 address consists of 8 groups of four hexadecimal digits separated by colons and which mainly consists
of 3 segments called Global Prefix which is of 48 bits, subnet part with 16 bits and Interface ID called as Host
part with 64 bits.
The first 3 octets constitute Global Prefix, the fourth octet constitute subnet part and the last four form the
Interface ID.
Rules : a) One set of 0's in the address can be replaced by :: but this can be done only once
b) One or any number of consecutive groups of 0 value can be replaced with two colons (::)
IPv6 Header
Version (4 bits) : IP version number (6)
Traffic Class (8 bits) : Used for QoS
Flow Label (20 bits) : Used for packet labelling
Payload Length (16 bits) : Length of the IPv6 payload
Next Header (8 bits) : Identifies the type of header following the IPv6 header
Hop Limit (8 bits) : Number of hops until the packet gets discarded.
Source Address (128 bits) : Source IP address
Destination Address (128 bits) : Destination IP address