Troubleshooting guide
4-4
ATM and Layer 3 Switch Router Troubleshooting Guide
OL-1969-01
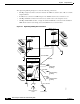
Chapter 4 Example Network
Example Networks
• T1 or E1—Using PVPs, connect to the WAN to reach remote sites such as WWW, FTP, Telnet, and
e-mail
• T3 or E3—Using PVPs, connect to the WAN to reach remote sites such as WWW, FTP, Telnet, and
e-mail
• T1 circuit emulation switch—Using PVP, connect to private branch exchange (PBX) or using
switched virtual circuit (SVC), connect to coder/decoder (CODEC) for constant bit rate (CBR)
video
• 25 Mbps—Connect to computer-aided design/computer-aided manufacturing (CAD/CAM) using a
soft permanent virtual circuit (soft PVC) that provides the following QoS:
–
10 Mbps: video
–
5 Mbps: audio
–
5 Mbps: unspecified bit rate (UBR) for data
• Frame Relay—Using PVC, connect to a telecommuter
Virtual Connections
The example network in Figure 4-2 has the following virtual connections:
• PVPs—Connections between buildings
• PVP tunnels—Connect to the remote site through the public network to avoid signalling
• SVCs—Connect to nodes that require longer data exchanges but infrequent connections
(for example, e-mail server, CAD/CAM connections)
• PVC—Connect to nodes that need quick, short access without signaling delay (for example, Domain
Name System [DNS] server connections)
• Soft PVC—Connect to the UNIX network interface cards (NICs) that do not support signaling
(for example, SGI workstations)
• LAN emulation (LANE), which has the following connection types:
–
LAN emulation client (LEC)—Typical application from Catalyst 5000 and Catalyst 5500 to the
switch router
–
LAN emulation configuration server/broadcast and unknown server (LECS/BUS)—Configure
on a low-usage switch router, because the application is very route processor intensive
• Tag switching—Connect all core switches