Troubleshooting guide
11-8
ATM and Layer 3 Switch Router Troubleshooting Guide
OL-1969-01
Chapter 11 Troubleshooting Layer 3 Network Connections
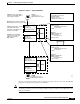
System Architecture
Step 3 Because the packet has been received on a particular VLAN, the search engine begins a search for the
MAC address and its corresponding port of exit.
Step 4 The destination MAC address is found. The microcontroller moves the frame from the internal memory
to the switching fabric. At the same time, the search engine returns relevant information such as QoS
classifications or ISL information to the switching fabric.
Step 5 The VPI and VCI are attached at the beginning of the packet. The VPI and VCI that are used correspond
to the particular quality of service being requested, the appropriate port of exit. The packet then goes
through the SAR (Segmentation and Reassembly), which segments the packet into 48-byte payloads.
The previously retrieved VPI and VCI values are written into the cell header to complete the 53-byte
ATM Cell.
Step 6 The frame moves into the shared fabric and is stored sequentially.
Step 7 The destination port is signaled by the switching-fabric ASIC to take the frame out of memory. The
destination port knows that it is receiving the correct frame because of the internal routing tag.
Step 8 The frame is re-encapsulated via ISL, if necessary, and sent out to the network.
System Architecture
The best way to understand the architecture of the Layer 3 enabled ATM switch router is to divide the
switch into the following three distinct, functional segments:
• Switch route processor
• Switch fabric
• Line cards
The switch route processor engine, show in Figure 11-4, is responsible for all address and route learning
and distribution. Because the Layer 3 enabled ATM switch router is designed as a distributed switching
system, the route processor (CPU) needs to ensure that all Layer 3 routes and Layer 2 MAC addresses
are maintained and the line cards are updated as needed. The route processor is also responsible for
handling all system management, including SNMP and remote monitoring (RMON) statistics.