Technical data
Dial Case Study Overview 1-3
Scenario Description
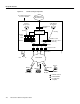
Figure 1-3 OSI Layer 2 and Layer 3 Elements
Table 1-1 summarizes the types of services provided by the headquarters POP to the remote nodes
and sites. For more information, see Table 1-2 on page 4.
Table 1-1 Scenarios and Site Characteristics Provided by Headquarters
Scenario
Remote
Hardware
1
1. This is the typical hardware required at the remote site.
Services Required Notes
Remote node modem Modem Asynchronous shell
2
(async shell)
Asynchronous PPP (async PPP)
2. Cisco IOS shell terminal services can be used for low-level troubleshooting on asynchronous connectivity. The shell is the service
you use to access the command line interface. The shell provides you with a terminal screen.
Dial in only
4
. Remote
devices are assigned an IP
address from a central pool.
Remote node ISDN ISDN routers using
port address
translation (PAT)
3
,
PC-based ISDN
terminal adapters
3. PAT = Port address translation. Easy IP is an implementation of PAT. PAT vastly simplifies IP addressing design when supporting
remote sites. This case study does not describe how to configure PAT. For more information, see the Dial Solutions Configuration
Guide. PAT is mentioned in this table to show you how the technology is positioned in the remote access paradigm.
Synchronous PPP (sync PPP) Dial in only
4
. PAT enabled.
Connecting devices are
assigned an IP address from a
central pool.
4. Unless otherwise stated, the terms “dial-in” and “dial-out” are from the perspective of the Cisco AS5300.
Remote office LAN Cisco 1604 Synchronous PPP Dial in and dial out
4
. Distinct
IP subnet. PAT not used.
Small office LAN Cisco 766 Synchronous PPP Dial in and dial out
4
. Distinct
IP subnet. PAT not used.
Headquarters
IP network
PSTN/ISDN
15582
10.1.1.10/24
10.1.254.3/24
PPP
10.1.254.4/24
PPP
10.1.3.1/24
10.1.4.1/24
10.1.254.1/24
PPP
Remote PC
PPP
Ethernet
Ethernet