Datasheet
Table Of Contents
- Cisco ONS 15454 SDH Reference Manual
- Contents
- About this Manual
- Shelf and FMEC Hardware
- 1.1 Overview
- 1.2 Front Door
- 1.3 Front Mount Electrical Connection
- 1.4 E1-75/120 Conversion Panel
- 1.5 Coaxial Cable
- 1.6 Twisted-Pair Balanced Cable
- 1.7 Ethernet Cables
- 1.8 Cable Routing and Management
- 1.9 Fiber Management
- 1.10 Fan-Tray Assembly
- 1.11 Power and Ground Description
- 1.12 Alarm, Timing, LAN, and Craft Pin Connections
- 1.13 Cards and Slots
- 1.14 Software and Hardware Compatibility
- Common Control Cards
- Electrical Cards
- 3.1 Electrical Card Overview
- 3.2 E1-N-14 Card
- 3.3 E1-42 Card
- 3.4 E3-12 Card
- 3.5 DS3i-N-12 Card
- 3.6 STM1E-12 Card
- 3.7 FILLER Card
- 3.8 FMEC-E1 Card
- 3.9 FMEC-DS1/E1 Card
- 3.10 FMEC E1-120NP Card
- 3.11 FMEC E1-120PROA Card
- 3.12 FMEC E1-120PROB Card
- 3.13 E1-75/120 Impedance Conversion Panel
- 3.14 FMEC-E3/DS3 Card
- 3.15 FMEC STM1E 1:1 Card
- 3.16 BLANK-FMEC Faceplate
- 3.17 MIC-A/P FMEC
- 3.18 MIC-C/T/P FMEC
- Optical Cards
- 4.1 Optical Card Overview
- 4.2 OC3 IR 4/STM1 SH 1310 Card
- 4.3 OC3 IR/STM1 SH 1310-8 Card
- 4.4 OC12 IR/STM4 SH 1310 Card
- 4.5 OC12 LR/STM4 LH 1310 Card
- 4.6 OC12 LR/STM4 LH 1550 Card
- 4.7 OC12 IR/STM4 SH 1310-4 Card
- 4.8 OC48 IR/STM16 SH AS 1310 Card
- 4.9 OC48 LR/STM16 LH AS 1550 Card
- 4.10 OC48 ELR/STM16 EH 100 GHz Cards
- 4.11 OC192 SR/STM64 IO 1310 Card
- 4.12 OC192 IR/STM64 SH 1550 Card
- 4.13 OC192 LR/STM64 LH 1550 Card
- 4.14 OC192 LR/STM64 LH ITU 15xx.xx Card
- 4.15 15454_MRC-12 Multirate Card
- 4.16 OC192SR1/STM64IO Short Reach and OC192/STM64 Any Reach Cards
- 4.17 SFPs and XFPs
- Ethernet Cards
- Storage Access Networking Cards
- Card Protection
- Cisco Transport Controller Operation
- Security
- Timing
- Circuits and Tunnels
- 11.1 Overview
- 11.2 Circuit Properties
- 11.3 Cross-Connect Card Bandwidth
- 11.4 DCC Tunnels
- 11.5 Multiple Destinations for Unidirectional Circuits
- 11.6 Monitor Circuits
- 11.7 SNCP Circuits
- 11.8 MS-SPRing Protection Channel Access Circuits
- 11.9 MS-SPRing VC4 Squelch Table
- 11.10 Section and Path Trace
- 11.11 Path Signal Label, C2 Byte
- 11.12 Automatic Circuit Routing
- 11.13 Manual Circuit Routing
- 11.14 Constraint-Based Circuit Routing
- 11.15 Virtual Concatenated Circuits
- 11.16 Bridge and Roll
- 11.17 Merged Circuits
- 11.18 Reconfigured Circuits
- 11.19 Server Trails
- SDH Topologies and Upgrades
- Management Network Connectivity
- 13.1 IP Networking Overview
- 13.2 IP Addressing Scenarios
- 13.2.1 Scenario 1: CTC and ONS 15454 SDH Nodes on Same Subnet
- 13.2.2 Scenario 2: CTC and ONS 15454 SDH Nodes Connected to a Router
- 13.2.3 Scenario 3: Using Proxy ARP to Enable an ONS 15454 SDH Gateway
- 13.2.4 Scenario 4: Default Gateway on CTC Computer
- 13.2.5 Scenario 5: Using Static Routes to Connect to LANs
- 13.2.6 Scenario 6: Using OSPF
- 13.2.7 Scenario 7: Provisioning the ONS 15454 SDH Proxy Server
- 13.2.8 Scenario 8: Dual GNEs on a Subnet
- 13.2.9 Scenario 9: IP Addressing with Secure Mode Enabled
- 13.3 Provisionable Patchcords
- 13.4 Routing Table
- 13.5 External Firewalls
- 13.6 Open GNE
- 13.7 TCP/IP and OSI Networking
- 13.7.1 Point-to-Point Protocol
- 13.7.2 Link Access Protocol on the D Channel
- 13.7.3 OSI Connectionless Network Service
- 13.7.4 OSI Routing
- 13.7.5 TARP
- 13.7.6 TCP/IP and OSI Mediation
- 13.7.7 OSI Virtual Routers
- 13.7.8 IP-over-CLNS Tunnels
- 13.7.9 OSI/IP Networking Scenarios
- 13.7.9.1 OSI/IP Scenario 1: IP OSS, IP DCN, ONS GNE, IP DCC, and ONS ENE
- 13.7.9.2 OSI/IP Scenario 2: IP OSS, IP DCN, ONS GNE, OSI DCC, and Other Vendor ENE
- 13.7.9.3 OSI/IP Scenario 3: IP OSS, IP DCN, Other Vendor GNE, OSI DCC, and ONS ENE
- 13.7.9.4 OSI/IP Scenario 4: Multiple ONS DCC Areas
- 13.7.9.5 OSI/IP Scenario 5: GNE Without an OSI DCC Connection
- 13.7.9.6 OSI/IP Scenario 6: IP OSS, OSI DCN, ONS GNE, OSI DCC, and Other Vendor ENE
- 13.7.9.7 OSI/IP Scenario 7: OSI OSS, OSI DCN, Other Vendor GNE, OSI DCC, and ONS NEs
- 13.7.9.8 OSI/IP Scenario 8: OSI OSS, OSI DCN, ONS GNE, OSI DCC, and Other Vendor NEs
- 13.7.10 Provisioning OSI in CTC
- Alarm Monitoring and Management
- 14.1 Overview
- 14.2 LCD Alarm Counts
- 14.3 Alarm Information
- 14.4 Alarm Severities
- 14.5 Alarm Profiles
- 14.6 Alarm Suppression
- 14.7 External Alarms and Controls
- Performance Monitoring
- 15.1 Threshold Performance Monitoring
- 15.2 Intermediate-Path Performance Monitoring
- 15.3 Pointer Justification Count Performance Monitoring
- 15.4 Performance Monitoring Parameter Definitions
- 15.5 Performance Monitoring for Electrical Cards
- 15.6 Performance Monitoring for Ethernet Cards
- 15.6.1 E-Series Ethernet Card Performance Monitoring Parameters
- 15.6.2 G-Series Ethernet Card Performance Monitoring Parameters
- 15.6.3 ML-Series Ethernet Card Performance Monitoring Parameters
- 15.6.4 CE-Series Ethernet Card Performance Monitoring Parameters
- 15.6.4.1 CE-Series Ether Ports Statistics Parameters
- 15.6.4.2 CE-Series Card Ether Ports Utilization Parameters
- 15.6.4.3 CE-Series Card Ether Ports History Parameters
- 15.6.4.4 CE-Series POS Ports Statistics Parameters
- 15.6.4.5 CE-Series Card POS Ports Utilization Parameters
- 15.6.4.6 CE-Series Card Ether Ports History Parameters
- 15.7 Performance Monitoring for Optical Cards
- 15.8 Performance Monitoring for the Fiber Channel Card
- SNMP
- 16.1 SNMP Overview
- 16.2 Basic SNMP Components
- 16.3 SNMP External Interface Requirement
- 16.4 SNMP Version Support
- 16.5 SNMP Message Types
- 16.6 SNMP Management Information Bases
- 16.7 SNMP Trap Content
- 16.8 SNMP Community Names
- 16.9 Proxy Over Firewalls
- 16.10 Remote Monitoring
- Hardware Specifications
- A.1 Shelf Specifications
- A.2 SFP and XFP Specifications
- A.3 General Card Specifications
- A.4 Common Control Card Specifications
- A.5 Electrical Card and FMEC Specifications
- A.5.1 E1-N-14 Card Specifications
- A.5.2 E1-42 Card Specifications
- A.5.3 E3-12 Card Specifications
- A.5.4 DS3i-N-12 Card Specifications
- A.5.5 STM1E-12 Card Specifications
- A.5.6 FILLER Card
- A.5.7 FMEC-E1 Specifications
- A.5.8 FMEC-DS1/E1 Specifications
- A.5.9 FMEC E1-120NP Specifications
- A.5.10 FMEC E1-120PROA Specifications
- A.5.11 FMEC E1-120PROB Specifications
- A.5.12 E1-75/120 Impedance Conversion Panel Specifications
- A.5.13 FMEC-E3/DS3 Specifications
- A.5.14 FMEC STM1E 1:1 Specifications
- A.5.15 BLANK-FMEC Specifications
- A.5.16 MIC-A/P Specifications
- A.5.17 MIC-C/T/P Specifications
- A.6 Optical Card Specifications
- A.6.1 OC3 IR 4/STM1 SH 1310 Card Specifications
- A.6.2 OC3 IR/STM1 SH 1310-8 Card Specifications
- A.6.3 OC12 IR/STM4 SH 1310 Card Specifications
- A.6.4 OC12 LR/STM4 LH 1310 Card Specifications
- A.6.5 OC12 LR/STM4 LH 1550 Card Specifications
- A.6.6 OC12 IR/STM4 SH 1310-4 Card Specifications
- A.6.7 OC48 IR/STM16 SH AS 1310 Card Specifications
- A.6.8 OC48 LR/STM16 LH AS 1550 Card Specifications
- A.6.9 OC48 ELR/STM16 EH 100 GHz Card Specifications
- A.6.10 OC192 SR/STM64 IO 1310 Card Specifications
- A.6.11 OC192 IR/STM64 SH 1550 Card Specifications
- A.6.12 OC192 LR/STM64 LH 1550 Card Specifications
- A.6.13 OC192 LR/STM64 LH ITU 15xx.xx Card Specifications
- A.6.14 15454_MRC-12 Card Specifications
- A.6.15 OC192SR1/STM64IO Short Reach Card Specifications
- A.6.16 OC192/STM64 Any Reach Card Specifications
- A.7 Ethernet Card Specifications
- A.8 Storage Access Networking Card Specifications
- Administrative and Service States
- Network Element Defaults
- C.1 Network Element Defaults Description
- C.2 Card Default Settings
- C.2.1 Configuration Defaults
- C.2.2 Threshold Defaults
- C.2.3 Defaults by Card
- C.2.3.1 E1-N-14 Card Default Settings
- C.2.3.2 E1-42 Card Default Settings
- C.2.3.3 E3-12 Card Default Settings
- C.2.3.4 DS3i-N-12 Card Default Settings
- C.2.3.5 STM1E-12 Card Default Settings
- C.2.3.6 Ethernet Card Default Settings
- C.2.3.7 STM-1 Card Default Settings
- C.2.3.8 STM1-8 Card Default Settings
- C.2.3.9 STM-4 Card Default Settings
- C.2.3.10 STM4-4 Card Default Settings
- C.2.3.11 STM-16 Card Default Settings
- C.2.3.12 STM-64 Card Default Settings
- C.2.3.13 STM64-XFP Default Settings
- C.2.3.14 MRC-12 Card Default Settings
- C.2.3.15 FC_MR-4 Card Default Settings
- C.3 Node Default Settings
- C.4 CTC Default Settings
- Index
11-16
Cisco ONS 15454 SDH Reference Manual, R7.0
October 2008
Chapter 11 Circuits and Tunnels
11.8 MS-SPRing Protection Channel Access Circuits
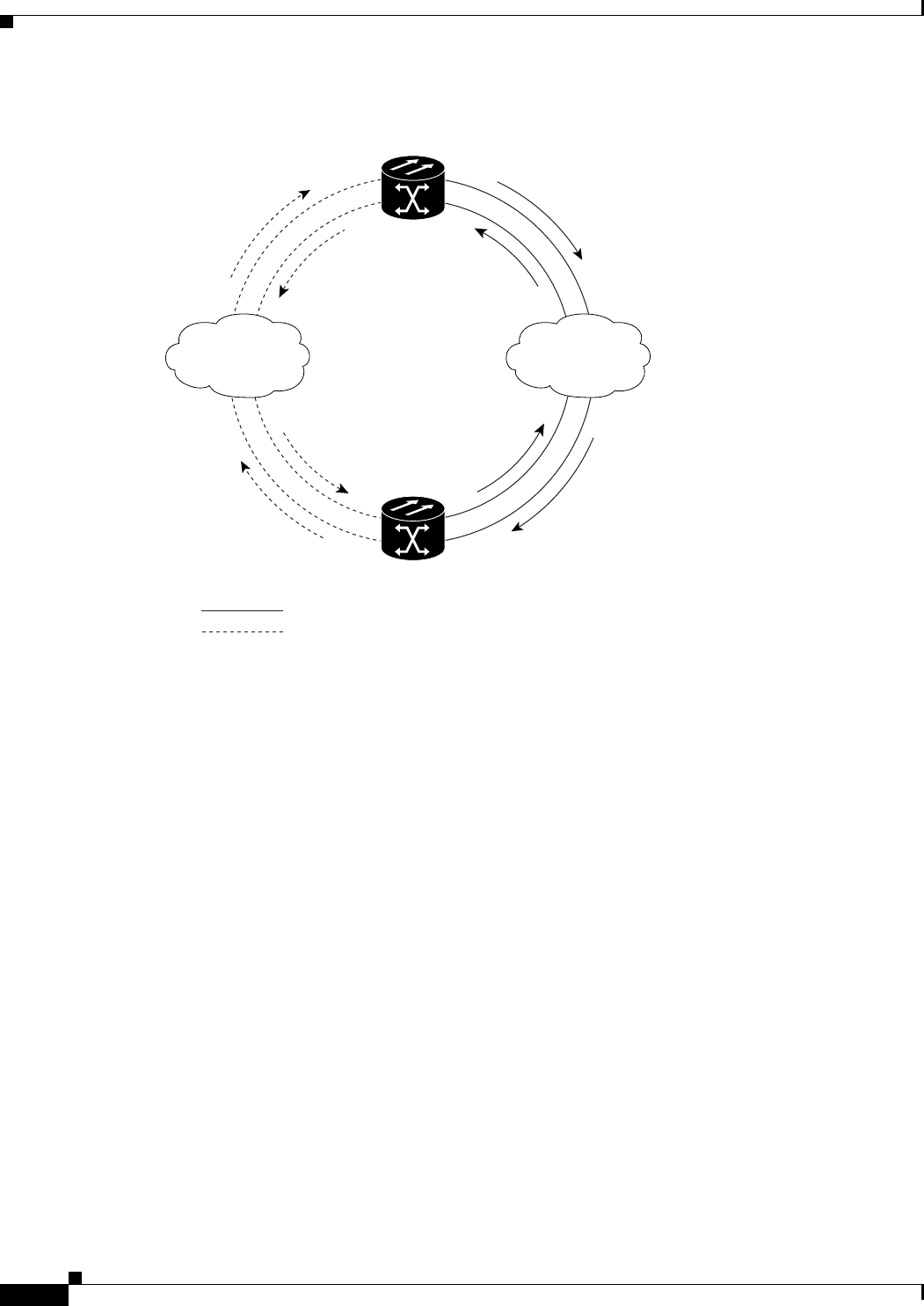
Figure 11-5 SNCP Go-and-Return Routing
11.8 MS-SPRing Protection Channel Access Circuits
You can provision circuits to carry traffic on MS-SPRing protection channels when conditions are fault
free. Traffic routed on MS-SPRing PCA circuits, called extra traffic, has lower priority than the traffic
on the working channels and has no means for protection. During ring or span switches, PCA circuits
are preempted and squelched. For example, in a two-fiber STM-16 MS-SPRing, STMs 9 to 16 can carry
extra traffic when no ring switches are active, but PCA circuits on these STMs are preempted when a
ring switch occurs. When the conditions that caused the ring switch are remedied and the ring switch is
removed, PCA circuits are restored if the MS-SPRing is provisioned as revertive.
Provisioning traffic on MS-SPRing protection channels is performed during circuit provisioning. The
Protection Channel Access check box appears whenever Fully Protected Path is unchecked on the circuit
creation wizard. Refer to the Cisco ONS 15454 SDH Procedure Guide for more information. When
provisioning PCA circuits, two considerations are important:
• If MS-SPRings are provisioned as nonrevertive, PCA circuits are not restored automatically after a
ring or span switch. You must switch the MS-SPRing manually.
• PCA circuits are routed on working channels when you upgrade a MS-SPRing from a two-fiber to
a four-fiber or from one STM-N speed to a higher STM-N speed. For example, if you upgrade a
two-fiber STM-16 MS-SPRing to an STM-64, STMs 9 to 16 on the STM-16 MS-SPRing become
working channels on the STM-64 MS-SPRing.
Node B
Go and Return working connection
Go and Return protecting connection
Node A
96953
Any network Any network










