user manual
Table Of Contents
- Cisco Content Services Switch Routing and Bridging Configuration Guide
- Contents
- Preface
- Configuring Interfaces and Circuits
- Interface and Circuit Overview
- Configuring Interfaces
- Configuring an Interface
- Entering a Description for the Interface
- Configuring Interface Duplex and Speed
- Setting Interface Maximum Idle Time
- Bridging an Interface to a VLAN
- Specifying VLAN Trunking for an Interface
- Configuring Spanning-Tree Bridging for a VLAN or a Trunked Interface
- Configuring Port Fast on an Interface
- Showing Interface Configurations
- Shutting Down an Interface
- Shutting Down All Interfaces
- Restarting an Interface
- Restarting All Interfaces
- Configuring Circuits
- Configuring RIP for an IP Interface
- Configuring the Switched Port Analyzer Feature
- Configuring Spanning-Tree Bridging for the CSS
- CSS Spanning-Tree Bridging Quick Start
- Configuring Spanning-Tree Bridge Aging-Time
- Configuring Spanning-Tree Bridge Forward-Time
- Configuring Spanning-Tree Bridge Hello-Time
- Configuring Spanning-Tree Bridge Max-Age
- Configuring Spanning-Tree Bridge Priority
- Disabling Bridge Spanning-Tree
- Showing Bridge Configurations
- Configuring Open Shortest Path First (OSPF)
- OSPF Overview
- CSS OSPF Configuration Quick Start
- Configuring OSPF on the CSS
- Configuring OSPF on a CSS IP Interface
- Showing OSPF Information
- OSPF Configuration in a Startup-Configuration File
- Configuring the Address Resolution Protocol
- Configuring Routing Information Protocol
- Configuring the Internet Protocol
- IP Configuration Quick Start
- Configuring an IP Route
- Disabling an Implicit Service for the Static Route Next Hop
- Configuring an IP Source Route
- Configuring the IP Record Route
- Configuring Box-to-Box Redundancy
- Configuring IP Equal-Cost Multipath
- Forwarding IP Subnet Broadcast Addressed Frames
- Configuring IP Unconditional Bridging
- Configuring IP Opportunistic Layer 3 Forwarding
- Showing IP Configuration Information
- Configuring the Cisco Discovery Protocol
- Configuring the DHCP Relay Agent
- Index
6-11
Cisco Content Services Switch Routing and Bridging Configuration Guide
OL-4580-01
Chapter 6 Configuring the Internet Protocol
Configuring IP Opportunistic Layer 3 Forwarding
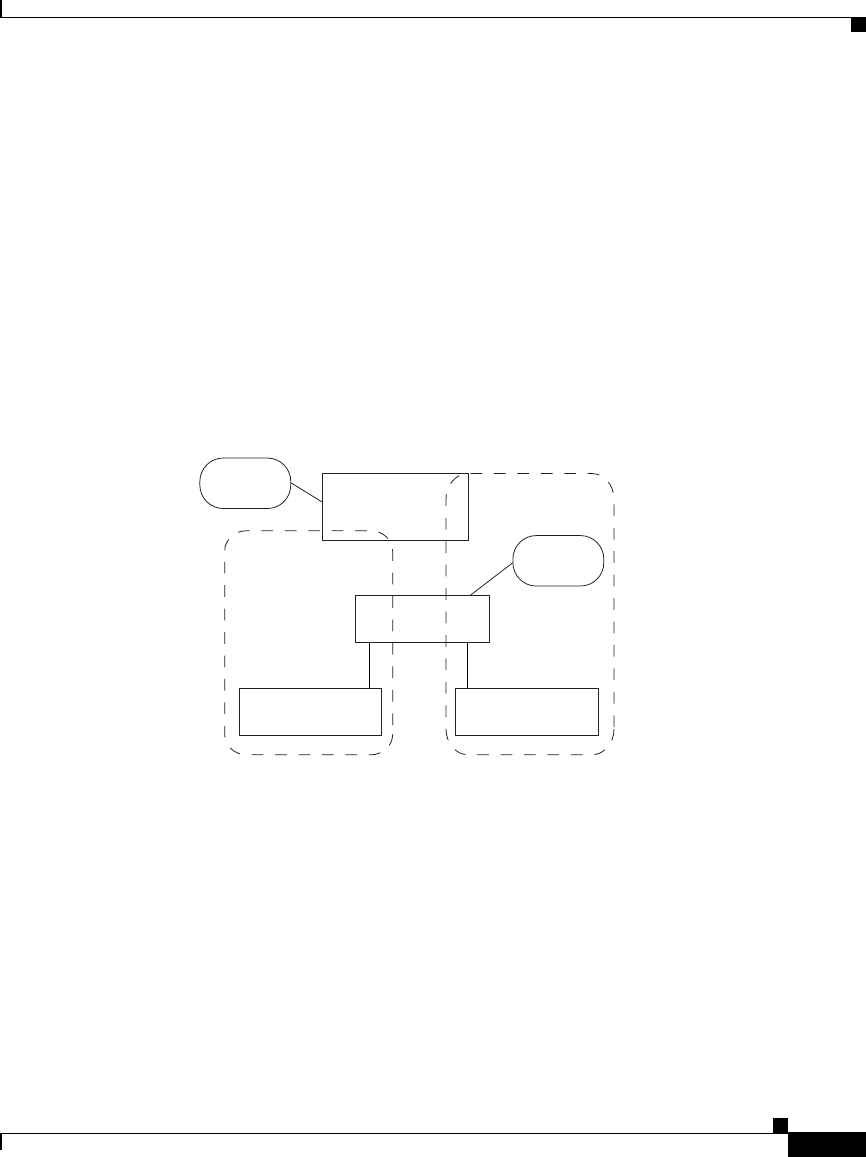
For example, Figure 6-1 shows a CSS connected to VLAN1 and VLAN2. Each
VLAN has an end station and an uplink to Router1. End stations A and B both
point to Router1 as their default router. When End Station A transmits a packet to
End Station B, it uses its default route to Router1. The packet contains Router1’s
destination MAC address. A traditional Layer 2 device forwards the packet to
Router1, and Router1 forwards the packet to End Station B on VLAN2.
Using opportunistic Layer 3 forwarding, the CSS inspects the IP packet header to
determine the destination IP address. Instead of forwarding the packet to Router1,
the CSS forwards the packet directly to End Station B. Because the CSS handles
the packet only once, the router and uplink are not used and network resources are
conserved.
Figure 6-1 Example of Opportunistic Layer 3 Forwarding
The options for this global configuration mode command are as follows:
• local (default) - Applies opportunistic Layer 3 forwarding if the destination
IP address belongs to a node that resides on one of the subnets directly
attached to the CSS and the CSS is aware of an ARP resolution for that node.
Because the local option is the default, use the no ip opportunistic command
to reconfigure IP opportunistic Layer 3 forwarding to the local setting.
• all - Applies opportunistic Layer 3 forwarding if the destination IP address
matches any entry in the CSS routing table. We do not recommend this option
if the topology includes multiple routers and the CSS does not know all of the
routes the routers are aware of.
End Station A
Subnet
VLAN2
VLAN1
Router1
(default)
End Station B
CSS
Internet
49383










