Network Card User Manual
Table Of Contents
- Cisco Aironet Wireless LAN Client Adapters Installation and Configuration Guide for MS-DOS
- Contents
- Preface
- Audience
- Purpose
- Organization
- Conventions
- Related Publications
- Obtaining Documentation
- Obtaining Technical Assistance
- Introduction to the Wireless LAN Adapters
- Parts of the Client Adapter
- Radio Ranges
- Data Transparency and Protocols
- System Configurations
- Coverage Options
- Safety Information
- Unpacking the Client Adapter
- Inserting the Client Adapter into a Computing Device
- Removing the Client Adapter
- Driver Overview
- Windows for Workgroups 3.11 NDIS2 Installation
- DOS NDIS2 Installation
- ODI Driver Installation
- Additional Requirements and Features
- Driver Keywords and Settings
- Site Survey and Link Test
- Loading New Firmware Versions
- DOS Utilities
- Accessing the Latest Troubleshooting Information
- Interpreting the Indicator LEDs
- Technical Specifications
- Channel Sets
- Maximum Power Levels and Antenna Gains
- Manufacturers Federal Communication Commission Declaration of Conformity Statement
- Department of Communications – Canada
- European Community, Switzerland, Norway, Iceland, and Liechtenstein
- Declaration of Conformity for RF Exposure
- Guidelines for Operating Cisco Aironet Wireless LAN Client Adapters in Japan
- Explosive Device Proximity Warning
- Lightning Activity Warning
- Installation Warning
- Circuit Breaker (15A) Warning
1-8
Cisco Aironet Wireless LAN Adapters Installation and Configuration Guide for MS-DOS
OL-1744-02
Chapter1 Overview
System Configurations
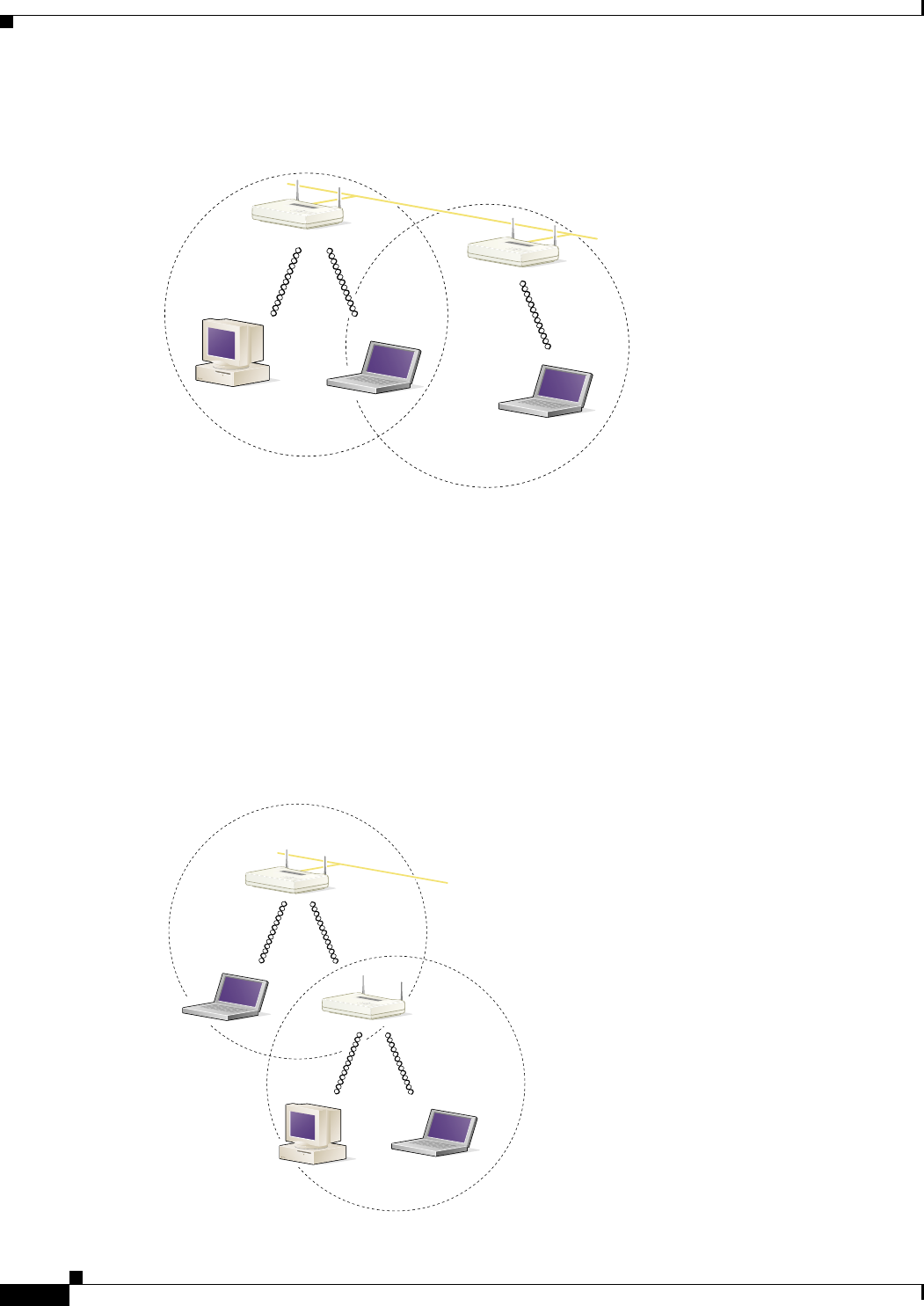
Figure 1-3 Wireless Infrastructure with Workstations Accessing a Wired LAN
Extended Infrastructure Using Repeaters
An access point can be configured as a stand-alone repeater to extend the range of your infrastructure,
or to overcome an RF blocking obstacle (Figure 1-4). The repeater forwards traffic between the Cisco
Aironet Wireless LAN Client Adapter equipped workstations and devices and the wired LAN by sending
packets to either another repeater or to another access point attached to the wired LAN. The data is sent
through whichever route provides the greatest performance for the client. Multiple repeater hops can be
supported in the path to the wired LAN.
Figure 1-4 Extended Infrastructure Using Repeaters
Access Point
(Root Unit)
Access Point
(Root Unit)
45835
Wired LAN
Access Point
(Root Unit)
Access Point
(Repeater)
45836
Wired LAN










