user manual
Table Of Contents
- Cisco Nexus 3000 NX-OS Layer 2 Switching Configuration Guide, Release 5.0(3)U3(1)
- Contents
- Preface
- New and Changed Information for this Release
- Overview
- Configuring Ethernet Interfaces
- Information About Ethernet Interfaces
- Configuring Ethernet Interfaces
- Configuring the UDLD Mode
- Changing an Interface Port Mode
- Configuring Interface Speed
- Disabling Link Negotiation
- Configuring the CDP Characteristics
- Enabling or Disabling CDP
- Enabling the Error-Disabled Detection
- Enabling the Error-Disabled Recovery
- Configuring the Error-Disabled Recovery Interval
- Configuring the Debounce Timer
- Configuring the Description Parameter
- Disabling and Restarting Ethernet Interfaces
- Displaying Interface Information
- Displaying Input Packet Discard Information
- Default Physical Ethernet Settings
- Configuring VLANs
- Configuring Private VLANs
- Information About Private VLANs
- Guidelines and Limitations for Private VLANs
- Configuring a Private VLAN
- Enabling Private VLANs
- Configuring a VLAN as a Private VLAN
- Associating Secondary VLANs with a Primary Private VLAN
- Configuring an Interface as a Private VLAN Host Port
- Configuring an Interface as a Private VLAN Promiscuous Port
- Configuring a Promiscuous Trunk Port
- Configuring an Isolated Trunk Port
- Configuring the Allowed VLANs for PVLAN Trunking Ports
- Configuring Native 802.1Q VLANs on Private VLANs
- Verifying the Private VLAN Configuration
- Configuring Access and Trunk Interfaces
- Configuring Switching Modes
- Configuring Rapid PVST+
- Information About Rapid PVST+
- Understanding STP
- Understanding Rapid PVST+
- Rapid PVST+ and IEEE 802.1Q Trunks
- Rapid PVST+ Interoperation with Legacy 802.1D STP
- Rapid PVST+ Interoperation with 802.1s MST
- Configuring Rapid PVST+
- Enabling Rapid PVST+
- Enabling Rapid PVST+ per VLAN
- Configuring the Root Bridge ID
- Configuring a Secondary Root Bridge
- Configuring the Rapid PVST+ Port Priority
- Configuring the Rapid PVST+ Pathcost Method and Port Cost
- Configuring the Rapid PVST+ Bridge Priority of a VLAN
- Configuring the Rapid PVST+ Hello Time for a VLAN
- Configuring the Rapid PVST+ Forward Delay Time for a VLAN
- Configuring the Rapid PVST+ Maximum Age Time for a VLAN
- Specifying the Link Type
- Restarting the Protocol
- Verifying Rapid PVST+ Configurations
- Information About Rapid PVST+
- Configuring Multiple Spanning Tree
- Information About MST
- Configuring MST
- MST Configuration Guidelines
- Enabling MST
- Entering MST Configuration Mode
- Specifying the MST Name
- Specifying the MST Configuration Revision Number
- Specifying the Configuration on an MST Region
- Mapping and Unmapping VLANs to MST Instances
- Mapping Secondary VLANs to Same MSTI as Primary VLANs for Private VLANs
- Configuring the Root Bridge
- Configuring a Secondary Root Bridge
- Configuring the Port Priority
- Configuring the Port Cost
- Configuring the Switch Priority
- Configuring the Hello Time
- Configuring the Forwarding-Delay Time
- Configuring the Maximum-Aging Time
- Configuring the Maximum-Hop Count
- Configuring PVST Simulation Globally
- Configuring PVST Simulation Per Port
- Specifying the Link Type
- Restarting the Protocol
- Verifying MST Configurations
- Configuring STP Extensions
- About STP Extensions
- Information About STP Extensions
- Configuring STP Extensions
- STP Extensions Configuration Guidelines
- Configuring Spanning Tree Port Types Globally
- Configuring Spanning Tree Edge Ports on Specified Interfaces
- Configuring Spanning Tree Network Ports on Specified Interfaces
- Enabling BPDU Guard Globally
- Enabling BPDU Guard on Specified Interfaces
- Enabling BPDU Filtering Globally
- Enabling BPDU Filtering on Specified Interfaces
- Enabling Loop Guard Globally
- Enabling Loop Guard or Root Guard on Specified Interfaces
- Verifying STP Extension Configuration
- About STP Extensions
- Configuring LLDP
- Configuring the MAC Address Table
- Configuring IGMP Snooping
- Configuring Traffic Storm Control
- INDEX
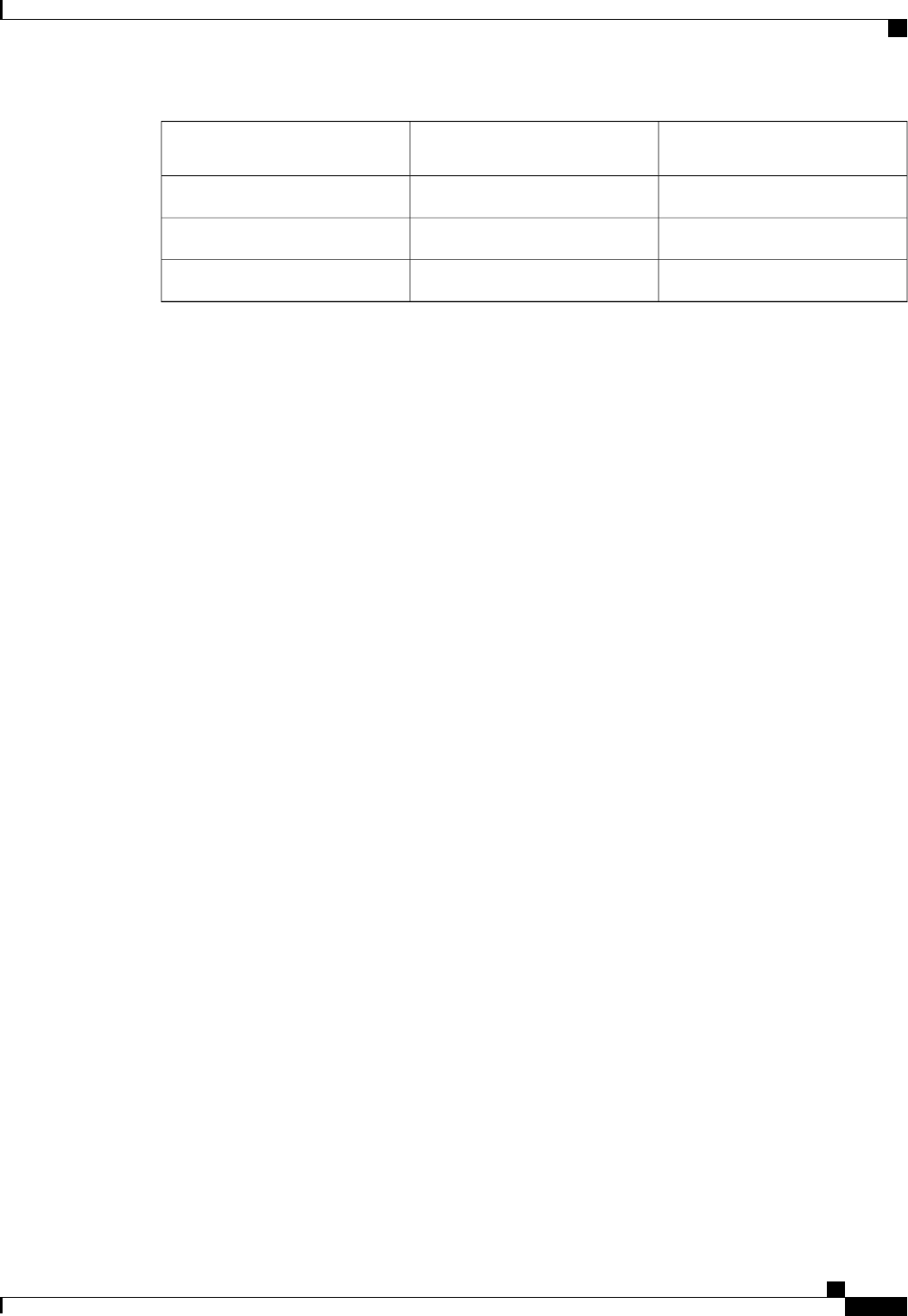
Long Path-cost Method of Port CostShort Path-cost Method of Port
Cost
Bandwidth
200,00019100 Mbps
20,00041 Gigabit Ethernet
2,000210 Gigabit Ethernet
You can assign lower cost values to LAN interfaces that you want STP to select first and higher cost values
to LAN interfaces that you want STP to select last. If all LAN interfaces have the same cost value, STP puts
the LAN interface with the lowest LAN interface number in the forwarding state and blocks other LAN
interfaces.
On access ports, you assign port cost by the port. On trunk ports, you assign the port cost by the VLAN; you
can configure the same port cost to all the VLANs on a trunk port.
Port Priority
If a loop occurs and multiple ports have the same path cost, Rapid PVST+ considers the port priority when
selecting which LAN port to put into the forwarding state. You can assign lower priority values to LAN ports
that you want Rapid PVST+ to select first and higher priority values to LAN ports that you want Rapid PVST+
to select last.
If all LAN ports have the same priority value, Rapid PVST+ puts the LAN port with the lowest LAN port
number in the forwarding state and blocks other LAN ports. The possible priority range is from 0 through
224 (the default is128), configurable in increments of 32. software uses the port priority value when the LAN
port is configured as an access port and uses VLAN port priority values when the LAN port is configured as
a trunk port.
Rapid PVST+ and IEEE 802.1Q Trunks
In a network of Cisco switches connected through 802.1Q trunks, the switches maintain one instance of STP
for each VLAN allowed on the trunks. However, non-Cisco 802.1Q switches maintain only one instance of
STP for all VLANs allowed on the trunks.
When you connect a Cisco switch to a non-Cisco switch through an 802.1Q trunk, the Cisco switch combines
the STP instance of the 802.1Q VLAN of the trunk with the STP instance of the non-Cisco 802.1Q switch.
However, all per-VLAN STP information that is maintained by Cisco switches is separated by a cloud of
non-Cisco 802.1Q switches. The non-Cisco 802.1Q cloud that separates the Cisco switches is treated as a
single trunk link between the switches.
Rapid PVST+ Interoperation with Legacy 802.1D STP
Rapid PVST+ can interoperate with switches that are running the legacy 802.1D protocol. The switch knows
that it is interoperating with equipment running 802.1D when it receives a BPDU version 0. The BPDUs for
Rapid PVST+ are version 2. If the BPDU received is an 802.1w BPDU version 2 with the proposal flag set,
the switch sends an agreement message after all of the other ports are synchronized. If the BPDU is an 802.1D
Cisco Nexus 3000 NX-OS Layer 2 Switching Configuration Guide, Release 5.0(3)U3(1)
OL-26590-01 77
Configuring Rapid PVST+
Rapid PVST+ and IEEE 802.1Q Trunks










