Manual
3-7 Copyright 2010 Cirrus Logic, Inc. DS732UM10
I2C Port
CS4953xx Hardware User’s Manual
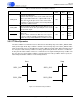
Figure 3-7. Stop Condition with ACK and NACK
If a slave cannot receive or transmit another complete byte of data until it has performed some other
function, for example servicing an internal interrupt, it can hold the SCP1_CLK line low to force the master
into a wait state. Data transfer then continues when the slave is ready for another byte of data and
releases SCP1_CLK.
3.3.3 I
2
C Messaging
Messaging to the CS4953xx using the I
2
C bus requires usage of all the information provided in the above
I
2
C Section 3.3.1 “I
2
C System Bus Description” on page 2 and Section 3.3.2 “I
2
C Bus Dynamics” on
page 4. Every I
2
C transaction to the CS4953xx will involve 4-byte words used for control and application
image download. A detailed description of the serial SPI communication mode is provided in this section.
This includes:
• A flow diagram and description for a serial I
2
C write
• A flow diagram and description for a serial I
2
C read
3.3.3.1 SCP1_BSY Behavior
The SCP1_BSY signal is not part of the I
2
C protocol, but it is provided so that the slave can signal to the
master that it cannot receive any more data. It performs the same function as that of holding SCP1_CLK
low to halt transmission. A falling edge of the SCP1_BSY
signal indicates the master must halt
transmission. Once the SCP1_BSY
signal goes high, the suspended transaction may continue. It is
important for the host to obey the SCP1_BSY
pin status for proper communication with the DSP.
Stop
S
CP1_CLK
S
CP1_SDA Data Byte
ACK
M
S MWrite
Read
S
M M
Stop
S
CP1_CLK
S
CP1_SDA Data Byte
NACK
M
S M
Write
Read
S
M M
M = Master Drives SDA
S = Slave Drives SDA