Manual
I2C Port
CS4953xx Hardware User’s Manual
DS732UM10 Copyright 2010 Cirrus Logic, Inc 3-6
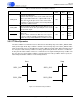
Figure 3-5. Data Byte with ACK and NACK
After an ACK or NACK from the master or slave, the slave must leave the SCP1_SDA line high so the
master can then generate either another Start condition as shown in Figure 3-6 to start a new transfer or a
Stop condition as shown in Figure 3-7 to abort the transfer.
Figure 3-6. Repeated Start Condition with ACK and NACK
Start
S
CP1_CLK
S
CP1_SDA A[6] A[5] A[4] A[3] A[2] A[1] A[0] R/W
ACK
Data Byte
ACK
M S M SWrite
M S S MRead
Start
S
CP1_CLK
S
CP1_SDA A[6] A[5] A[4] A[3] A[2] A[1] A[0] R/W
ACK
Data Byte
NACK
M S M SWrite
M S S MRead
M = Master Drives SDA
S = Slave Drives SDA
SCP1_CLK
SCP1_SDA
Data Byte
NACK
Start
A[6] A[5] A[4] A[3] A[2] A[1] A[0] R/W
ACK
M S M S
W
rite
S M M S
R
ead
M = Master Drives SDA
S = Slave Drives SDA
SCP1_CLK
SCP1_SDA
Data Byte
ACK
Start
A[6] A[5] A[4] A[3] A[2] A[1] A[0] R/W
ACK
M S M S
W
rite
S M M S
R
ead