User Manual
Table Of Contents
- 1. Pin Descriptions
- 2. Typical Connection Diagram
- 3. Characteristic and Specifications
- Recommended Operating Conditions
- Absolute Maximum Ratings
- Analog Input Characteristics
- ADC Digital Filter Characteristics
- Analog Output Characteristics
- Analog Passthrough Characteristics
- PWM Output Characteristics
- Headphone Output Power Characteristics
- Line Output Voltage Level Characteristics
- Combined DAC Interpolation and onChip Analog FIlter Response
- Switching Specifications - Serial Port
- Switching Specifications - I²C Control Port
- DC Electrical Characteristics
- Digital Interface Specifications and Characteristics
- Power Consumption
- 4. Applications
- 4.1 Overview
- 4.2 Analog Inputs
- 4.3 Analog Outputs
- 4.4 Analog In to Analog Out Passthrough
- 4.5 PWM Outputs
- 4.6 Serial Port Clocking
- 4.7 Digital Interface Formats
- 4.8 Initialization
- 4.9 Recommended Power-up Sequence
- 4.10 Recommended Power-Down Sequence
- 4.11 Required Initialization Settings
- 4.12 Control Port Operation
- 5. Register Quick Reference
- 6. Register Description
- 6.1 Chip I.D. and Revision Register (Address 01h) (Read Only)
- 6.2 Power Control 1 (Address 02h)
- 6.3 Power Control 2 (Address 03h)
- 6.4 Power Control 3 (Address 04h)
- 6.5 Clocking Control (Address 05h)
- 6.6 Interface Control 1 (Address 06h)
- 6.7 Interface Control 2 (Address 07h)
- 6.8 Input x Select: ADCA and PGAA (Address 08h), ADCB and PGAB (Address 09h)
- 6.9 Analog and HPF Control (Address 0Ah)
- 6.10 ADC HPF Corner Frequency (Address 0Bh)
- 6.11 Misc. ADC Control (Address 0Ch)
- 6.12 Playback Control 1 (Address 0Dh)
- 6.13 Miscellaneous Controls (Address 0Eh)
- 6.14 Playback Control 2 (Address 0Fh)
- 6.15 MICx Amp Control:MIC A (Address 10h) and MIC B (Address 11h)
- 6.16 PGAx Vol. and ALCx Transition Ctl.: ALC, PGA A (Address 12h) and ALC, PGA B (Address 13h)
- 6.17 Passthrough x Volume: PASSAVOL (Address 14h) and PASSBVOL (Address 15h)
- 6.18 ADCx Volume Control: ADCAVOL (Address 16h) and ADCBVOL (Address 17h)
- 6.19 ADCx Mixer Volume: ADCA (Address 18h) and ADCB (Address 19h)
- 6.20 PCMx Mixer Volume: PCMA (Address 1Ah) and PCMB (Address 1Bh)
- 6.21 Beep Frequency and On Time (Address 1Ch)
- 6.22 Beep Volume and Off Time (Address 1Dh)
- 6.23 Beep and Tone Configuration (Address 1Eh)
- 6.24 Tone Control (Address 1Fh)
- 6.25 Master Volume Control: MSTA (Address 20h) and MSTB (Address 21h)
- 6.26 Headphone Volume Control: HPA (Address 22h) and HPB (Address 23h)
- 6.27 Speaker Volume Control: SPKA (Address 24h) and SPKB (Address 25h)
- 6.28 ADC and PCM Channel Mixer (Address 26h)
- 6.29 Limiter Control 1, Min/Max Thresholds (Address 27h)
- 6.30 Limiter Control 2, Release Rate (Address 28h)
- 6.31 Limiter Attack Rate (Address 29h)
- 6.32 ALC Enable and Attack Rate (Address 2Ah)
- 6.33 ALC Release Rate (Address 2Bh)
- 6.34 ALC Threshold (Address 2Ch)
- 6.35 Noise Gate Control (Address 2Dh)
- 6.36 Status (Address 2Eh) (Read Only)
- 6.37 Battery Compensation (Address 2Fh)
- 6.38 VP Battery Level (Address 30h) (Read Only)
- 6.39 Speaker Status (Address 31h) (Read Only)
- 6.40 Charge Pump Frequency (Address 34h)
- 7. Analog Performance Plots
- 8. Example System Clock Frequencies
- 9. PCB Layout Considerations
- 10. ADC and DAC Digital Filters
- 11. Parameter Definitions
- 12. Package Dimensions
- 13. Ordering Information
- 14. References
- 15. Revision History
38 DS680F2
CS42L52
3/1/13
1. Write 0x99 to register 0x00.
2. Write 0xBA to register 0x3E.
3. Write 0x80 to register 0x47.
4. Write 1 to bit 7 in register 0x32.
5. Write 00 to bit 7 in register 0x32.
6. Write 0x00 to register 0x00.
4.12 Control Port Operation
The control port is used to access the registers, allowing the CODEC to be configured for the desired oper-
ational modes and formats. The operation of the control port may be completely asynchronous with respect
to the audio sample rates. However, to avoid potential interference problems, the control port pins should
remain static if no operation is required.
The control port operates using an I²C interface with the CODEC acting as a slave device.
4.12.1 I²C Control
SDA is a bidirectional data line. Data is clocked into and out of the device by the clock, SCL. The AD0 pin
sets the LSB of the chip address; ‘0’ when connected to DGND, ‘1’ when connected to VL. This pin may
be driven by a host controller or directly connected to VL or DGND. The AD0 pin state is sensed and the
LSB of the chip address is set upon the release of the RESET
signal (a low-to-high transition).
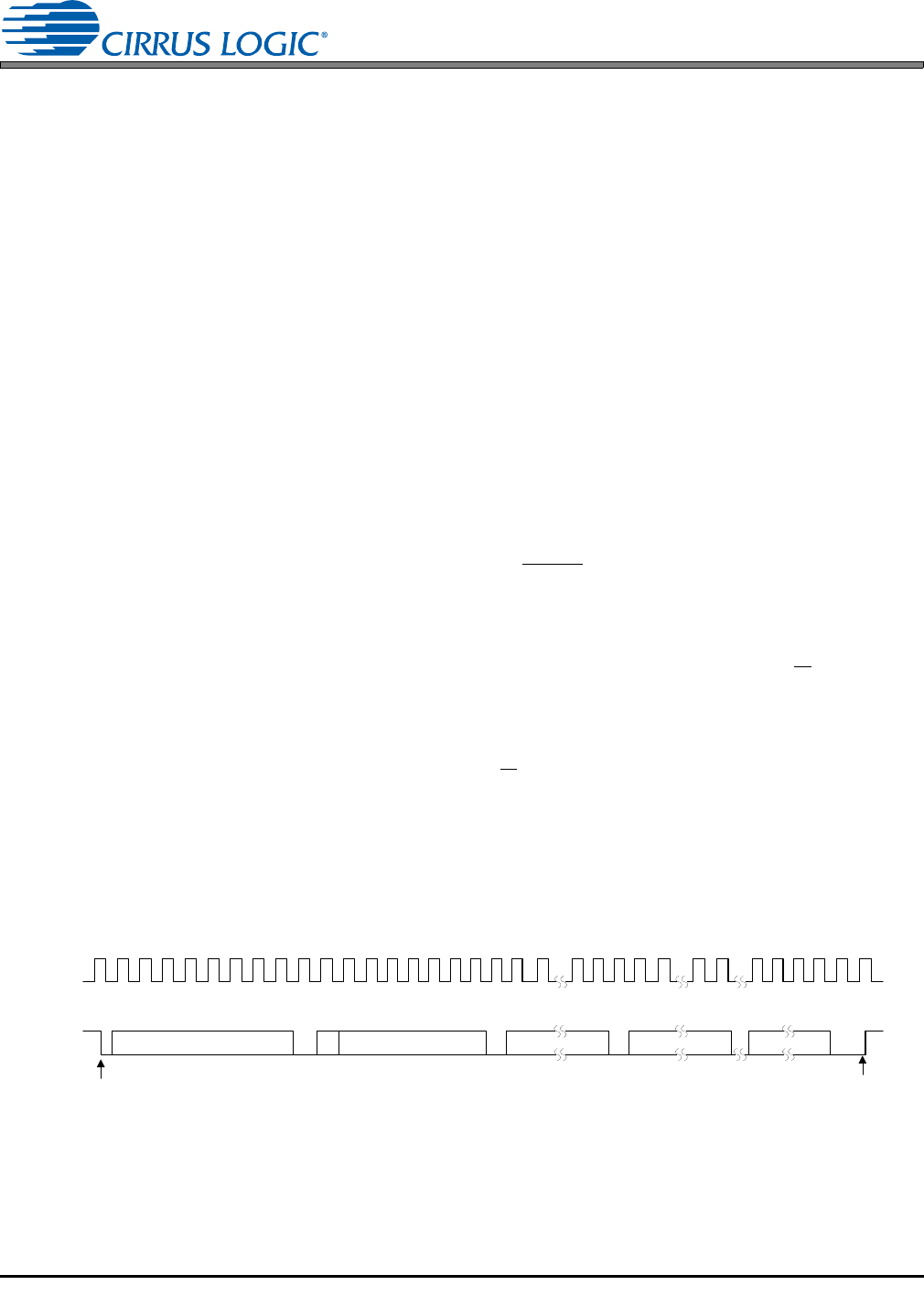
The signal timings for a read and write cycle are shown in Figure 20 and Figure 21. A Start condition is
defined as a falling transition of SDA while the clock is high. A Stop condition is defined as a rising tran-
sition of SDA while the clock is high. All other transitions of SDA occur while the clock is low. The first byte
sent to the CS42L52 after a Start condition consists of a 7-bit chip address field and a R/W
bit (high for a
read, low for a write).
The upper 6 bits of the address field are fixed at 100101. To communicate with the CS42L52, the chip
address field, which is the first byte sent to the CS42L52, should match 100101 followed by the setting of
the AD0 pin. The eighth bit of the address is the R/W
bit. If the operation is a write, the next byte is the
Memory Address Pointer (MAP), which selects the register to be read or written. If the operation is a read,
the contents of the register pointed to by the MAP will be output. Setting the auto-increment bit in MAP
allows successive reads or writes of consecutive registers. Each byte is separated by an acknowledge
bit. The ACK bit is output from the CS42L52 after each input byte is read and is input to the CS42L52 from
the microcontroller after each transmitted byte.
4 5 6 7 24 25
SCL
CHIP ADDRESS (WRITE) MAP BYTE DATA
DATA +1
START
ACK
STOP
ACKACKACK
1 0 0 1 0 1 AD0 0
SDA
INCR 6 5 4 3 2 1 0 7 6 1 0 7 6 1 0 7 6 1 0
0 1 2 3 8 9 12 16 17 18 19 10 11 13 14 15 27 28
26
DATA +n
Figure 20. Control Port Timing, I²C Write