User's Manual
Table Of Contents
- Quick-Start
- Precautions when Using this Product
- Contents
- Getting Acquainted— Read This First!
- Chapter 1 Basic Operation
- Chapter 2 Manual Calculations
- Chapter 3 List Function
- Chapter 4 Equation Calculations
- Chapter 5 Graphing
- 5-1 Sample Graphs
- 5-2 Controlling What Appears on a Graph Screen
- 5-3 Drawing a Graph
- 5-4 Storing a Graph in Picture Memory
- 5-5 Drawing Two Graphs on the Same Screen
- 5-6 Manual Graphing
- 5-7 Using Tables
- 5-8 Dynamic Graphing
- 5-9 Graphing a Recursion Formula
- 5-10 Changing the Appearance of a Graph
- 5-11 Function Analysis
- Chapter 6 Statistical Graphs and Calculations
- Chapter 7 Financial Calculation (TVM)
- Chapter 8 Programming
- Chapter 9 Spreadsheet
- Chapter 10 eActivity
- Chapter 11 System Settings Menu
- Chapter 12 Data Communications
- Appendix
20070201
2-4-10
Function Calculations
k Permutation and Combination
u Permutation u Combination
• Be sure to specify Comp for Mode in the Setup screen.
Example 1 To calculate the possible number of different arrangements using 4
items selected from among 10 items
Formula Operation
10 P 4 = 5040
10 K 6 (g )3 (PROB)2 ( n P r ) 4 w
Example 2 To calculate the possible number of different combinations of 4 items
that can be selected from among 10 items
Formula Operation
10 C 4 = 210
10 K 6 (g )3 (PROB)3 (
n C r ) 4 w
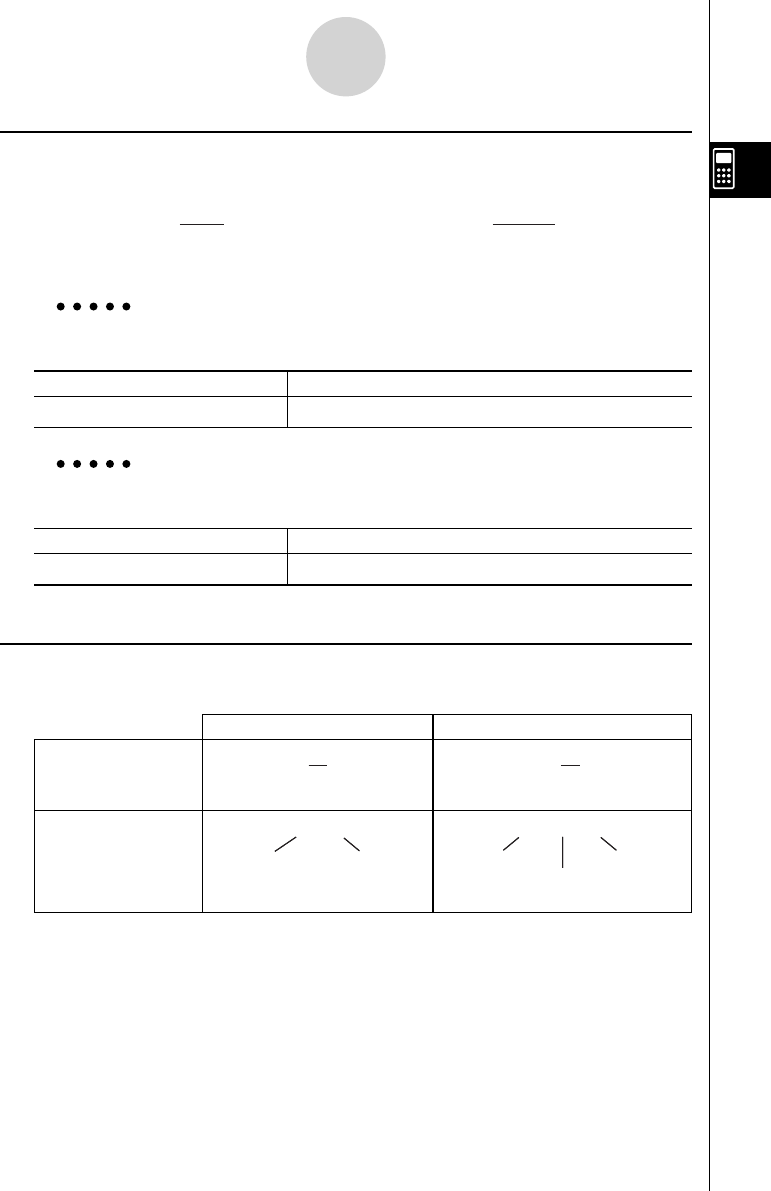
k Fractions
How you should input fractions depends on the input mode that is currently selected.
Improper Fraction Mixed Fraction
Math input mode
Linear input mode
Numerator Denominator
Integer Part Denominator
Numerator
• For information about the Math input mode, see “Input Operations in the Math Input Mode”
on page 1-3-10.
• Fraction calculation results are always reduced before being displayed.
n
!
n
!
n
P
r
=
n
C
r
=
(
n
–
r
)!
r
!(
n
–
r
)!
n
!
n
!
n
P
r
=
n
C
r
=
(
n
–
r
)!
r
!(
n
–
r
)!
7
3
1
3
2
7 { 32 { 1 { 3
($7c3)(1$(()2e1c3)
(7$3)(2$1$3)
7
3
1
3
2
7 { 32 { 1 { 3
($7c3)(1$(()2e1c3)
(7$3)(2$1$3)