User's Manual
Table Of Contents
- Quick-Start
- Precautions when Using this Product
- Contents
- Getting Acquainted— Read This First!
- Chapter 1 Basic Operation
- Chapter 2 Manual Calculations
- Chapter 3 List Function
- Chapter 4 Equation Calculations
- Chapter 5 Graphing
- 5-1 Sample Graphs
- 5-2 Controlling What Appears on a Graph Screen
- 5-3 Drawing a Graph
- 5-4 Storing a Graph in Picture Memory
- 5-5 Drawing Two Graphs on the Same Screen
- 5-6 Manual Graphing
- 5-7 Using Tables
- 5-8 Dynamic Graphing
- 5-9 Graphing a Recursion Formula
- 5-10 Changing the Appearance of a Graph
- 5-11 Function Analysis
- Chapter 6 Statistical Graphs and Calculations
- Chapter 7 Financial Calculation (TVM)
- Chapter 8 Programming
- Chapter 9 Spreadsheet
- Chapter 10 eActivity
- Chapter 11 System Settings Menu
- Chapter 12 Data Communications
- Appendix
20070201
u To recall data from a File Memory to a spreadsheet
1. On the spreadsheet, select the upper left cell of the range where you want the recalled
data to be input.
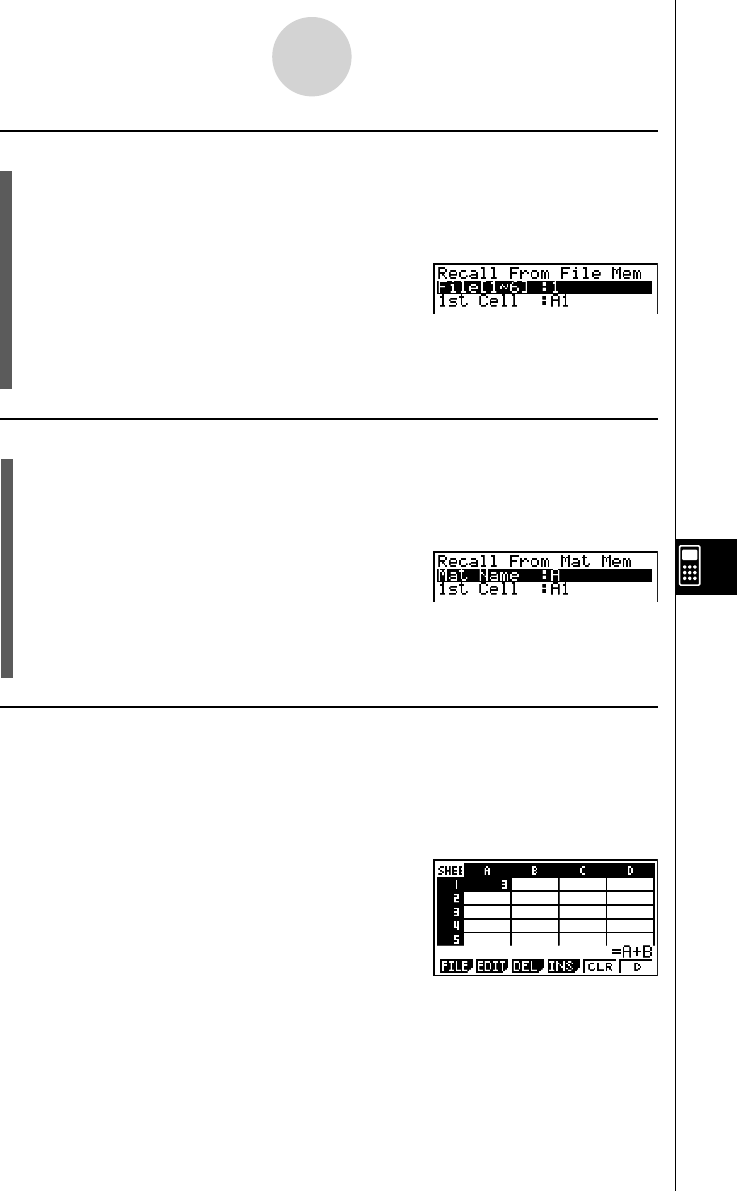
2. Press 6 (g )4 (RCL)2 (FILE) to display a data recall screen like the one shown
below.
• The “1st Cell” setting will show the name of the cell
you selected in step 1.
3. Input the File number (1 to 6) of the File Memory whose data you want to recall, and
then press w .
4. Press 6 (EXE) or the w key to recall the data.
u To recall data from a Mat Memory to a spreadsheet
1. On the spreadsheet, select the upper left cell of the range where you want the recalled
data to be input.
2. Press 6 (g )4 (RCL)3 (MAT) to display a data recall screen like the one shown
below.
• The “1st Cell” setting will show the name of the cell
you selected in step 1.
3. Input the name (A to Z) of the Mat Memory whose data you want to recall, and then
press w .
4. Press 6 (EXE) or the w key to recall the data.
u To use a variable in a spreadsheet
You can include variable names (A to Z) in constants or formulas you input into
spreadsheet cells. When you do, the value currently assigned to the applicable variable to
be recalled.
If 1 is assigned to variable A and 2 is assigned to variable B, for example, inputting =A+B
into cell A1 will cause 3 to be displayed for cell A1.
9-8-5
Using Memory in the S
•
SHT Mode