User's Manual
Table Of Contents
- Quick-Start
- Precautions when Using this Product
- Contents
- Getting Acquainted— Read This First!
- Chapter 1 Basic Operation
- Chapter 2 Manual Calculations
- Chapter 3 List Function
- Chapter 4 Equation Calculations
- Chapter 5 Graphing
- 5-1 Sample Graphs
- 5-2 Controlling What Appears on a Graph Screen
- 5-3 Drawing a Graph
- 5-4 Storing a Graph in Picture Memory
- 5-5 Drawing Two Graphs on the Same Screen
- 5-6 Manual Graphing
- 5-7 Using Tables
- 5-8 Dynamic Graphing
- 5-9 Graphing a Recursion Formula
- 5-10 Changing the Appearance of a Graph
- 5-11 Function Analysis
- Chapter 6 Statistical Graphs and Calculations
- Chapter 7 Financial Calculation (TVM)
- Chapter 8 Programming
- Chapter 9 Spreadsheet
- Chapter 10 eActivity
- Chapter 11 System Settings Menu
- Chapter 12 Data Communications
- Appendix
20070201
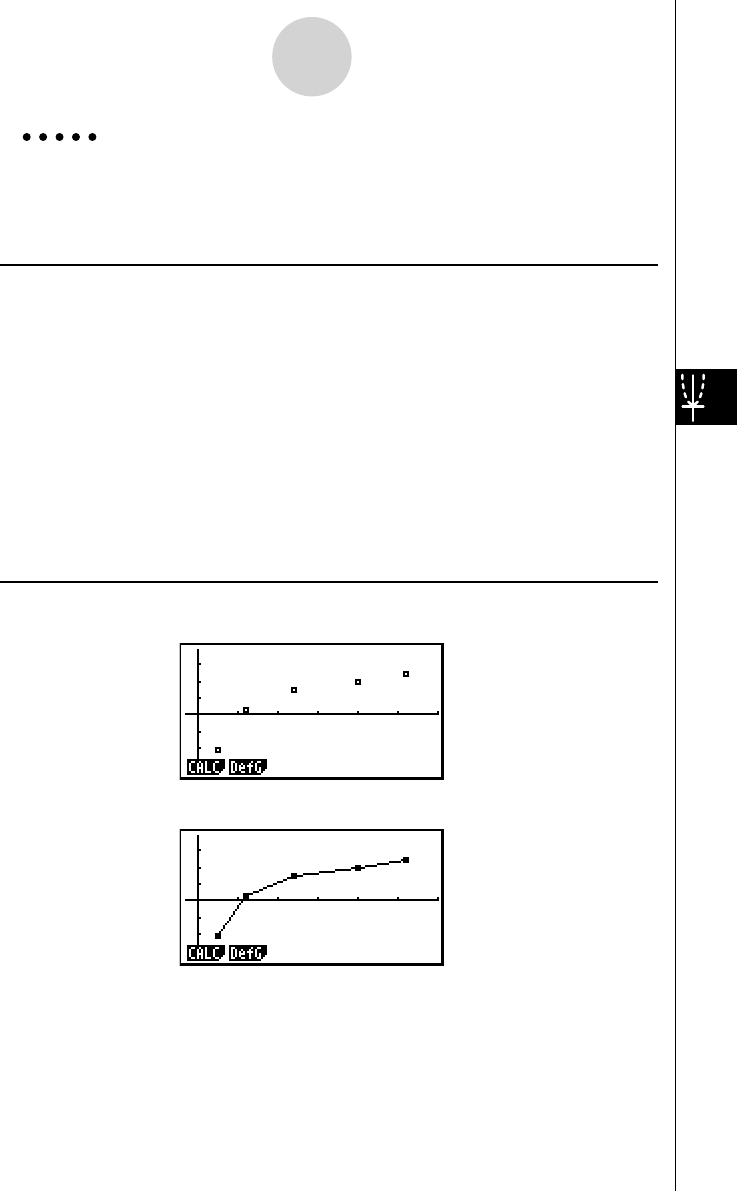
Example Input the two sets of data shown below. Next, plot the data on a
scatter diagram and connect the dots to produce an
xy line graph.
0.5, 1.2, 2.4, 4.0, 5.2 ( x List)
–2.1, 0.3, 1.5, 2.0, 2.4 (
y List)
Procedure
1 m STAT
2 a.f w b.c w
c.e w e w f.c w
e
- c.b w a.d w
b.f w c w c.e w
3 (Scatter diagram) 1 (GRPH)6 (SET)c 1 (Scat)J
1 (GPH1)
3 ( xy line graph) 1 (GRPH)6 (SET)c 2 (
xy )J
1 (GPH1)
Result Screen
(Scatter diagram)
( xy line graph)
6-3-2
Calculating and Graphing Paired-Variable Statistical Data










