User's Manual
Table Of Contents
- Quick-Start
- Precautions when Using this Product
- Contents
- Getting Acquainted— Read This First!
- Chapter 1 Basic Operation
- Chapter 2 Manual Calculations
- Chapter 3 List Function
- Chapter 4 Equation Calculations
- Chapter 5 Graphing
- 5-1 Sample Graphs
- 5-2 Controlling What Appears on a Graph Screen
- 5-3 Drawing a Graph
- 5-4 Storing a Graph in Picture Memory
- 5-5 Drawing Two Graphs on the Same Screen
- 5-6 Manual Graphing
- 5-7 Using Tables
- 5-8 Dynamic Graphing
- 5-9 Graphing a Recursion Formula
- 5-10 Changing the Appearance of a Graph
- 5-11 Function Analysis
- Chapter 6 Statistical Graphs and Calculations
- Chapter 7 Financial Calculation (TVM)
- Chapter 8 Programming
- Chapter 9 Spreadsheet
- Chapter 10 eActivity
- Chapter 11 System Settings Menu
- Chapter 12 Data Communications
- Appendix
20070201
5-10-7
Changing the Appearance of a Graph
k Changing the Graph Background
You can use the Setup screen to specify the memory contents of any picture memory area
(Pict 1 through Pict 20) as the Background item. When you do, the contents of the
corresponding memory area is used as the background of the graph screen.
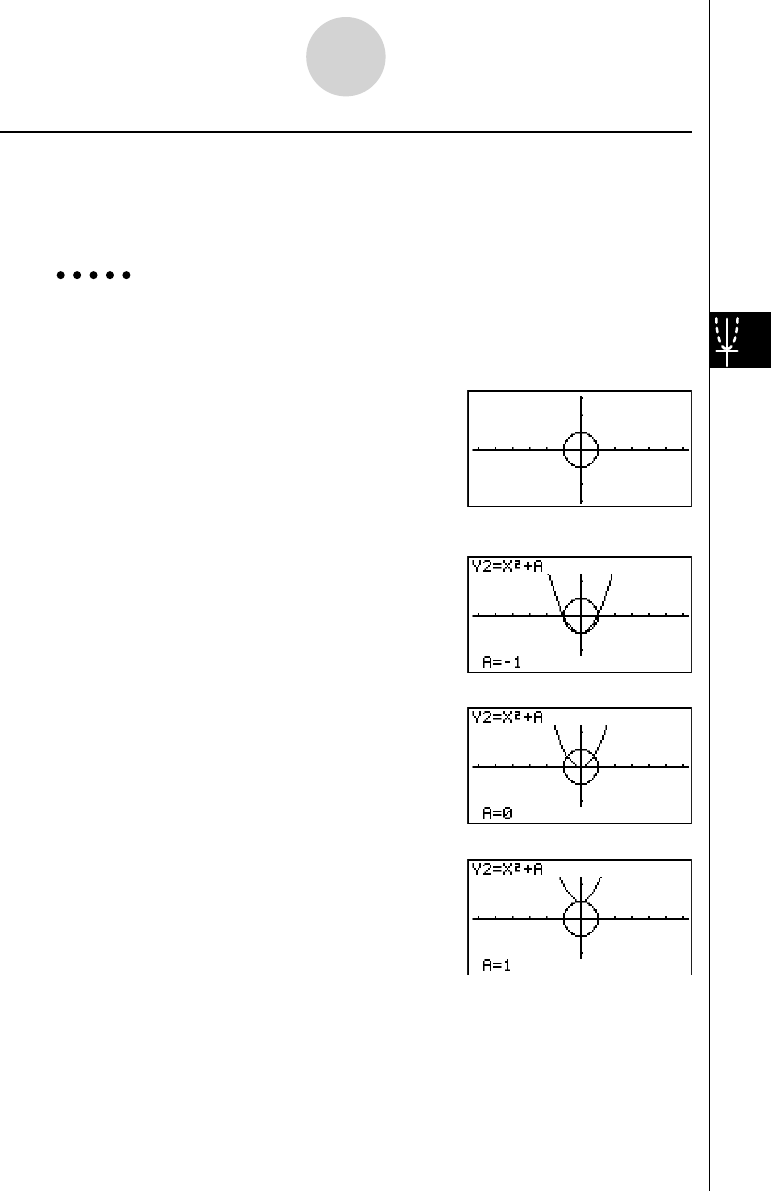
Example 1 With the circle graph X
2
+ Y
2
= 1 as the background, use Dynamic
Graph to graph Y = X
2
+ A as variable A changes value from –1 to 1 in
increments of 1.
Recall the background graph.
(X
2
+ Y
2
= 1)
!m (SET UP)ccccc
2 (PICT)b wJ
(When the graph for X
2
+ Y
2
= 1 is stored
in Pict 1)
Draw the dynamic graph.
(Y = X
2
– 1)
↓↑
(Y = X
2
)
↓↑
(Y = X
2
+ 1)
• See “5-8 Dynamic Graphing” for details on using the Dynamic Graph feature.