User's Manual
Table Of Contents
- Quick-Start
- Precautions when Using this Product
- Contents
- Getting Acquainted— Read This First!
- Chapter 1 Basic Operation
- Chapter 2 Manual Calculations
- Chapter 3 List Function
- Chapter 4 Equation Calculations
- Chapter 5 Graphing
- 5-1 Sample Graphs
- 5-2 Controlling What Appears on a Graph Screen
- 5-3 Drawing a Graph
- 5-4 Storing a Graph in Picture Memory
- 5-5 Drawing Two Graphs on the Same Screen
- 5-6 Manual Graphing
- 5-7 Using Tables
- 5-8 Dynamic Graphing
- 5-9 Graphing a Recursion Formula
- 5-10 Changing the Appearance of a Graph
- 5-11 Function Analysis
- Chapter 6 Statistical Graphs and Calculations
- Chapter 7 Financial Calculation (TVM)
- Chapter 8 Programming
- Chapter 9 Spreadsheet
- Chapter 10 eActivity
- Chapter 11 System Settings Menu
- Chapter 12 Data Communications
- Appendix
20070201
5-3-1
Drawing a Graph
5-3 Drawing a Graph
You can store up to 20 functions in memory. Functions in memory can be edited, recalled,
and graphed.
k Specifying the Graph Type
Before you can store a graph function in memory, you must fi rst specify its graph type.
1. While the Graph relation list is on the display, press 3 (TYPE) to display the graph
type menu, which contains the following items.
• { Y= } / { r= } / { Parm } / { X=c } ... {rectangular coordinate}/{polar coordinate}/{parametric}/
{X=constant}*
1
graph
• { Y> } / { Y< } / { Y t } / { Y s } ... {Y> f
( x )}/{Y< f
( x )}/{Y> f
( x )}/{Y< f
( x )} inequality graph
• { CONV }
• {
' Y= } / { ' Y> } / { ' Y< } / { ' Y t } / { ' Y s }
... {changes the function type of the selected expression}
2. Press the function key that corresponds to the graph type you want to specify.
k Storing Graph Functions
u To store a rectangular coordinate function (Y=) *
2
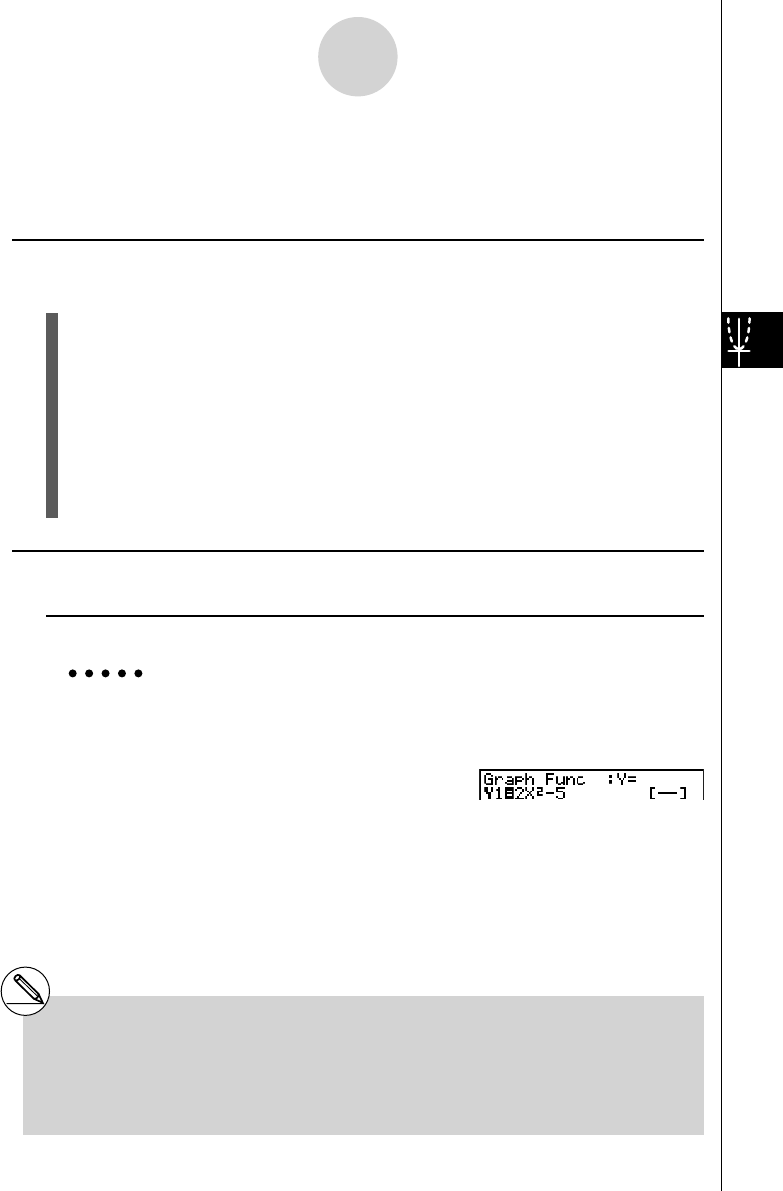
Example To store the following expression in memory area Y1 :
y = 2 x
2
– 5
3 (TYPE)1 (Y=) (Specifi es rectangular coordinate expression.)
c vx -f (Inputs expression.)
w (Stores expression.)
*
1
Attempting to draw a graph for an expression
in which X is input for an X = constant
expression results in an error.
*
2
A function cannot be stored into a memory area that
already contains a function of a different type from
the one you are trying to store. Select a memory
area that contains a function that is the same type
as the one you are storing, or delete the function in
the memory area to which you are trying to store.










