User's Manual
Table Of Contents
- Quick-Start
- Precautions when Using this Product
- Contents
- Getting Acquainted— Read This First!
- Chapter 1 Basic Operation
- Chapter 2 Manual Calculations
- Chapter 3 List Function
- Chapter 4 Equation Calculations
- Chapter 5 Graphing
- 5-1 Sample Graphs
- 5-2 Controlling What Appears on a Graph Screen
- 5-3 Drawing a Graph
- 5-4 Storing a Graph in Picture Memory
- 5-5 Drawing Two Graphs on the Same Screen
- 5-6 Manual Graphing
- 5-7 Using Tables
- 5-8 Dynamic Graphing
- 5-9 Graphing a Recursion Formula
- 5-10 Changing the Appearance of a Graph
- 5-11 Function Analysis
- Chapter 6 Statistical Graphs and Calculations
- Chapter 7 Financial Calculation (TVM)
- Chapter 8 Programming
- Chapter 9 Spreadsheet
- Chapter 10 eActivity
- Chapter 11 System Settings Menu
- Chapter 12 Data Communications
- Appendix
20070201
4-2-2
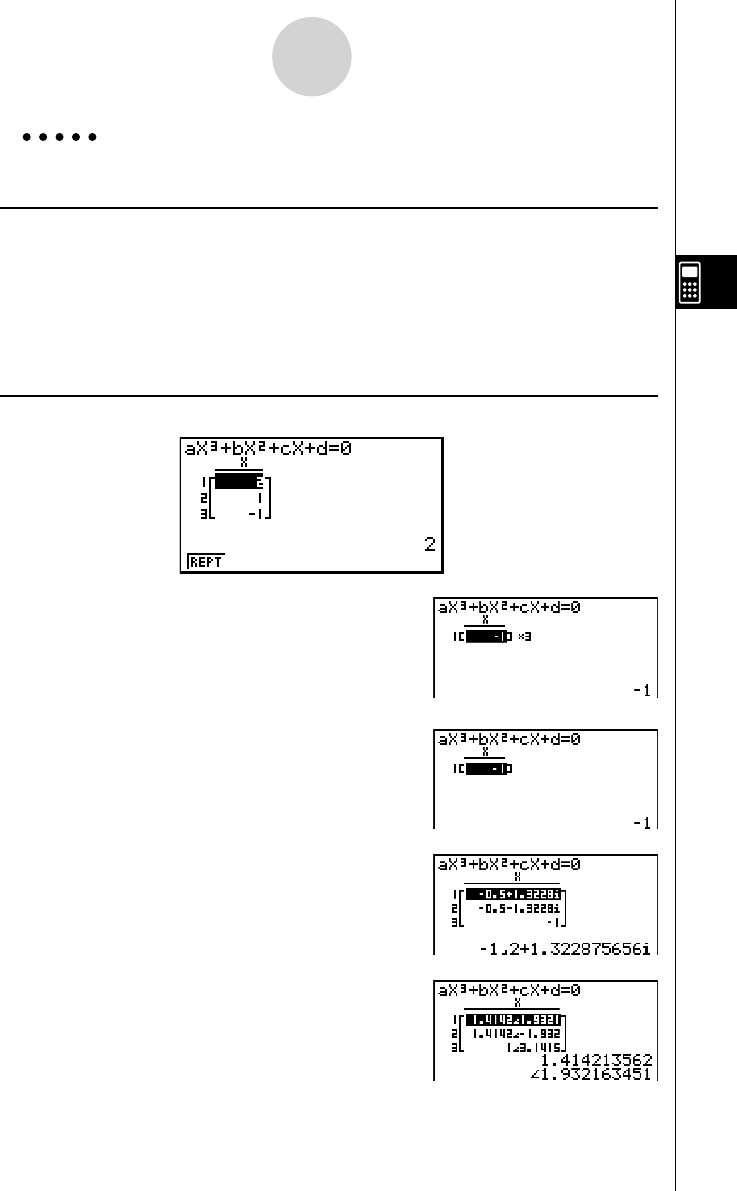
Quadratic and Cubic Equations
Example To solve the cubic equation (Angle unit = Rad)
x
3
– 2 x
2
– x + 2 = 0
Procedure
1 m EQUA
2 2 (POLY)
2 (3)
3 b w- c w- b w c w
4 1 (SOLV)
Result Screen
Multiple Solutions (Example: x
3
+ 3 x
2
+ 3 x + 1 = 0)
Complex Number Solution (Example:
x
3
+ 2 x
2
+ 3 x + 2 = 0)
Complex Mode: Real (page 1-8-2)
Complex Mode:
a + bi
Complex Mode:
r ∠
θ










