User's Manual
Table Of Contents
- Quick-Start
- Precautions when Using this Product
- Contents
- Getting Acquainted— Read This First!
- Chapter 1 Basic Operation
- Chapter 2 Manual Calculations
- Chapter 3 List Function
- Chapter 4 Equation Calculations
- Chapter 5 Graphing
- 5-1 Sample Graphs
- 5-2 Controlling What Appears on a Graph Screen
- 5-3 Drawing a Graph
- 5-4 Storing a Graph in Picture Memory
- 5-5 Drawing Two Graphs on the Same Screen
- 5-6 Manual Graphing
- 5-7 Using Tables
- 5-8 Dynamic Graphing
- 5-9 Graphing a Recursion Formula
- 5-10 Changing the Appearance of a Graph
- 5-11 Function Analysis
- Chapter 6 Statistical Graphs and Calculations
- Chapter 7 Financial Calculation (TVM)
- Chapter 8 Programming
- Chapter 9 Spreadsheet
- Chapter 10 eActivity
- Chapter 11 System Settings Menu
- Chapter 12 Data Communications
- Appendix
20070201
u Matrix Data Input Format [OPTN] - [MAT] - [Mat]
The following shows the format you should use when inputting data to create a matrix using
the Mat command.
= [ [a
11
, a
12
, ..., a
1
n
] [a
21
, a
22
, ..., a
2
n
] .... [a
m
1
, a
m
2
, ..., a
mn
] ]
→
Mat [letter A through Z]
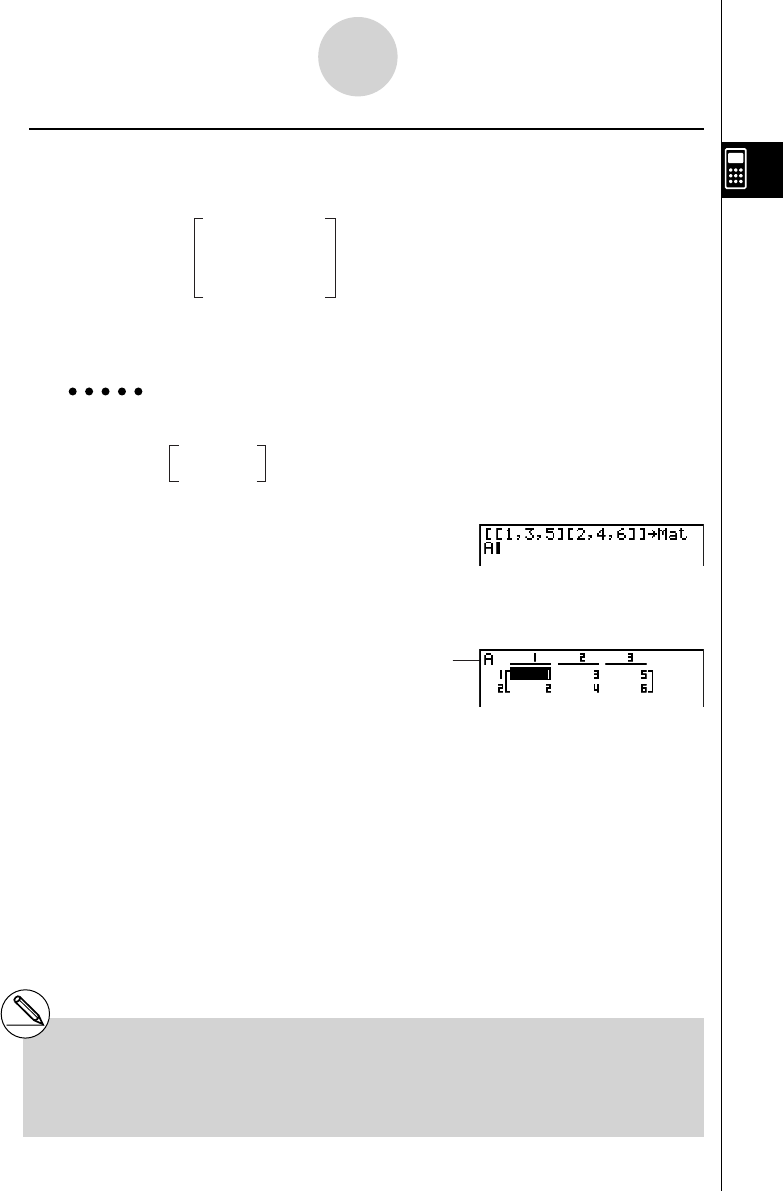
Example 1 To input the following data as Matrix A :
! + ( [ )! + ( [ )b,d,f
! - ( ] )! + ( [ )c,e,g
! - ( ] )! - ( ] )a K 2 (MAT)
1 (Mat)av (A)
w
Matrix name
a11
a
12
...
a
1n
a
21
a
22
...
a
2n
a
m1
a
m2
...
a
mn
...
...
...
a
11
a
12
...
a
1n
a
21
a
22
...
a
2n
a
m1
a
m2
...
a
mn
...
...
...
1 3 5
2 4 6
1 3 5
2 4 6
2-8-11
Matrix Calculations
# You can also use ! c (Mat) in place of
K 2 (MAT)1 (Mat).
# The maximum value of both
m and n is 255.
# An error occurs if memory becomes full as you
are inputting data.
# You can also use the above format inside a
program that inputs matrix data.










