User's Manual
Table Of Contents
- Quick-Start
- Precautions when Using this Product
- Contents
- Getting Acquainted— Read This First!
- Chapter 1 Basic Operation
- Chapter 2 Manual Calculations
- Chapter 3 List Function
- Chapter 4 Equation Calculations
- Chapter 5 Graphing
- 5-1 Sample Graphs
- 5-2 Controlling What Appears on a Graph Screen
- 5-3 Drawing a Graph
- 5-4 Storing a Graph in Picture Memory
- 5-5 Drawing Two Graphs on the Same Screen
- 5-6 Manual Graphing
- 5-7 Using Tables
- 5-8 Dynamic Graphing
- 5-9 Graphing a Recursion Formula
- 5-10 Changing the Appearance of a Graph
- 5-11 Function Analysis
- Chapter 6 Statistical Graphs and Calculations
- Chapter 7 Financial Calculation (TVM)
- Chapter 8 Programming
- Chapter 9 Spreadsheet
- Chapter 10 eActivity
- Chapter 11 System Settings Menu
- Chapter 12 Data Communications
- Appendix
20070201
k Integration Calculations [OPTN] - [CALC] - [ ∫ dx ]
To perform integration calculations, fi rst display the function analysis menu and then input the
values using the syntax below.
K 4 (CALC)4 ( ∫ dx ) f ( x ) , a , b , tol )
(
a : start point, b : end point, tol : tolerance)
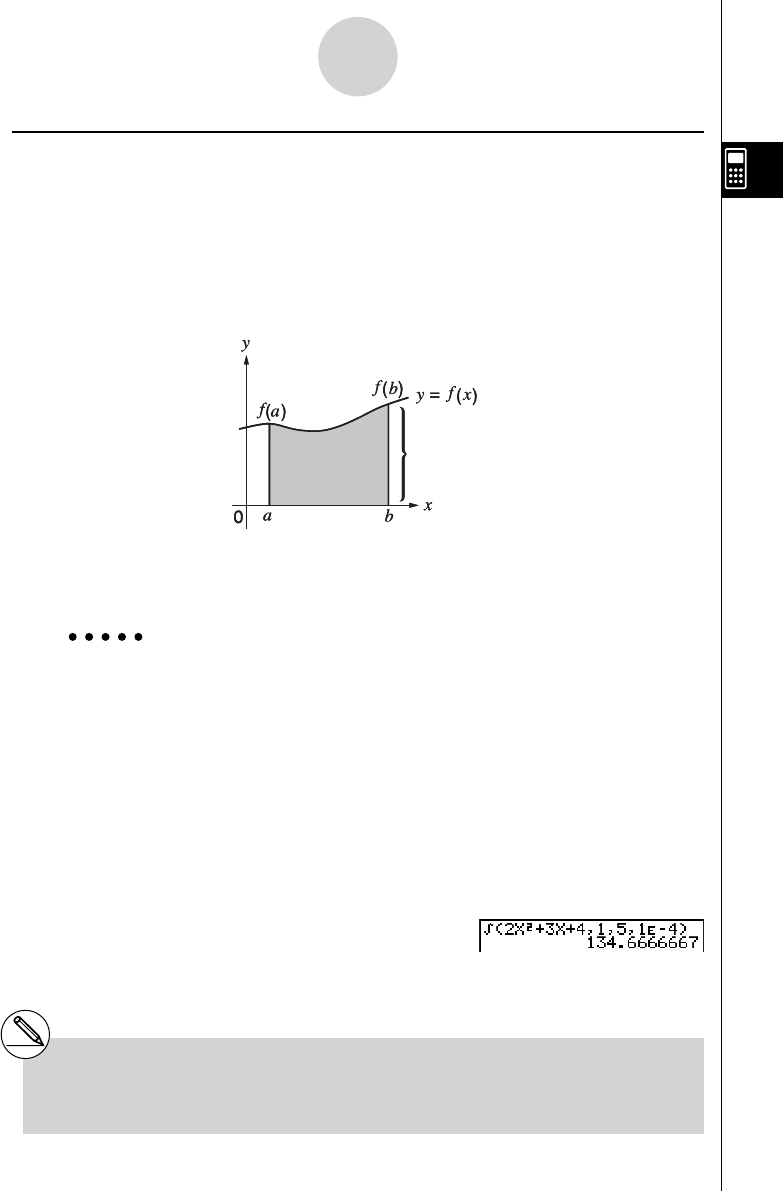
Area of
∫
a
b
f
(
x
)
dx
is calculated
As shown in the illustration above, integration calculations are performed by calculating
integral values from a through b for the function y = f ( x ) where a < x < b , and f ( x ) > 0. This in
effect calculates the surface area of the shaded area in the illustration.
Example To perform the integration calculation for the function shown
below, with a tolerance of “ tol ” = 1
E - 4
Input the function
f
( x ).
A K 4 (CALC)4 ( ∫
dx )c vx +d v +e,
Input the start point and end point.
b,f,
Input the tolerance value.
b E- e)
w
∫
(
f
(
x
),
a
,
b
,
tol
)
⇒
∫
a
b
f
(
x
)
d
x
∫
(
f
(
x
),
a
,
b
,
tol
)
⇒
∫
a
b
f
(
x
)
d
x
∫
1
5
(2x
2
+ 3x + 4) dx
∫
1
5
(2x
2
+ 3x + 4) dx
2-5-7
Numerical Calculations
# If f ( x ) < 0 where a < x < b , the surface area
calculation produces negative values (surface
area × – 1).










