User Manual
Table Of Contents
- Contents
- Getting Acquainted — Read This First!
- Chapter 1 Basic Operation
- Chapter 2 Manual Calculations
- 1. Basic Calculations
- 2. Special Functions
- 3. Specifying the Angle Unit and Display Format
- 4. Function Calculations
- 5. Numerical Calculations
- 6. Complex Number Calculations
- 7. Binary, Octal, Decimal, and Hexadecimal Calculations with Integers
- 8. Matrix Calculations
- 9. Vector Calculations
- 10. Metric Conversion Calculations
- Chapter 3 List Function
- Chapter 4 Equation Calculations
- Chapter 5 Graphing
- 1. Sample Graphs
- 2. Controlling What Appears on a Graph Screen
- 3. Drawing a Graph
- 4. Saving and Recalling Graph Screen Contents
- 5. Drawing Two Graphs on the Same Screen
- 6. Manual Graphing
- 7. Using Tables
- 8. Modifying a Graph
- 9. Dynamic Graphing
- 10. Graphing a Recursion Formula
- 11. Graphing a Conic Section
- 12. Drawing Dots, Lines, and Text on the Graph Screen (Sketch)
- 13. Function Analysis
- Chapter 6 Statistical Graphs and Calculations
- 1. Before Performing Statistical Calculations
- 2. Calculating and Graphing Single-Variable Statistical Data
- 3. Calculating and Graphing Paired-Variable Statistical Data (Curve Fitting)
- 4. Performing Statistical Calculations
- 5. Tests
- 6. Confidence Interval
- 7. Distribution
- 8. Input and Output Terms of Tests, Confidence Interval, and Distribution
- 9. Statistic Formula
- Chapter 7 Financial Calculation
- Chapter 8 Programming
- Chapter 9 Spreadsheet
- Chapter 10 eActivity
- Chapter 11 Memory Manager
- Chapter 12 System Manager
- Chapter 13 Data Communication
- Chapter 14 Geometry
- Chapter 15 Picture Plot
- Chapter 16 3D Graph Function
- Appendix
- Examination Mode
- E-CON4 Application (English)
- 1. E-CON4 Mode Overview
- 2. Sampling Screen
- 3. Auto Sensor Detection (CLAB Only)
- 4. Selecting a Sensor
- 5. Configuring the Sampling Setup
- 6. Performing Auto Sensor Calibration and Zero Adjustment
- 7. Using a Custom Probe
- 8. Using Setup Memory
- 9. Starting a Sampling Operation
- 10. Using Sample Data Memory
- 11. Using the Graph Analysis Tools to Graph Data
- 12. Graph Analysis Tool Graph Screen Operations
- 13. Calling E-CON4 Functions from an eActivity
2-40
k Selecting a Number System
You can specify decimal, hexadecimal, binary, or octal as the default number system using the
Setup screen.
u To perform a binary, octal, decimal, or hexadecimal calculation
[SET UP] - [Mode] - [Dec]/[Hex]/[Bin]/[Oct]
1. In the Main Menu, select Run-Matrix .
2. Press !m(SET UP). Move the highlighting to “Mode”, and then specify the default
number system by pressing 2(Dec), 3(Hex), 4(Bin), or 5(Oct) for the Mode setting.
3. Press J to change to the screen for calculation input. This causes a function menu with
the following items to appear.
• { d~o } / { LOGIC } / { DISPLAY } ... {number system specification}/{bitwise operation}/
{decimal/hexadecimal/binary/octal conversion} menu
u To specify a number system for an input value
You can specify a number system for each individual value you input. Press 1(d~o) to display
a menu of number system symbols. Press the function key that corresponds to the symbol you
want to select and then input the value.
• { d } / { h } / { b } / { o } ... {decimal}/{hexadecimal}/{binary}/{octal}
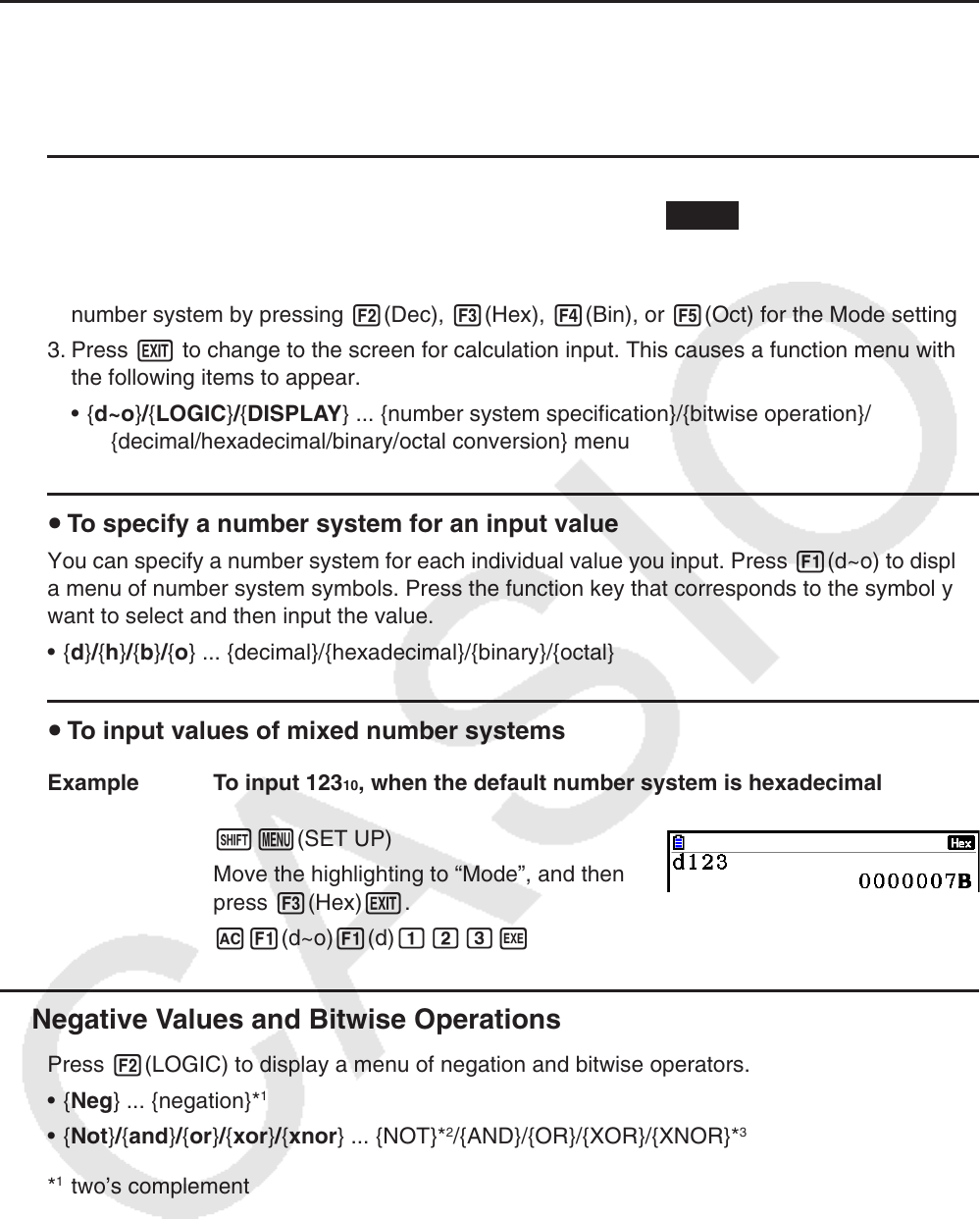
u To input values of mixed number systems
Example To input 123 10 , when the default number system is hexadecimal
!m(SET UP)
Move the highlighting to “Mode”, and then
press 3(Hex) J.
A1(d~o) 1(d) bcdw
k Negative Values and Bitwise Operations
Press 2(LOGIC) to display a menu of negation and bitwise operators.
• { Neg } ... {negation}*
1
• { Not } / { and } / { or } / { xor } / { xnor } ... {NOT}*
2
/{AND}/{OR}/{XOR}/{XNOR}*
3
*
1
two’s complement
*
2
one’s complement (bitwise complement)
*
3
bitwise AND, bitwise OR, bitwise XOR, bitwise XNOR










