User Manual
Table Of Contents
- Contents
- Getting Acquainted — Read This First!
- Chapter 1 Basic Operation
- Chapter 2 Manual Calculations
- 1. Basic Calculations
- 2. Special Functions
- 3. Specifying the Angle Unit and Display Format
- 4. Function Calculations
- 5. Numerical Calculations
- 6. Complex Number Calculations
- 7. Binary, Octal, Decimal, and Hexadecimal Calculations with Integers
- 8. Matrix Calculations
- 9. Vector Calculations
- 10. Metric Conversion Calculations
- Chapter 3 List Function
- Chapter 4 Equation Calculations
- Chapter 5 Graphing
- 1. Sample Graphs
- 2. Controlling What Appears on a Graph Screen
- 3. Drawing a Graph
- 4. Saving and Recalling Graph Screen Contents
- 5. Drawing Two Graphs on the Same Screen
- 6. Manual Graphing
- 7. Using Tables
- 8. Modifying a Graph
- 9. Dynamic Graphing
- 10. Graphing a Recursion Formula
- 11. Graphing a Conic Section
- 12. Drawing Dots, Lines, and Text on the Graph Screen (Sketch)
- 13. Function Analysis
- Chapter 6 Statistical Graphs and Calculations
- 1. Before Performing Statistical Calculations
- 2. Calculating and Graphing Single-Variable Statistical Data
- 3. Calculating and Graphing Paired-Variable Statistical Data (Curve Fitting)
- 4. Performing Statistical Calculations
- 5. Tests
- 6. Confidence Interval
- 7. Distribution
- 8. Input and Output Terms of Tests, Confidence Interval, and Distribution
- 9. Statistic Formula
- Chapter 7 Financial Calculation
- Chapter 8 Programming
- Chapter 9 Spreadsheet
- Chapter 10 eActivity
- Chapter 11 Memory Manager
- Chapter 12 System Manager
- Chapter 13 Data Communication
- Chapter 14 Geometry
- Chapter 15 Picture Plot
- Chapter 16 3D Graph Function
- Appendix
- Examination Mode
- E-CON4 Application (English)
- 1. E-CON4 Mode Overview
- 2. Sampling Screen
- 3. Auto Sensor Detection (CLAB Only)
- 4. Selecting a Sensor
- 5. Configuring the Sampling Setup
- 6. Performing Auto Sensor Calibration and Zero Adjustment
- 7. Using a Custom Probe
- 8. Using Setup Memory
- 9. Starting a Sampling Operation
- 10. Using Sample Data Memory
- 11. Using the Graph Analysis Tools to Graph Data
- 12. Graph Analysis Tool Graph Screen Operations
- 13. Calling E-CON4 Functions from an eActivity
14-62
k Generating an Animation Table
Under default settings, an animation causes a specified point to move along a specified line
segment, circle, or arc in 20 steps. You can configure the calculator to generate a table,
called an “animation table”, which records the coordinates of each step, the length of the line
segment, the area of the object, etc.
Any of the following data can be added to the animation table: coordinates (
x, y), distance/
length, slope, radius, circumference, perimeter, area, angle, supplementary angle, vector
segments (x, y), and expression.
u To add columns to the animation table
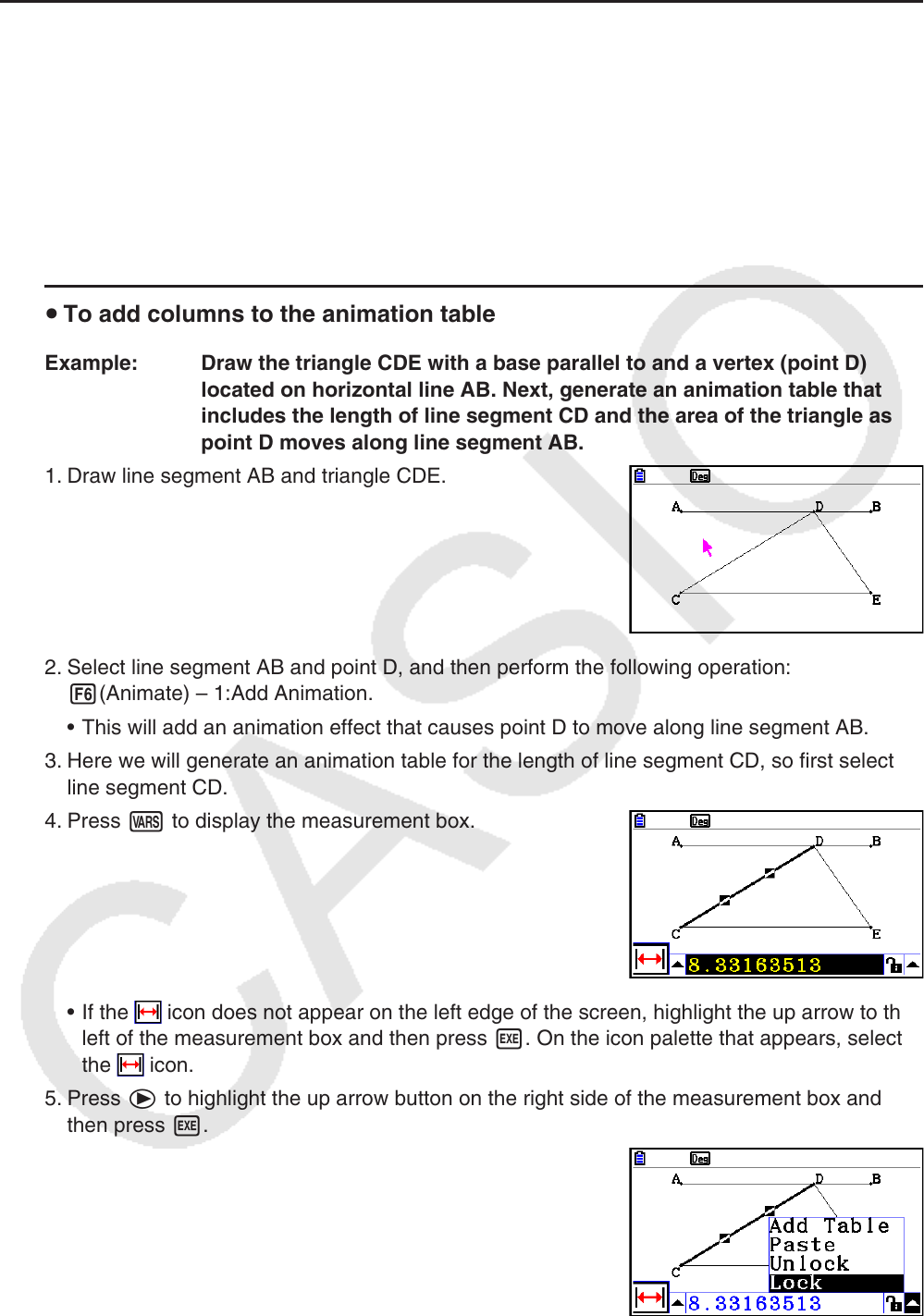
Example: Draw the triangle CDE with a base parallel to and a vertex (point D)
located on horizontal line AB. Next, generate an animation table that
includes the length of line segment CD and the area of the triangle as
point D moves along line segment AB.
1. Draw line segment AB and triangle CDE.
2. Select line segment AB and point D, and then perform the following operation:
6(Animate) – 1:Add Animation.
• This will add an animation effect that causes point D to move along line segment AB.
3. Here we will generate an animation table for the length of line segment CD, so first select
line segment CD.
4. Press J to display the measurement box.
• If the
icon does not appear on the left edge of the screen, highlight the up arrow to the
left of the measurement box and then press w. On the icon palette that appears, select
the icon.
5. Press e to highlight the up arrow button on the right side of the measurement box and
then press w.
• This will display a menu.










