User Manual
Table Of Contents
- Contents
- Getting Acquainted — Read This First!
- Chapter 1 Basic Operation
- Chapter 2 Manual Calculations
- 1. Basic Calculations
- 2. Special Functions
- 3. Specifying the Angle Unit and Display Format
- 4. Function Calculations
- 5. Numerical Calculations
- 6. Complex Number Calculations
- 7. Binary, Octal, Decimal, and Hexadecimal Calculations with Integers
- 8. Matrix Calculations
- 9. Vector Calculations
- 10. Metric Conversion Calculations
- Chapter 3 List Function
- Chapter 4 Equation Calculations
- Chapter 5 Graphing
- 1. Sample Graphs
- 2. Controlling What Appears on a Graph Screen
- 3. Drawing a Graph
- 4. Saving and Recalling Graph Screen Contents
- 5. Drawing Two Graphs on the Same Screen
- 6. Manual Graphing
- 7. Using Tables
- 8. Modifying a Graph
- 9. Dynamic Graphing
- 10. Graphing a Recursion Formula
- 11. Graphing a Conic Section
- 12. Drawing Dots, Lines, and Text on the Graph Screen (Sketch)
- 13. Function Analysis
- Chapter 6 Statistical Graphs and Calculations
- 1. Before Performing Statistical Calculations
- 2. Calculating and Graphing Single-Variable Statistical Data
- 3. Calculating and Graphing Paired-Variable Statistical Data (Curve Fitting)
- 4. Performing Statistical Calculations
- 5. Tests
- 6. Confidence Interval
- 7. Distribution
- 8. Input and Output Terms of Tests, Confidence Interval, and Distribution
- 9. Statistic Formula
- Chapter 7 Financial Calculation
- Chapter 8 Programming
- Chapter 9 Spreadsheet
- Chapter 10 eActivity
- Chapter 11 Memory Manager
- Chapter 12 System Manager
- Chapter 13 Data Communication
- Chapter 14 Geometry
- Chapter 15 Picture Plot
- Chapter 16 3D Graph Function
- Appendix
- Examination Mode
- E-CON4 Application (English)
- 1. E-CON4 Mode Overview
- 2. Sampling Screen
- 3. Auto Sensor Detection (CLAB Only)
- 4. Selecting a Sensor
- 5. Configuring the Sampling Setup
- 6. Performing Auto Sensor Calibration and Zero Adjustment
- 7. Using a Custom Probe
- 8. Using Setup Memory
- 9. Starting a Sampling Operation
- 10. Using Sample Data Memory
- 11. Using the Graph Analysis Tools to Graph Data
- 12. Graph Analysis Tool Graph Screen Operations
- 13. Calling E-CON4 Functions from an eActivity
9-35
u Example: To store column data in list memory
1. In a single column, select the range of cells you want to store in list memory.
• For example, you could select A1:A10.
2. Press 6( g) 3(STORE) 2(LIST).
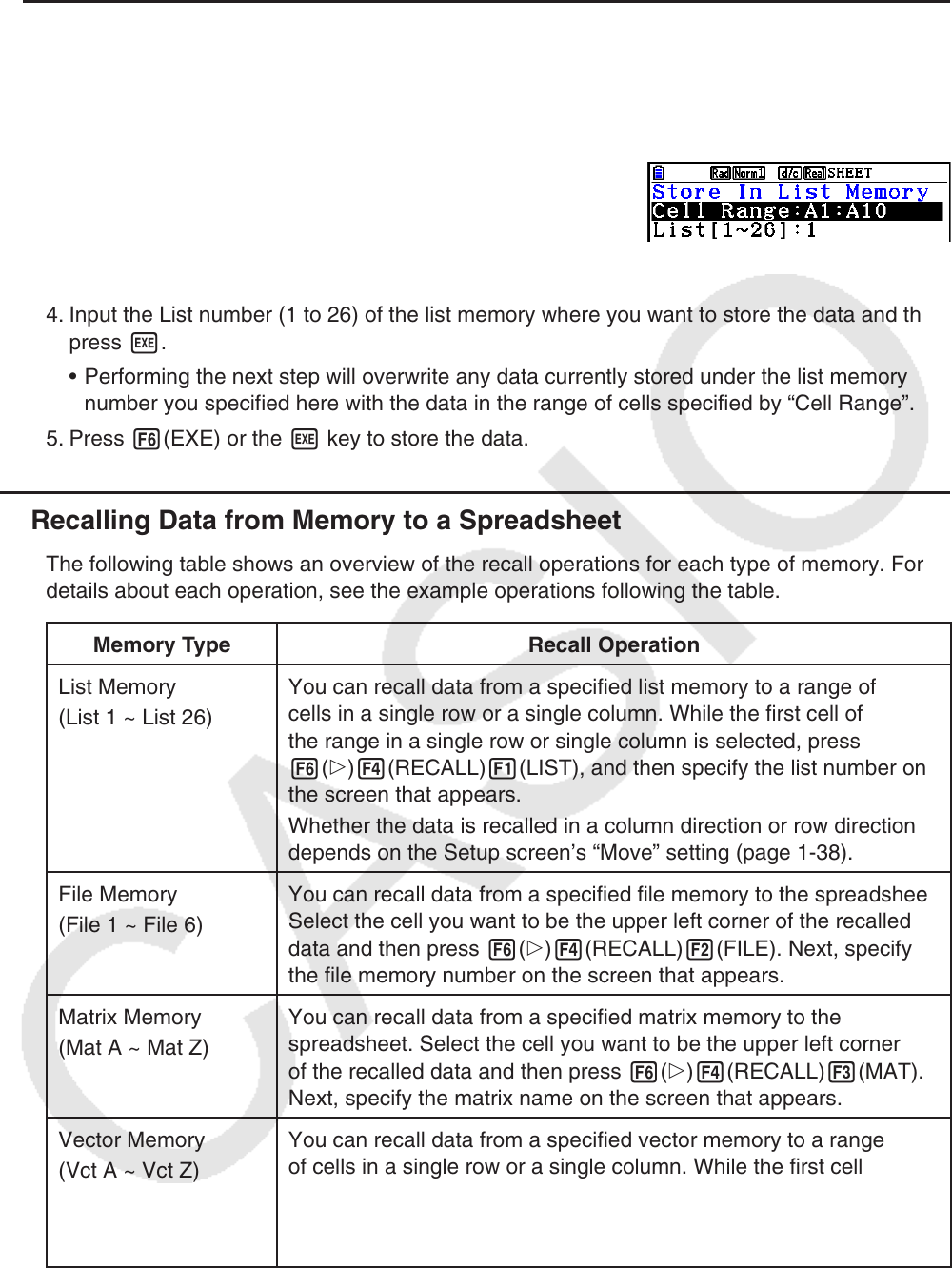
• This will display a screen like the one shown to the right.
The “Cell Range” setting will show the range of cells you
selected in step 1.
3. Press c to move the highlighting to “List[1~26]”.
4. Input the List number (1 to 26) of the list memory where you want to store the data and then
press w.
• Performing the next step will overwrite any data currently stored under the list memory
number you specified here with the data in the range of cells specified by “Cell Range”.
5. Press 6(EXE) or the w key to store the data.
k Recalling Data from Memory to a Spreadsheet
The following table shows an overview of the recall operations for each type of memory. For
details about each operation, see the example operations following the table.
Memory Type Recall Operation
List Memory
(List 1 ~ List 26)
You can recall data from a specified list memory to a range of
cells in a single row or a single column. While the first cell of
the range in a single row or single column is selected, press
6( g) 4(RECALL) 1(LIST), and then specify the list number on
the screen that appears.
Whether the data is recalled in a column direction or row direction
depends on the Setup screen’s “Move” setting (page
1-38).
File Memory
(File 1 ~ File 6)
You can recall data from a specified file memory to the spreadsheet.
Select the cell you want to be the upper left corner of the recalled
data and then press 6( g) 4(RECALL) 2(FILE). Next, specify
the file memory number on the screen that appears.
Matrix Memory
(Mat A ~ Mat Z)
You can recall data from a specified matrix memory to the
spreadsheet. Select the cell you want to be the upper left corner
of the recalled data and then press 6( g) 4(RECALL) 3(MAT).
Next, specify the matrix name on the screen that appears.
Vector Memory
(Vct A ~ Vct Z)
You can recall data from a specified vector memory to a range
of cells in a single row or a single column. While the first cell
of the range in a single row or single column is selected, press
6( g)4(RECALL)4(VCT), and then specify the vector name on
the screen that appears.










