User Manual
Table Of Contents
- Contents
- Getting Acquainted — Read This First!
- Chapter 1 Basic Operation
- Chapter 2 Manual Calculations
- 1. Basic Calculations
- 2. Special Functions
- 3. Specifying the Angle Unit and Display Format
- 4. Function Calculations
- 5. Numerical Calculations
- 6. Complex Number Calculations
- 7. Binary, Octal, Decimal, and Hexadecimal Calculations with Integers
- 8. Matrix Calculations
- 9. Vector Calculations
- 10. Metric Conversion Calculations
- Chapter 3 List Function
- Chapter 4 Equation Calculations
- Chapter 5 Graphing
- 1. Sample Graphs
- 2. Controlling What Appears on a Graph Screen
- 3. Drawing a Graph
- 4. Saving and Recalling Graph Screen Contents
- 5. Drawing Two Graphs on the Same Screen
- 6. Manual Graphing
- 7. Using Tables
- 8. Modifying a Graph
- 9. Dynamic Graphing
- 10. Graphing a Recursion Formula
- 11. Graphing a Conic Section
- 12. Drawing Dots, Lines, and Text on the Graph Screen (Sketch)
- 13. Function Analysis
- Chapter 6 Statistical Graphs and Calculations
- 1. Before Performing Statistical Calculations
- 2. Calculating and Graphing Single-Variable Statistical Data
- 3. Calculating and Graphing Paired-Variable Statistical Data (Curve Fitting)
- 4. Performing Statistical Calculations
- 5. Tests
- 6. Confidence Interval
- 7. Distribution
- 8. Input and Output Terms of Tests, Confidence Interval, and Distribution
- 9. Statistic Formula
- Chapter 7 Financial Calculation
- Chapter 8 Programming
- Chapter 9 Spreadsheet
- Chapter 10 eActivity
- Chapter 11 Memory Manager
- Chapter 12 System Manager
- Chapter 13 Data Communication
- Chapter 14 Geometry
- Chapter 15 Picture Plot
- Chapter 16 3D Graph Function
- Appendix
- Examination Mode
- E-CON4 Application (English)
- 1. E-CON4 Mode Overview
- 2. Sampling Screen
- 3. Auto Sensor Detection (CLAB Only)
- 4. Selecting a Sensor
- 5. Configuring the Sampling Setup
- 6. Performing Auto Sensor Calibration and Zero Adjustment
- 7. Using a Custom Probe
- 8. Using Setup Memory
- 9. Starting a Sampling Operation
- 10. Using Sample Data Memory
- 11. Using the Graph Analysis Tools to Graph Data
- 12. Graph Analysis Tool Graph Screen Operations
- 13. Calling E-CON4 Functions from an eActivity
9-19
3. Using Special Spreadsheet
Mode Commands
The Spreadsheet
mode has a number of special commands like CellSum(, which returns
the sum of a range of cells, and CellIf(, which specifies branching conditions. These special
commands can be used inside of formulas.
k Special Spreadsheet
Mode Command List
“Input Key Operation” operations can be performed during cell input only.
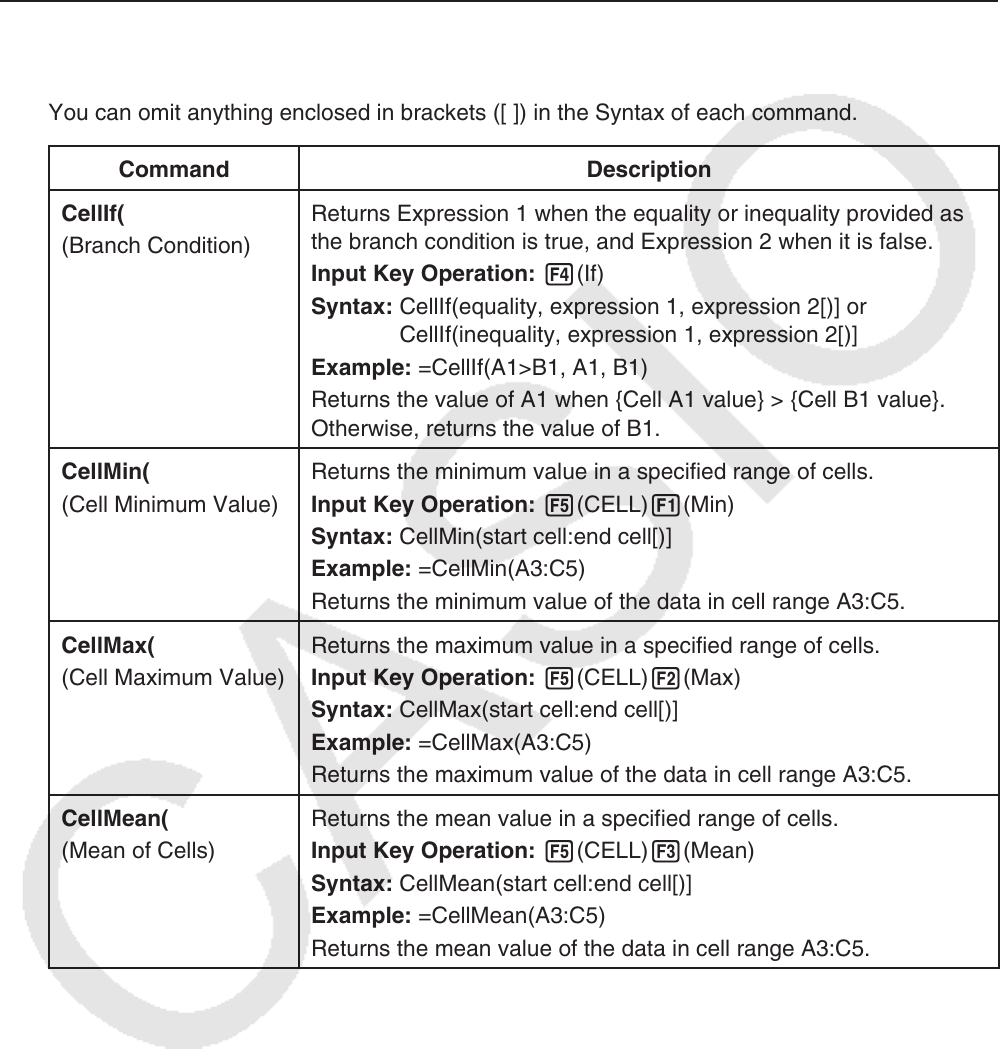
You can omit anything enclosed in brackets ([ ]) in the Syntax of each command.
Command Description
CellIf(
(Branch Condition)
Returns Expression 1 when the equality or inequality provided as
the branch condition is true, and Expression 2 when it is false.
Input Key Operation: 4(If)
Syntax: CellIf(equality, expression 1, expression 2[)] or
CellIf(inequality, expression 1, expression 2[)]
Example: =CellIf(A1>B1, A1, B1)
Returns the value of A1 when {Cell A1 value} > {Cell B1 value}.
Otherwise, returns the value of B1.
CellMin(
(Cell Minimum Value)
Returns the minimum value in a specified range of cells.
Input Key Operation: 5(CELL) 1(Min)
Syntax: CellMin(start cell:end cell[)]
Example: =CellMin(A3:C5)
Returns the minimum value of the data in cell range A3:C5.
CellMax(
(Cell Maximum Value)
Returns the maximum value in a specified range of cells.
Input Key Operation: 5(CELL) 2(Max)
Syntax: CellMax(start cell:end cell[)]
Example: =CellMax(A3:C5)
Returns the maximum value of the data in cell range A3:C5.
CellMean(
(Mean of Cells)
Returns the mean value in a specified range of cells.
Input Key Operation: 5(CELL) 3(Mean)
Syntax: CellMean(start cell:end cell[)]
Example: =CellMean(A3:C5)
Returns the mean value of the data in cell range A3:C5.










