User Manual
Table Of Contents
- Contents
- Getting Acquainted — Read This First!
- Chapter 1 Basic Operation
- Chapter 2 Manual Calculations
- 1. Basic Calculations
- 2. Special Functions
- 3. Specifying the Angle Unit and Display Format
- 4. Function Calculations
- 5. Numerical Calculations
- 6. Complex Number Calculations
- 7. Binary, Octal, Decimal, and Hexadecimal Calculations with Integers
- 8. Matrix Calculations
- 9. Vector Calculations
- 10. Metric Conversion Calculations
- Chapter 3 List Function
- Chapter 4 Equation Calculations
- Chapter 5 Graphing
- 1. Sample Graphs
- 2. Controlling What Appears on a Graph Screen
- 3. Drawing a Graph
- 4. Saving and Recalling Graph Screen Contents
- 5. Drawing Two Graphs on the Same Screen
- 6. Manual Graphing
- 7. Using Tables
- 8. Modifying a Graph
- 9. Dynamic Graphing
- 10. Graphing a Recursion Formula
- 11. Graphing a Conic Section
- 12. Drawing Dots, Lines, and Text on the Graph Screen (Sketch)
- 13. Function Analysis
- Chapter 6 Statistical Graphs and Calculations
- 1. Before Performing Statistical Calculations
- 2. Calculating and Graphing Single-Variable Statistical Data
- 3. Calculating and Graphing Paired-Variable Statistical Data (Curve Fitting)
- 4. Performing Statistical Calculations
- 5. Tests
- 6. Confidence Interval
- 7. Distribution
- 8. Input and Output Terms of Tests, Confidence Interval, and Distribution
- 9. Statistic Formula
- Chapter 7 Financial Calculation
- Chapter 8 Programming
- Chapter 9 Spreadsheet
- Chapter 10 eActivity
- Chapter 11 Memory Manager
- Chapter 12 System Manager
- Chapter 13 Data Communication
- Chapter 14 Geometry
- Chapter 15 Picture Plot
- Chapter 16 3D Graph Function
- Appendix
- Examination Mode
- E-CON4 Application (English)
- 1. E-CON4 Mode Overview
- 2. Sampling Screen
- 3. Auto Sensor Detection (CLAB Only)
- 4. Selecting a Sensor
- 5. Configuring the Sampling Setup
- 6. Performing Auto Sensor Calibration and Zero Adjustment
- 7. Using a Custom Probe
- 8. Using Setup Memory
- 9. Starting a Sampling Operation
- 10. Using Sample Data Memory
- 11. Using the Graph Analysis Tools to Graph Data
- 12. Graph Analysis Tool Graph Screen Operations
- 13. Calling E-CON4 Functions from an eActivity
9-1
Chapter 9 Spreadsheet
The Spreadsheet application provides you with powerful, take-along-anywhere spreadsheet
capabilities.
All of the operations in this section are performed in the Spreadsheet
mode.
Note
A Memory ERROR may occur during a Spreadsheet mode operation if main memory capacity
is low. If this happens, delete some input data or Memory mode data in order to increase
available free space.
1. Spreadsheet Basics and the Function Menu
Selecting Spreadsheet
on the Main Menu will display a spreadsheet screen. Entering the
Spreadsheet
mode automatically creates a new spreadsheet file named “SHEET”.
The spreadsheet screen shows a number of cells (squares) and the data contained in each
cell.
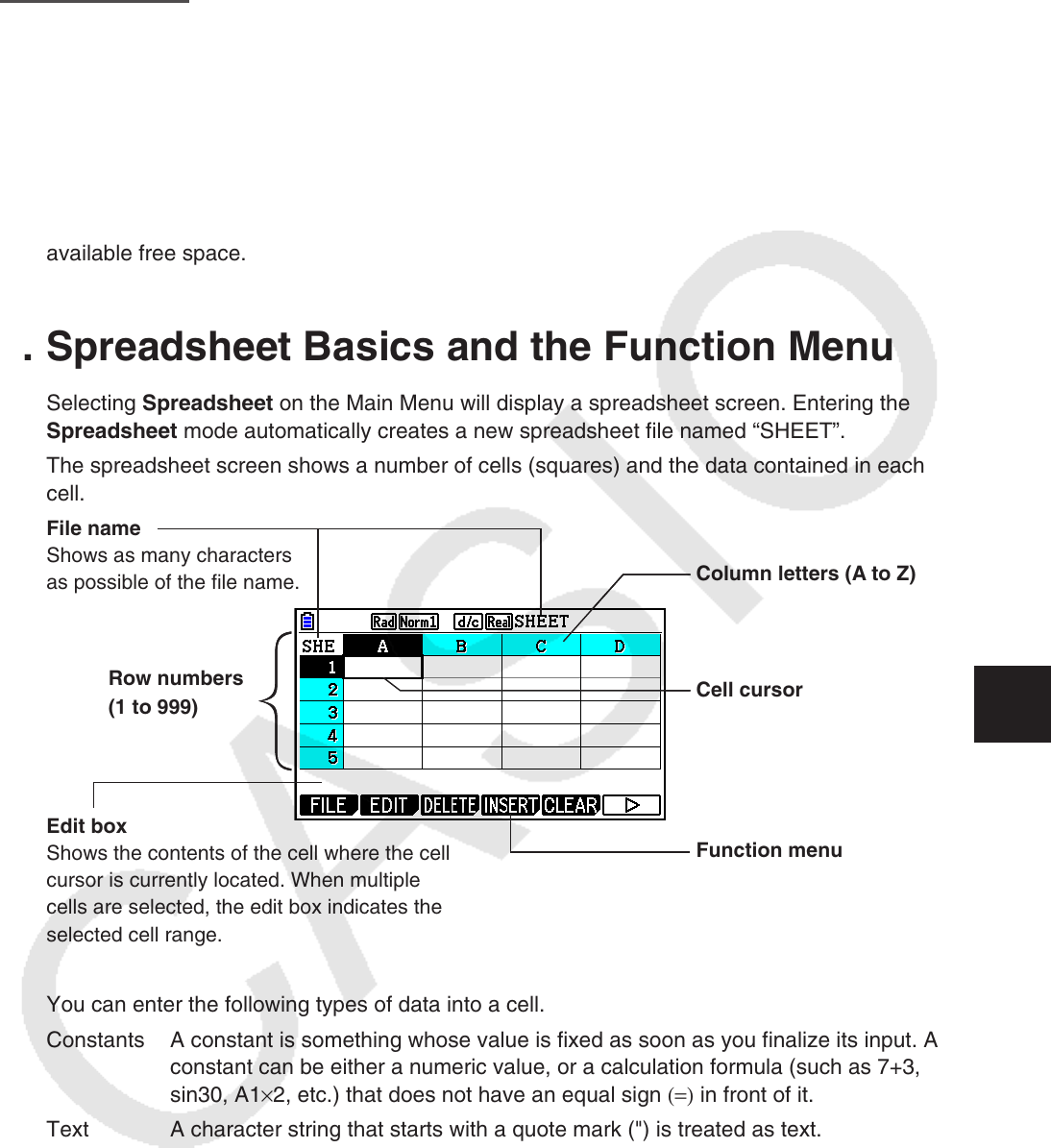
File name
Shows as many characters
as possible of the fi le name.
Column letters (A to Z)
Row numbers
(1 to 999)
Cell cursor
Edit box
Shows the contents of the cell where the cell
cursor is currently located. When multiple
cells are selected, the edit box indicates the
selected cell range.
Function menu
You can enter the following types of data into a cell.
Constants A constant is something whose value is fixed as soon as you finalize its input. A
constant can be either a numeric value, or a calculation formula (such as 7+3,
sin30, A1 × 2, etc.) that does not have an equal sign (=) in front of it.
Text A character string that starts with a quote mark (") is treated as text.
Formula A formula that starts out with an equal sign (=) , such as =A1 × 2, is executed as it
is written.
Note that complex numbers are not supported in the Spreadsheet
mode.
Spreadsheet Mode Restrictions
The maximum file size that can be handled by the Spreadsheet mode is 30KB. Note,
however, that the actual maximum file size depends on the type of data input into the
spreadsheet and condition formatting settings. Also note that the maximum file size changes
in accordance with the amount of main memory available.
9










