User Manual
Table Of Contents
- Contents
- Getting Acquainted — Read This First!
- Chapter 1 Basic Operation
- Chapter 2 Manual Calculations
- 1. Basic Calculations
- 2. Special Functions
- 3. Specifying the Angle Unit and Display Format
- 4. Function Calculations
- 5. Numerical Calculations
- 6. Complex Number Calculations
- 7. Binary, Octal, Decimal, and Hexadecimal Calculations with Integers
- 8. Matrix Calculations
- 9. Vector Calculations
- 10. Metric Conversion Calculations
- Chapter 3 List Function
- Chapter 4 Equation Calculations
- Chapter 5 Graphing
- 1. Sample Graphs
- 2. Controlling What Appears on a Graph Screen
- 3. Drawing a Graph
- 4. Saving and Recalling Graph Screen Contents
- 5. Drawing Two Graphs on the Same Screen
- 6. Manual Graphing
- 7. Using Tables
- 8. Modifying a Graph
- 9. Dynamic Graphing
- 10. Graphing a Recursion Formula
- 11. Graphing a Conic Section
- 12. Drawing Dots, Lines, and Text on the Graph Screen (Sketch)
- 13. Function Analysis
- Chapter 6 Statistical Graphs and Calculations
- 1. Before Performing Statistical Calculations
- 2. Calculating and Graphing Single-Variable Statistical Data
- 3. Calculating and Graphing Paired-Variable Statistical Data (Curve Fitting)
- 4. Performing Statistical Calculations
- 5. Tests
- 6. Confidence Interval
- 7. Distribution
- 8. Input and Output Terms of Tests, Confidence Interval, and Distribution
- 9. Statistic Formula
- Chapter 7 Financial Calculation
- Chapter 8 Programming
- Chapter 9 Spreadsheet
- Chapter 10 eActivity
- Chapter 11 Memory Manager
- Chapter 12 System Manager
- Chapter 13 Data Communication
- Chapter 14 Geometry
- Chapter 15 Picture Plot
- Chapter 16 3D Graph Function
- Appendix
- Examination Mode
- E-CON4 Application (English)
- 1. E-CON4 Mode Overview
- 2. Sampling Screen
- 3. Auto Sensor Detection (CLAB Only)
- 4. Selecting a Sensor
- 5. Configuring the Sampling Setup
- 6. Performing Auto Sensor Calibration and Zero Adjustment
- 7. Using a Custom Probe
- 8. Using Setup Memory
- 9. Starting a Sampling Operation
- 10. Using Sample Data Memory
- 11. Using the Graph Analysis Tools to Graph Data
- 12. Graph Analysis Tool Graph Screen Operations
- 13. Calling E-CON4 Functions from an eActivity
1-23
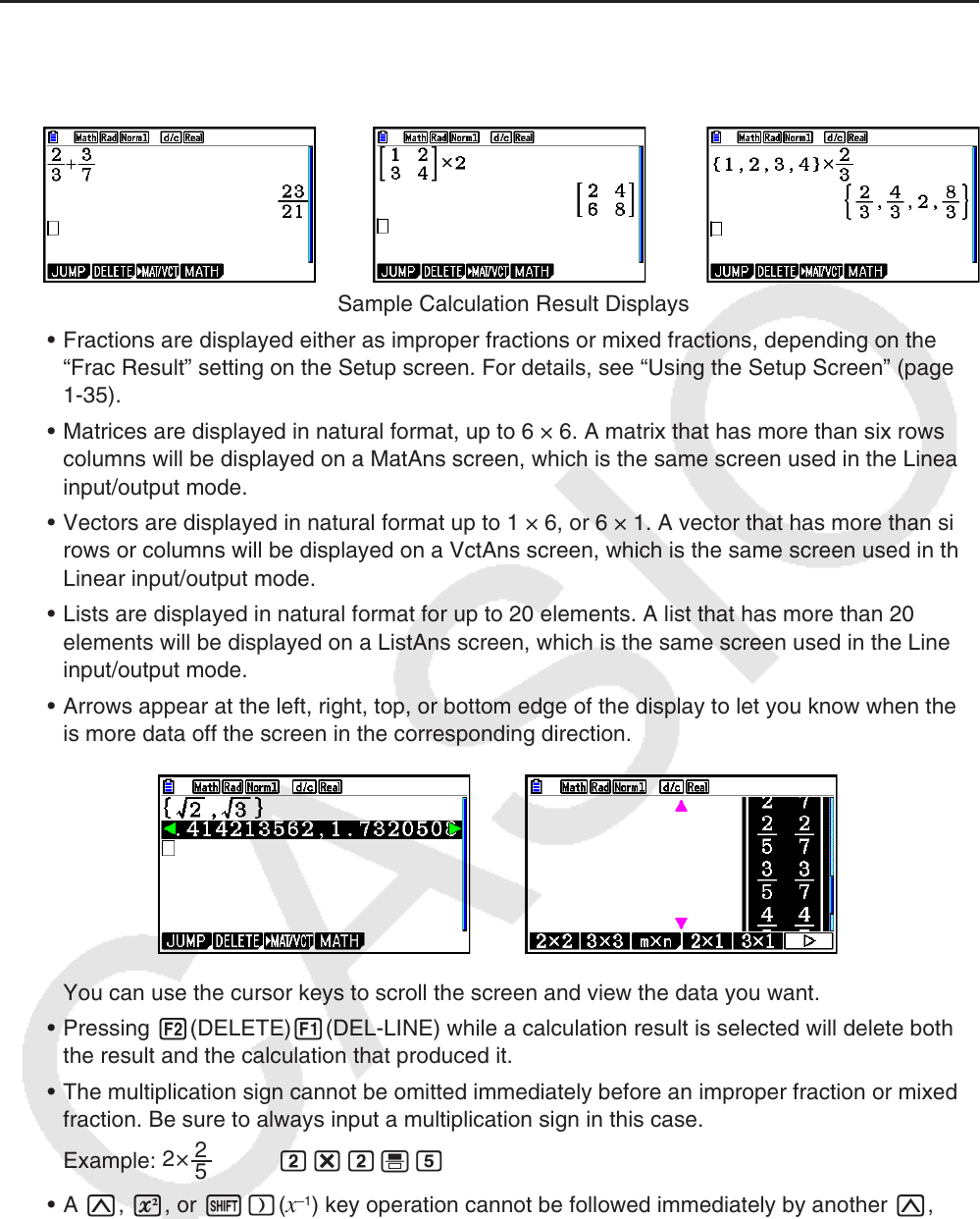
k Math Input/Output Mode Calculation Result Display
Fractions, matrices, vectors, and lists produced by Math input/output mode calculations are
displayed in natural format, just as they appear in your textbook.
Sample Calculation Result Displays
• Fractions are displayed either as improper fractions or mixed fractions, depending on the
“Frac Result” setting on the Setup screen. For details, see “Using the Setup Screen” (page
1-35).
• Matrices are displayed in natural format, up to 6 × 6. A matrix that has more than six rows or
columns will be displayed on a MatAns screen, which is the same screen used in the Linear
input/output mode.
• Vectors are displayed in natural format up to 1 × 6, or 6 × 1. A vector that has more than six
rows or columns will be displayed on a VctAns screen, which is the same screen used in the
Linear input/output mode.
• Lists are displayed in natural format for up to 20 elements. A list that has more than 20
elements will be displayed on a ListAns screen, which is the same screen used in the Linear
input/output mode.
• Arrows appear at the left, right, top, or bottom edge of the display to let you know when there
is more data off the screen in the corresponding direction.
You can use the cursor keys to scroll the screen and view the data you want.
• Pressing 2(DELETE)1(DEL-LINE) while a calculation result is selected will delete both
the result and the calculation that produced it.
• The multiplication sign cannot be omitted immediately before an improper fraction or mixed
fraction. Be sure to always input a multiplication sign in this case.
Example:
2×
2
5
c*c'f
• A M, x, or !)(
x
–1
) key operation cannot be followed immediately by another M,
x, or !)(x
–1
) key operation. In this case, use parentheses to keep the key operations
separate.
Example: (3
2
)
–1
(dx)!)(x
–1
)










