User Manual
Table Of Contents
- Contents
- Getting Acquainted — Read This First!
- Chapter 1 Basic Operation
- Chapter 2 Manual Calculations
- 1. Basic Calculations
- 2. Special Functions
- 3. Specifying the Angle Unit and Display Format
- 4. Function Calculations
- 5. Numerical Calculations
- 6. Complex Number Calculations
- 7. Binary, Octal, Decimal, and Hexadecimal Calculations with Integers
- 8. Matrix Calculations
- 9. Vector Calculations
- 10. Metric Conversion Calculations
- Chapter 3 List Function
- Chapter 4 Equation Calculations
- Chapter 5 Graphing
- 1. Sample Graphs
- 2. Controlling What Appears on a Graph Screen
- 3. Drawing a Graph
- 4. Saving and Recalling Graph Screen Contents
- 5. Drawing Two Graphs on the Same Screen
- 6. Manual Graphing
- 7. Using Tables
- 8. Modifying a Graph
- 9. Dynamic Graphing
- 10. Graphing a Recursion Formula
- 11. Graphing a Conic Section
- 12. Drawing Dots, Lines, and Text on the Graph Screen (Sketch)
- 13. Function Analysis
- Chapter 6 Statistical Graphs and Calculations
- 1. Before Performing Statistical Calculations
- 2. Calculating and Graphing Single-Variable Statistical Data
- 3. Calculating and Graphing Paired-Variable Statistical Data (Curve Fitting)
- 4. Performing Statistical Calculations
- 5. Tests
- 6. Confidence Interval
- 7. Distribution
- 8. Input and Output Terms of Tests, Confidence Interval, and Distribution
- 9. Statistic Formula
- Chapter 7 Financial Calculation
- Chapter 8 Programming
- Chapter 9 Spreadsheet
- Chapter 10 eActivity
- Chapter 11 Memory Manager
- Chapter 12 System Manager
- Chapter 13 Data Communication
- Chapter 14 Geometry
- Chapter 15 Picture Plot
- Chapter 16 3D Graph Function
- Appendix
- Examination Mode
- E-CON4 Application (English)
- 1. E-CON4 Mode Overview
- 2. Sampling Screen
- 3. Auto Sensor Detection (CLAB Only)
- 4. Selecting a Sensor
- 5. Configuring the Sampling Setup
- 6. Performing Auto Sensor Calibration and Zero Adjustment
- 7. Using a Custom Probe
- 8. Using Setup Memory
- 9. Starting a Sampling Operation
- 10. Using Sample Data Memory
- 11. Using the Graph Analysis Tools to Graph Data
- 12. Graph Analysis Tool Graph Screen Operations
- 13. Calling E-CON4 Functions from an eActivity
6-70
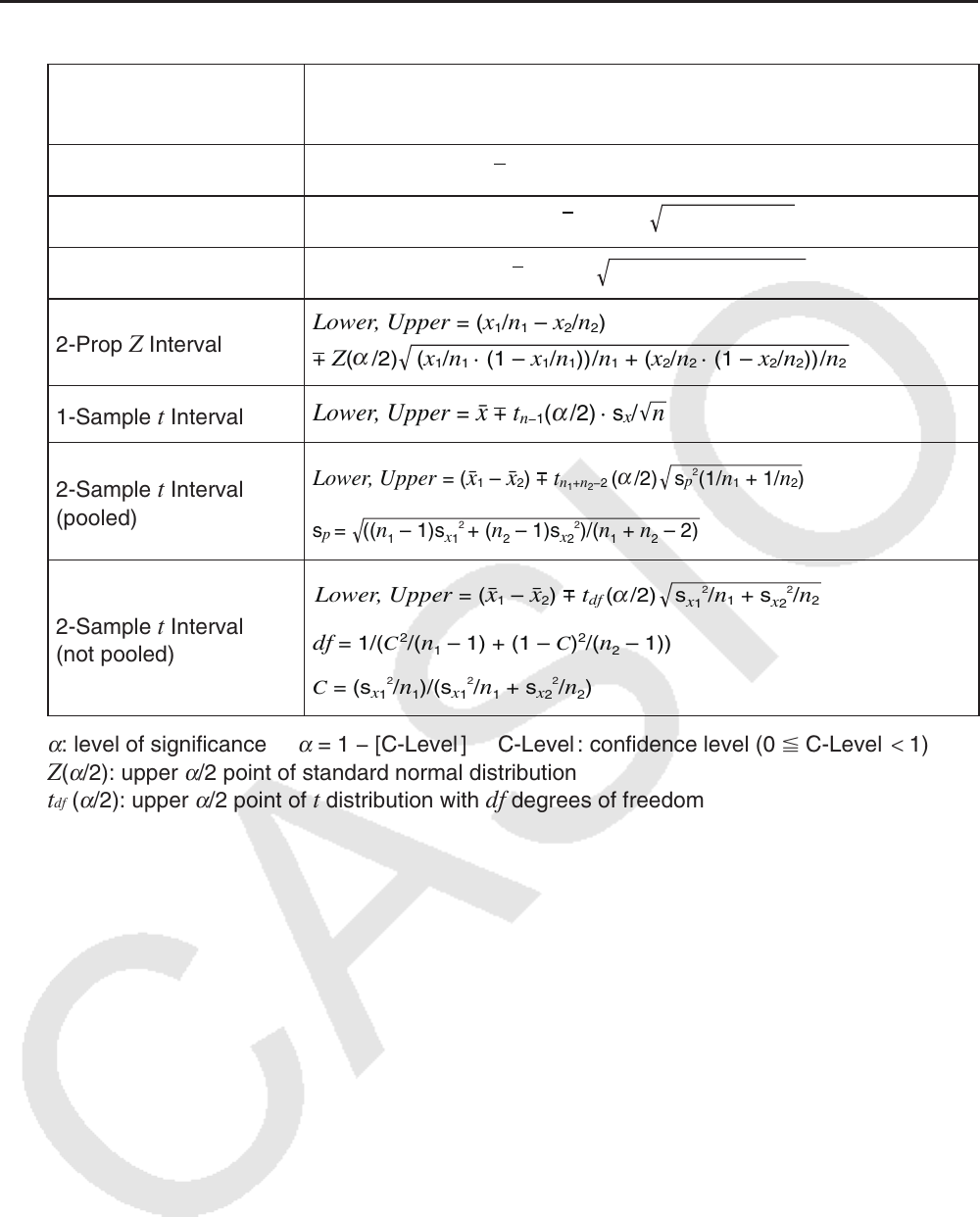
k Confidence Interval
Confidence Interval
Lower: confidence interval lower limit
Upper: confidence interval upper limit
1-Sample
Z Interval
Lower, Upper = o + Z( /2) · σ/
'
n
α
2-Sample Z Interval
Lower, Upper = (o
1
– o
2
) + Z( /2) σ /n
1
+ σ /n
2
2
1
2
2
α
1-Prop
Z Interval
Lower, Upper = x/n + Z( /2) 1/n · (x/n · (1 – x/n))
α
2-Prop
Z Interval
Lower, Upper = (x
1
/
n
1
–
x
2
/
n
2
)
+ Z( /2) (x
1
/
n
1
· (1 –
x
1
/
n
1
))/
n
1
+ (
x
2
/
n
2
· (1 –
x
2
/
n
2
))/
n
2
α
1-Sample
t Interval
Lower, Upper = o + t
n−1
( /2)
· s
x
/'n
α
2-Sample
t Interval
(pooled)
Lower, Upper = (o
1
– o
2
) + t
n
1
+n
2
−2
( /2) s
p
2
(1/n
1
+ 1/n
2
)
s
p
= ((n
1
– 1)s
x
1
2
+ (n
2
– 1)s
x
2
2
)/(n
1
+ n
2
– 2)
α
2-Sample
t Interval
(not pooled)
Lower, Upper
= (o
1
– o
2
) +
t
df
( /2) s
x
1
2
/
n
1
+ s
x
2
2
/
n
2
df
= 1/(C
2
/(
n
1
– 1) + (1 – C)
2
/(
n
2
– 1))
α
C = (s
x
1
2
/
n
1
)/(s
x
1
2
/
n
1
+ s
x
2
2
/
n
2
)
α
: level of significance
α
= 1 − [C-Level ] C-Level : confidence level (0 C-Level < 1)
Z (
α
/2): upper
α
/2 point of standard normal distribution
t
df
(
α
/2): upper
α
/2 point of t distribution with df degrees of freedom










