User Manual
Table Of Contents
- Contents
- Getting Acquainted — Read This First!
- Chapter 1 Basic Operation
- Chapter 2 Manual Calculations
- 1. Basic Calculations
- 2. Special Functions
- 3. Specifying the Angle Unit and Display Format
- 4. Function Calculations
- 5. Numerical Calculations
- 6. Complex Number Calculations
- 7. Binary, Octal, Decimal, and Hexadecimal Calculations with Integers
- 8. Matrix Calculations
- 9. Vector Calculations
- 10. Metric Conversion Calculations
- Chapter 3 List Function
- Chapter 4 Equation Calculations
- Chapter 5 Graphing
- 1. Sample Graphs
- 2. Controlling What Appears on a Graph Screen
- 3. Drawing a Graph
- 4. Saving and Recalling Graph Screen Contents
- 5. Drawing Two Graphs on the Same Screen
- 6. Manual Graphing
- 7. Using Tables
- 8. Modifying a Graph
- 9. Dynamic Graphing
- 10. Graphing a Recursion Formula
- 11. Graphing a Conic Section
- 12. Drawing Dots, Lines, and Text on the Graph Screen (Sketch)
- 13. Function Analysis
- Chapter 6 Statistical Graphs and Calculations
- 1. Before Performing Statistical Calculations
- 2. Calculating and Graphing Single-Variable Statistical Data
- 3. Calculating and Graphing Paired-Variable Statistical Data (Curve Fitting)
- 4. Performing Statistical Calculations
- 5. Tests
- 6. Confidence Interval
- 7. Distribution
- 8. Input and Output Terms of Tests, Confidence Interval, and Distribution
- 9. Statistic Formula
- Chapter 7 Financial Calculation
- Chapter 8 Programming
- Chapter 9 Spreadsheet
- Chapter 10 eActivity
- Chapter 11 Memory Manager
- Chapter 12 System Manager
- Chapter 13 Data Communication
- Chapter 14 Geometry
- Chapter 15 Picture Plot
- Chapter 16 3D Graph Function
- Appendix
- Examination Mode
- E-CON4 Application (English)
- 1. E-CON4 Mode Overview
- 2. Sampling Screen
- 3. Auto Sensor Detection (CLAB Only)
- 4. Selecting a Sensor
- 5. Configuring the Sampling Setup
- 6. Performing Auto Sensor Calibration and Zero Adjustment
- 7. Using a Custom Probe
- 8. Using Setup Memory
- 9. Starting a Sampling Operation
- 10. Using Sample Data Memory
- 11. Using the Graph Analysis Tools to Graph Data
- 12. Graph Analysis Tool Graph Screen Operations
- 13. Calling E-CON4 Functions from an eActivity
6-12
k Calculation Methods for the Std and OnData Settings
Q1, Q3 and Med can be calculated in accordance with the Setup screen’s “Q1Q3 Type”
setting as described below.
u Std
(1) When all Frequency values are integers
With this calculation method, processing depends on whether the number of elements
n in the
population is an even number or odd number.
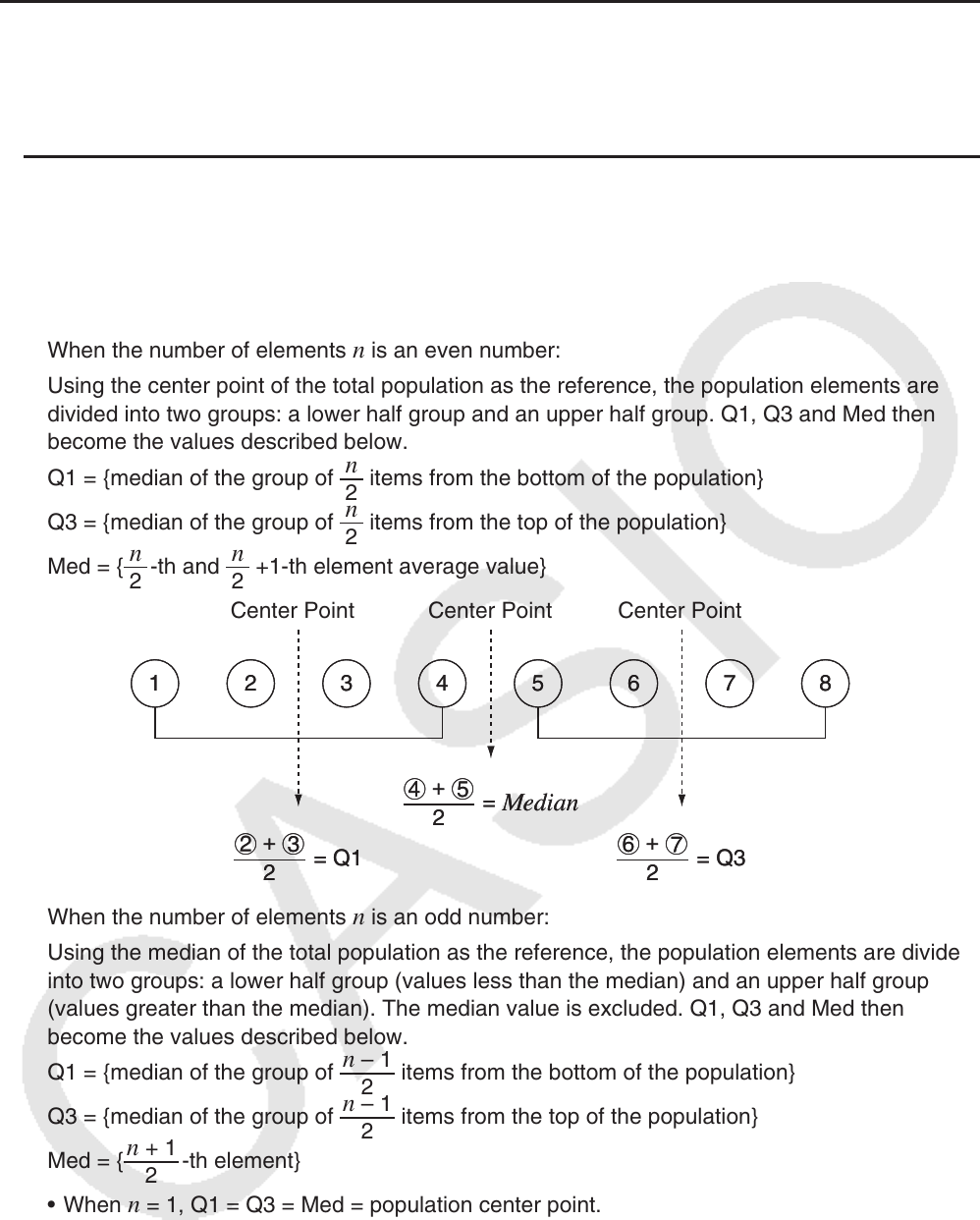
When the number of elements
n is an even number:
Using the center point of the total population as the reference, the population elements are
divided into two groups: a lower half group and an upper half group. Q1, Q3 and Med then
become the values described below.
Q1 = {median of the group of
2
n
items from the bottom of the population}
Q3 = {median of the group of
2
n
items from the top of the population}
Med = {
2
n
-th and
2
n
+1-th element average value}
Center Point Center Point Center Point
When the number of elements
n is an odd number:
Using the median of the total population as the reference, the population elements are divided
into two groups: a lower half group (values less than the median) and an upper half group
(values greater than the median). The median value is excluded. Q1, Q3 and Med then
become the values described below.
Q1 = {median of the group of
2
n
– 1
items from the bottom of the population}
Q3 = {median of the group of
2
n
– 1
items from the top of the population}
Med = {
2
n
+ 1
-th element}
• When
n = 1, Q1 = Q3 = Med = population center point.
2
4
+
5
=
Median
= Q1
2
2
+
3
= Q3
2
6
+
7
12345678
2
4
+
5
=
Median
= Q1
2
2
+
3
= Q3
2
6
+
7
12345678










