User's Manual Part 3
Release8OperationsGuide
Issue2,November2007 Draft5forRegula toryReview 423
26.8 INTERPRETINGDATAINTHEBRIDGINGTABLE(ALL)
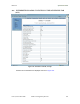
An example of the Bridging Table tab is displayed in Figure 148.
Figure 148: Bridging Table tab of AP, example
If NAT (network address translation) is not active on the SM, then the Bridging Table tab
provides the MAC address of all devices that are attached to registered SMs (identified
by LUIDs). The bridging table allows data to be sent to the correct module as follows:
◦ For the AP, the uplink is from RF to Ethernet. Thus, when a packet arrives in the
RF interface to the AP, the AP reads the MAC address from the inbound packet
and creates a bridging table entry of the source MAC address on the other end of
the RF interface.
◦ For the SM, BHM, and BHS, the uplink is from Ethernet to RF. Thus, when a
packet arrives in the Ethernet interface to one of these modules, the module
reads the MAC address from the inbound packet and creates a bridging table
entry of the source MAC address on the other end of the Ethernet interface.